Painful and disabling, muscle contractures are also the main cause of
back, neck and lumbar pain. Overtraining, poor posture, repetitive
movements exhaust the muscle which then suffers a dysfunction in its
contraction/release mechanisms. The stress of competition
can also
accentuate or trigger this phenomenon, as can a vitamin deficiency.
The causes of muscle contractures
Although the actual causes are not well known, it is thought that certain muscle fibres, overtired, remain contracted due to a lack of energy. Indeed, for a muscle to contract, the calcium level in the muscle fibre must increase. In order for a muscle to contract, the calcium level in the muscle fibre has to increase, and for the same muscle to relax, the calcium level has to decrease.
However, during a session that is too strenuous, the calcium is difficult to remove from the muscle cell. This makes it difficult to relax and leads to contracture. It can also come from a reflex contraction which aims to protect the muscle following a major stretch or an inflammation.
A contracture looks like a cramp in a very specific place, like a small ball in the muscle. The pain is usually not very strong at first but increases gradually. The pain is felt on contraction, stretching and palpation. It differs from cramp in that it lasts much longer.
When "the damage is done" it is important to treat the contracture immediately. Myorelaxant drugs are to be avoided because they cause many side effects, fortunately natural and effective solutions exist!
SOLUTIONS AGAINST MUSCULAR CONTRACTURES
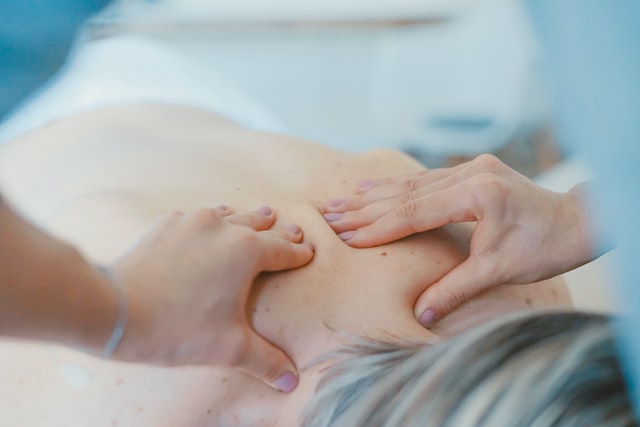
As soon as a contracture appears, it is preferable to stop all physical activity to let the muscle rest and to apply a source of heat to the painful area (hot compresses, hot shower, heating patches) and to provide massages to relax the muscle.
- To soothe the pain without taking anti-inflammatory drugs, Turmeric and White Willow extracts will have an equally effective action on pain and inflammation.
- To relax the muscle, skullcap, a small plant of the mint family, native to North America, will act on specific receptors in the brain which will instruct the nervous system to relax the muscle concerned.
- Finally, a supply of calcium, potassium and magnesium will restore the electrolyte balance at the heart of the muscle cells, thus restoring the relaxation mechanism.