In recent years, people have been eating as they please without knowing exactly what they are getting. Habits have made it necessary to live to eat and not to eat to live, buying food in supermarkets or other places without knowing if the products are fresh or not. And this is a great concern in today's society. So isn't it important to inform the public about healthy eating?
Starting with the macronutrient well known to all despite being excluded: carbohydrates. The aim of this review is to deliver as much information as possible so that there are no more secrets for consumers, and so that the carbohydrate will be appreciated at its true value.
What are carbohydrates?
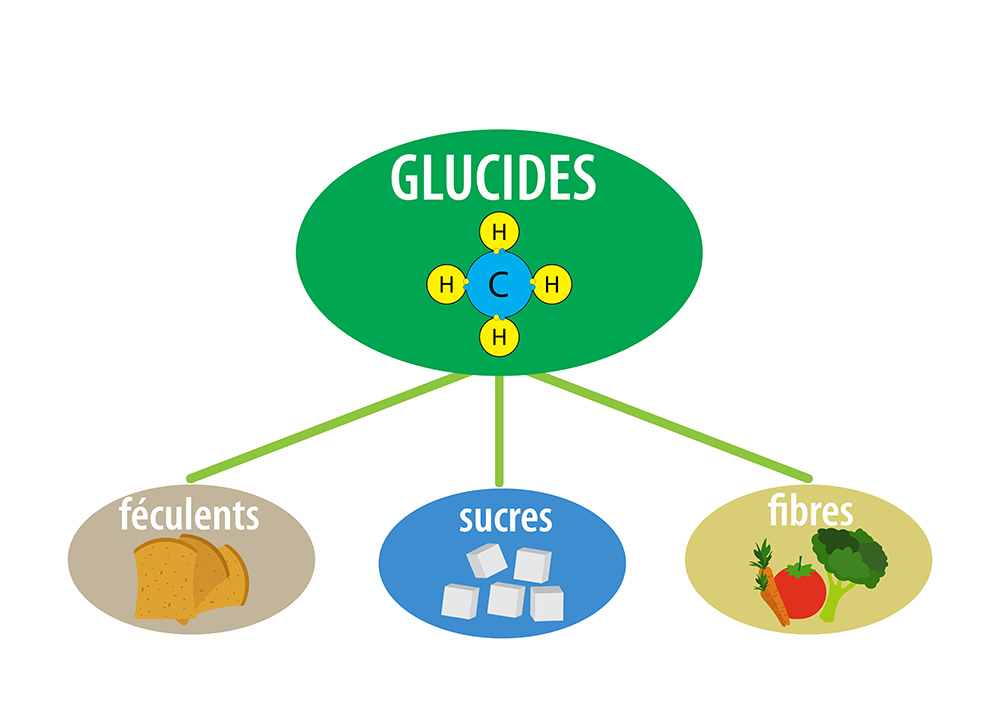
Also known as carbohydrate, carbohydrate is a member of the macronutrient family along with protein and fat. The macronutrient is what the body needs most in various amounts in order to generate energy. There are two types of carbohydrates: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Their structure is what makes the difference. Simple carbohydrates are monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose) and disaccharides (lactose, sucrose, maltose).
For complex carbohydrates, there are the digestible polysaccharides, which are the starches (amylose and amylopectin) and the non-digestible polysaccharides, which are the dietary fibres (cellulose).
The elementary particle of the carbohydrate is present once in the monosaccharide while the disaccharide contains it twice and more than twice for the polysaccharide. This part is a bit scientific but not to be overlooked and important to know.
The glycemic index from its origin
The glycemic index, a much used term but very few know exactly what it means, so what exactly is its definition?
