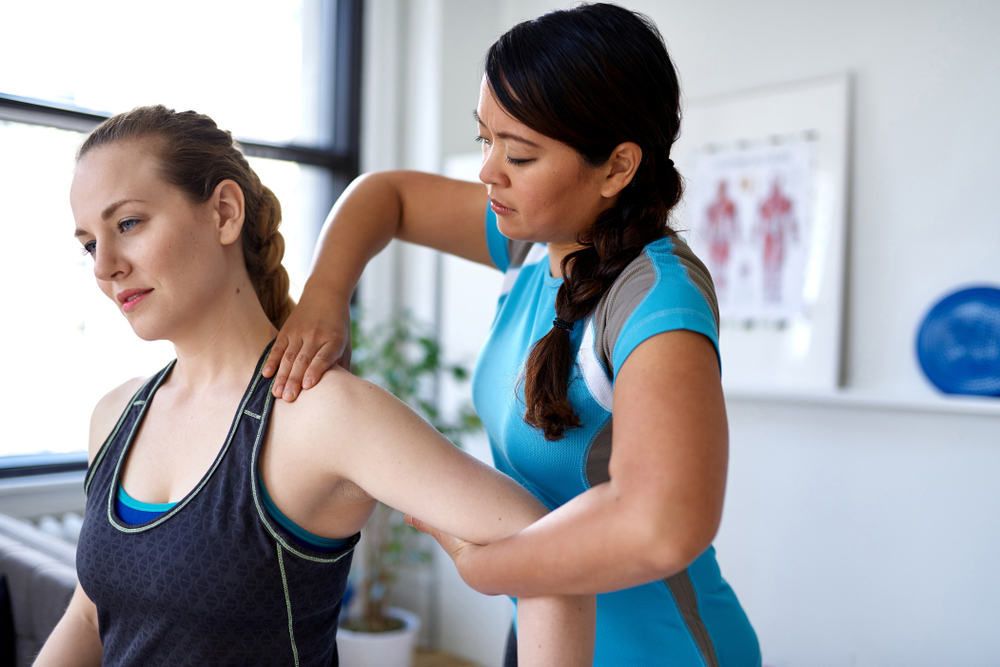
The maintenance of joint mobility in any sport is of fundamental importance.It allows the maintenance of a freedom of movement necessary to perform the majority of sporting activities.When this mobility is effective, the risks of injury during the practice of certain physical activities are reduced.Stretching is an effective way to maintain or increase this mobility.
What is joint mobility?
Joint mobility can be defined as all the movements that a joint makes possible.It is the ability of the musculo-tendinous composition to accommodate the osteo-articular amplitude.In clearer terms, it is the amplitude offered by a joint.It is therefore the ability to move a joint.In simple language, it is synonymous with flexibility.This flexibility is general when it concerns all joints, and local when it is targeted at a particular joint.
It varies from one individual to another, depending on several parameters such as age, sex, type of sport, etc.For example, each individual at a young age has a high degree of joint mobility, which tends to decrease due to certain postures or unbalanced sports practice.The maintenance or loss of joint mobility is in fact directly linked to lifestyle.
The limits of joint mobility
An effort to improve is always possible, however, muscles have their limits, which present themselves in sprains or injuries when not observed:
First of all, there is the capsulo-ligamentary limit: the capsulo-ligamentary system has the role of stabilising the joints.An example of a limit is the extension of the knee with the tensioning of the cruciate and lateral ligaments, then the contact of the muscle masses, by the flexion of the knee and the contact of the hamstrings. Next, the muscle limit which can occur during knee extension and hip flexion with the tensioning of the hamstrings.Finally,the bony limit, visible during knee flexion and contact of the calves against the hamstrings.
How to improve joint mobility?
First of all, it is important to know the joint physiology of the person concerned so that the work carried out is precise and in accordance with the specific characteristics of each practitioner.
In general, the gain in mobility is achieved by improving the flexibility of the muscles.However,we must be careful not to stretch the capsulo-ligamentary systems.Indeed, this practice, carried out regularly, or in the wrong way, could increase the traumatic risks, particularly recurrent subluxations, often present in dancers.
