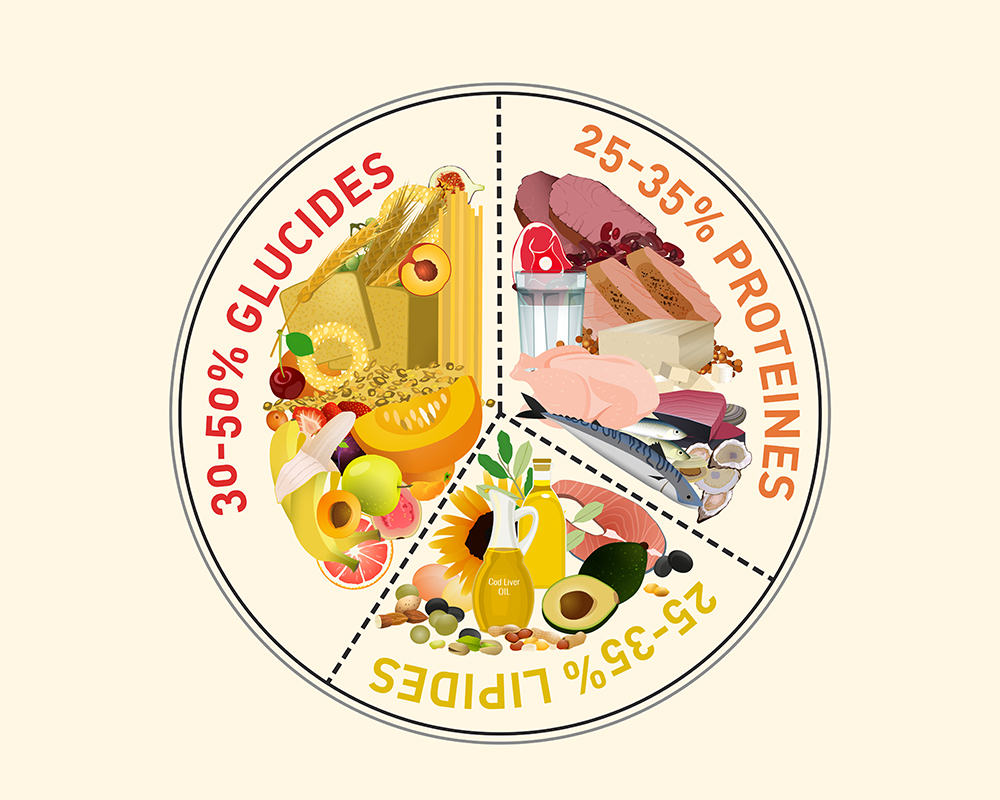
Carbohydrates, proteins and fats are the basic components of macronutrients. Nutrients that come from food and provide energy to the body. They are responsible for the proper functioning of its vital functions. Everything you need to know about these macronutrients will be explained here.
FIRST OF ALL, CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates are the main energy providers that the human body needs most in its diet for the brain especially, as well as for all other physical activities. The basic elements of carbohydrates are monosaccharides which are also called simple carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are classified in different ways depending on their chain length:
- First there are the monosaccharides which are glucose or grape sugar, then fructose or fruit sugar and galactose or milk sugar.
- Then there are the disaccharides which include sucrose (industrial sugar), lactose.
- Not forgetting the oligosaccharides which contain raffinose
- And finally the polysaccharides which are also called complex carbohydrates where there is amylopectin (vegetable starch), glycogen (animal starch) and insulin.
Carbohydrates are stored in the body in two very different ways: one third is in the liver as glycogen, and two thirds is in the muscles.
During physical exertion, these glycogen reserves are where the human body draws its energy source, and are then replenished through a good carbohydrate-rich diet.
According to The Academy for Nutrition and Dietetics, carbohydrates should make up at least 50% of an adult's daily energy needs. It is also recommended to prioritise complex carbohydrates which, unlike simple carbohydrates, do not lead to high carbohydrate levels. They keep the body fuller for longer. They are also very rich in minerals, contain fibre, contribute to the health of the intestinal flora and lower cholesterol levels.
Foods that are rich in complex carbohydrates are:
Of course, fruit is the richest in complex carbohydrates, followed by vegetables, legumes, and not to be forgotten cereals and seeds, sweet potatoes, wholemeal products and plain rice.
The source foods for simple carbohydrates are:
Firstly sugar, followed by bleached or refined flour products, sweets or candies and sweetened soft drinks and fruit juices.
To contribute to a healthy intestinal flora, it is necessary to regularly consume pre- and probiotics, which are often combined with carbohydrates.
SECONDLY, PROTEINS
Proteins are the composition of a set of amino acids that are linked together by chains. The human body is composed of a total of 20 amino acids. Proteins are in charge of many functions within the body. While amino acids are divided into 3 different categories: the essential category (the body cannot make them itself so they need to be supplied through the diet), the conditionally essential and the non-essential.
Proteins act as hormones, enzymes and antibodies in the immune system that protect the body against various infections. They are also present in some structures of the body (connective tissue, skin, hair and muscle fibres).
About 60% of the proteins in the body are found in the muscles. However, these reserves are not a direct source of energy, but building blocks for the body.
As a general rule, it is strongly advised to take 1g of protein per 1kg daily, i. e. the amount to be consumed per day varies according to the body weight of an individual. But if the objective is to gain muscle mass, the amount can be increased to between 1. 2 and 1. 8g per kg of body weight. If the person is a keen sportsman, then he should always take protein fused with carbohydrates after each activity. The reason is very simple, after consuming carbohydrates, the body will release insulin, a hormone that promotes anabolism and that will promote muscle growth.
The foods with the most protein are:
Meat is the most recommended food for maximum protein, after fish and seafood. Then milk and dairy products, eggs, legumes, cereal products, nuts and soya products.
Note that it is also advisable to know how to combine certain foods in order to have an important biological value in each diet.
AND FINALLY LIPIDS
Fats are very important to promote the taste of a food. They are very present in the daily diet in solid form, for example butter, coconut fats, or in liquid form, hence vegetable oils.
Fatty acids are categorised as follows:
- saturated fatty acids such as meat, dairy products, butter, coconut oil,
- also monounsaturated fatty acids
- polyunsaturated fatty acids such as olive oil, linseed oil, rapeseed oil, safflower oil, wheat germ oil, cold water fish, nuts and avocados.
Omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids are also part of the family of polyunsaturated fatty acids which are important and must be calibrated in the diet. They are found as mentioned above in freshwater fish such as salmon, mackerel and herring, safflower oil, linseed oil and walnuts. The ratio of omega 3 to omega 6 should be around 1:5.
Unsaturated fatty acids are necessary to regulate the metabolism and contribute to the elasticity of cell membranes. They also promote the fluidity of the blood and are important for the growth and multiplication of cells. In addition, they provide an important fatty acid content, and for lipids they facilitate the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K, which are also known as fat-soluble vitamins.
While animal fats also contain cholesterol, which is synthesised through exposure to the sun. It will subsequently supply vitamin D to the skin.
Cholesterol also contributes to the creation of hormones. However, frequent consumption of foods rich in cholesterol is strongly discouraged as it may promote the development of cardiovascular disease.
The fat content of an adult male's daily diet should be between 30-35% with 20-25% unsaturated fat and a maximum of 10% saturated fat.
To conclude
In conclusion, all 3 macronutrients are extremely important for health and for ensuring certain functions of the human body. It is advisable to adopt a balanced diet in order to provide the body with everything it needs to function 100% every day(see even calculating your macronutrient intake). But above all to prevent all forms of disease.