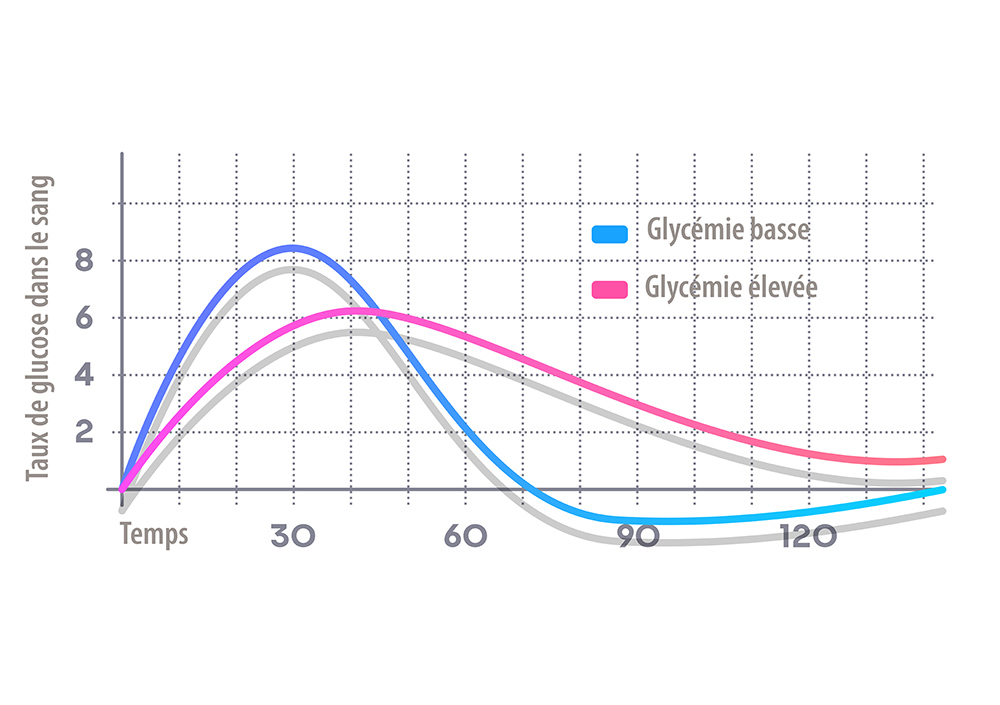
Simple carbohydrates pass directly into the bloodstream because processing in them is not necessary. They will therefore quickly raise blood sugar levels, and therefore have a high glycaemic index. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, need to be processed, so the more complex the molecule, the longer it takes to process it, and the lower the glycemic index
. It is important to know that the glycemic index will be affected by the presence of other macro-nutrients (fat and protein) which usually lower the index. Also, it will change depending on the cooking process, as well as other forms of processing undergone.
The higher the glycemic index foods are consumed, the more insulin is produced. At this stage, the pancreas is under great strain and gets tired quite quickly. It is therefore advisable to eat low GI (glycaemic index) carbohydrates.
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Simply put, the purpose of carbohydrates is to provide energy to the metabolism (and thus increase sports performance).
Similar to a car where you need to inject fuel to make it go. One gram of carbohydrate is the equivalent of 4kcal (kilocalories) to the body. Before entering the bloodstream, all the carbohydrates that have been consumed are converted into monosaccharides.
The basic monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose) make their way into the bloodstream, whereas disaccharides and polysaccharides require more time for processing. The monosaccharides that are processed by the liver are not glucose to glucose.
The body uses glucose to fuel all cells (muscle, heart, etc. ) but not least the nerve cells. This is one of the reasons why it is important to consume a minimum of glucose per day. The brain needs 140g of glucose per day for an individual.
What are the benefits of carbohydrates?
They control your appetite
To begin with, through complex carbohydrates, but especially fibre, humans can feel full quite quickly and will not have to ask for food for a long time.
They raise the blood sugar level
As mentioned before, the body absorbs simple carbohydrates (especially glucose) quite quickly. Thus the blood sugar level rises very quickly and feeds the sugar in the metabolism. This is very important in the athlete as well as in a diabetic person who is susceptible to hypoglycaemia. (cf:are carbohydrates to be consumed before or after training?)
To sleep well
It is with the help of carbohydrates that tryptophan (amino acid) arrives in the brain. This is the first factor that triggers serotonin, which is itself synthesised to provide melatonin. And so the latter generates good, restful sleep.
How to regulate carbohydrates?
What is the risk if a person consumes a lot or very little carbohydrate?
- Lack of carbohydrates
The risks of eating less carbohydrate for the average person:
- loss of bone density
- too much cholesterol
- increased risk of urinary stones
- impairing the development and function of the nervous system
- feel unwell
- being perpetually tired
- an increase in tooth decay
- increased risk of certain types of cancer
- being overweight or even obese (see how carbohydrates make us fat)
- in the long term, an increased risk of type 2 diabetes
So what is the right amount to take?
For an individual, it is advisable to take a carbohydrate level of around 55% of calories daily. To illustrate this, for an accomplished use of 2000 kcal, 55% of this should be carbohydrate nutrients, equivalent to 1100 kcal. As mentioned earlier, 1g of carbohydrate is worth 4 kcal. So over the course of a day, it is necessary to consume around 275g of carbohydrate for an individual.