The importance of stretching on joint mobility
The best flexibility exercises are stretches.They allow the joints to protect themselves from extreme positions such as squats or bench presses.For an educator, it is necessary to adapt the stretching methods and use an appropriate pedagogy, in accordance with the physiology of the practitioner.These stretches also depend on the strength of the muscle in question.
Neuromuscular spindles are spindle-shaped mechanoreceptors located in parallel in the muscle fibre.They are therefore sensitive to sudden stretching , during which there is a myotatic reflex.This reflex consists of the neuromuscular spindle reflexively transferring a nerve impulse to the alpha motor neurons of the muscle, which then contracts.
Muscle tone is generated by the appearance of an activating reticulum, which depends on the degree of activation of the exercises for the practitioner.This is achieved by an excitatory synapse of the gamma motor neuron, which sends an efferent input from the intramuscular fibres, causing contraction and then stretching of the neuromuscular spindle.The afferent spindle transfers an impulse, eventually causing the muscle to contract concentrically.
How to do stretching properly?
Compared to a machine, the muscle can be disorganised into two passive components and one active component, which are the connective tissue, the tendons and the sarcomeres respectively.When stretching the connective tissue, which is a passive component, the sarcomeres, the active component, must be released as much as possible.
Passive or active stretching?
What we must conclude is that gamma activity is unfavourable to stretching.It prevents the muscles from relaxing completely.This is why muscle tone must be taken into account when stretching.If it is weak, passive, slow and progressive stretching is recommended.If it is high, a relaxing technique or active stretching can be considered, in which the muscle tone decreases and passive stretching takes over.Active stretching, on the other hand, consists in locally inhibiting muscle tone.
These explanations are theoretical.In order to better understand them, illustrations are necessary.A relaxed athlete attends a stretching class in the morning.Since it is a suitable environment, the educator opts for passive stretching using gravity.The instruction would be to exhale slowly during the stretching.It should be progressive, with pain limited to 20-30 seconds.A second example is an athlete attending a stretching class in the evening.Since it is a noisy environment, active stretching is recommended: contraction - relaxation - stretching.In this case, the partner stretches the hamstrings and holds this posture for 20 seconds.There will then be a reaction of the neuromuscular spindle and an adjustment of the length of the muscle, through gramma activity, so that the muscle prepares itself for the next stretch.In this way, there is an isometric contraction of the hamstrings without any shortening with partner opposition for 6 seconds.
Passive stretching limits the traumatic risks associated with abrupt activities, since it makes very little demand on the myotatic reflex.The disadvantage is that it increases the motor reserve of active stretching.
Golgi organ stretching and lifting best practices
As far as the Golgi organ is concerned, which is located in the tendon, it is a passive component that is sensitive to tension.It tends to relax the muscle.The practitioner must therefore release the tension for 3 seconds and then his partner pulls again and holds the position for 30 seconds.
The "lifter", a bodybuilding practice, solicits the muscles and pushes the body to go beyond itself, in often uncomfortable positions. Its practitioners must observe a certain vigilance, since a strong solicitation of the tonic muscles causes a softening of the phasic muscles.
It is therefore important to remember to stretch all the muscles regularly, starting with the tonic muscles.With the necessary materials and knowledge of physiology, the educator can propose a beneficial and not unpleasant work of mobilisation of the joints for the practitioners.However, it is not advisable to carry out stretching after an intense session.It would be better to wait a few days to allow the muscles to relax.
FOR MORE INFORMATION
Our other resources
SPORT AND JOINTS: BEWARE OF BREAKING UP
.
TENDINITY AND OSTEOPATHIC
TREATMENT
tendonitis in musculature
OSTEO-ARTICULAR RISKS
INFLAMMATION,
AN EVIL NOT TO BE MISSED
THE JOINT SYSTEM OF THE SHOULDER
HOW
TO PRESERVE YOUR JOINTS?
KNEE JOINTS