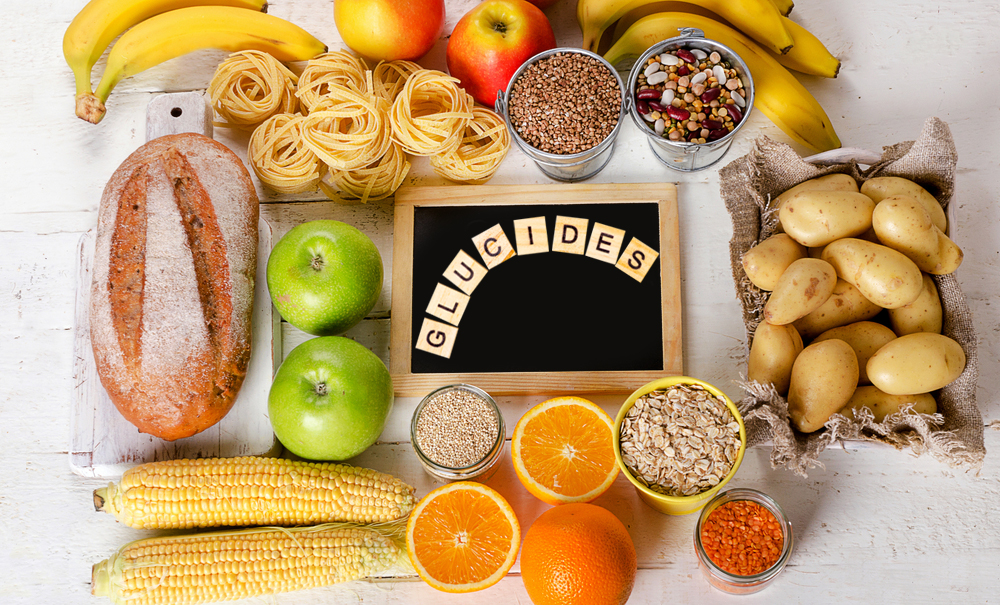
Where are carbohydrates found?
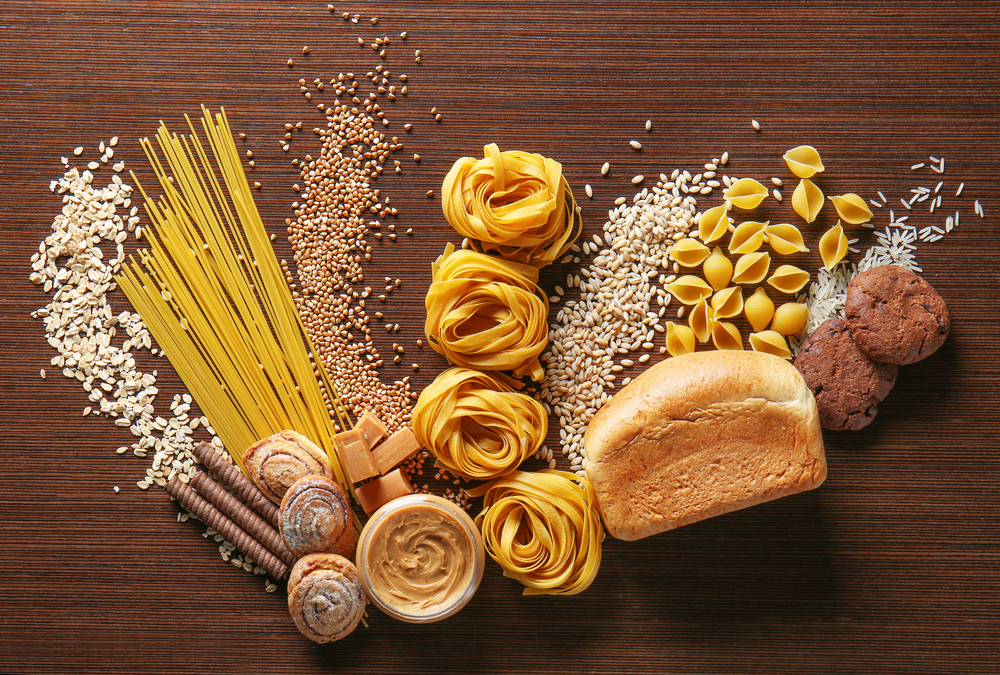
Carbohydrates are found in many foods, especially in plants. They are very rare as in the natural food. Whereas carbohydrates are found in large quantities in cakes, biscuits or sweetened drinks (there are even sweeteners). That's why experts advise minimising the consumption of these products. The simple carbohydrate, or fructose, is mostly found in fruit, honey and corn, in natural form. Another simple carbohydrate such as lactose is found in milk. Sucrose which is a disaccharide (basic molecules), formed of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule, they are found in beet, sugar and cane sugar. In conclusion, maltose is made up of two glucose molecules.
For dietary complex carbohydrates, starches, they are mostly found generally in vegetable types such as potatoes, beans, lentils, chickpeas, but also cereal grains such as rice, wheat and corn etc. . . Fibre or non-assimilable complex carbohydrate is mainly found in fruits, vegetables and dried fruits such as almonds, walnuts, etc.