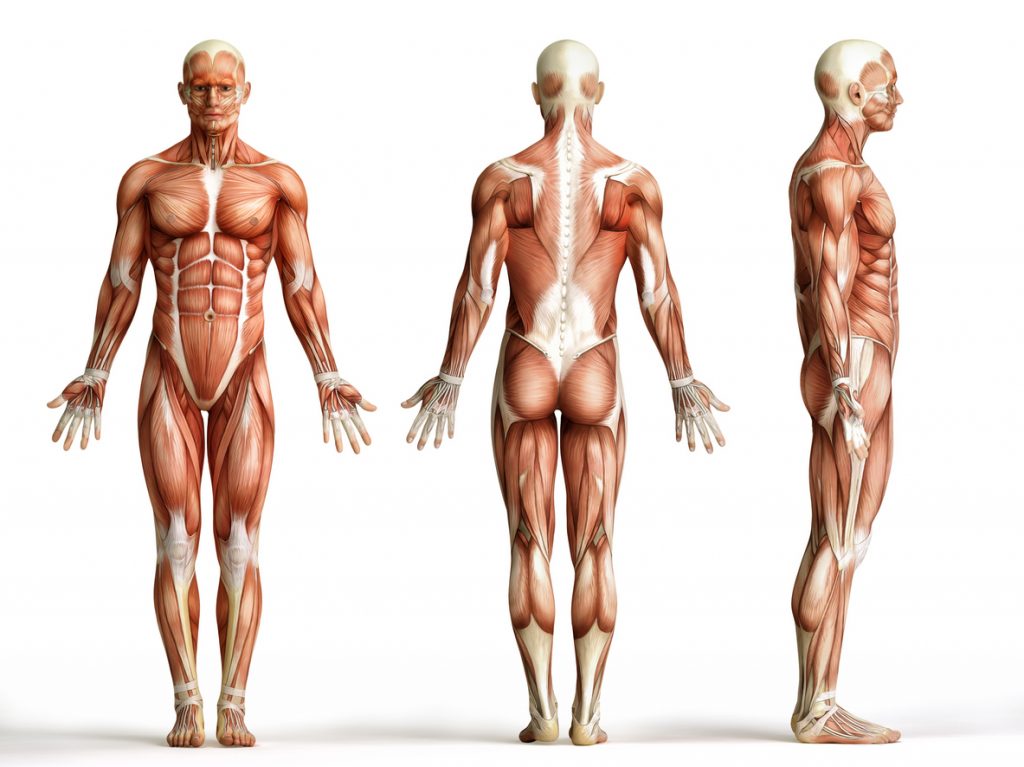
For any bodybuilding enthusiast or fan, before you really dive in. The first thing to remember is how your body will react to the sport and what its limits are. Indeed, the human body is made up of a complex network of more than 640 muscles all of which have either motor function, or to maintain the dynamism of the body and still other functions.
It is essential to know the basis of the muscle groups in order to build a beautiful body. This will facilitate a better analysis of the body itself, as well as a correction of the movements, and an adaptation and targeting of the essential parts for a good muscular catch. To know the basics about the muscles, here are a few paragraphs that detail the superficial muscles.
The muscles of the upper body
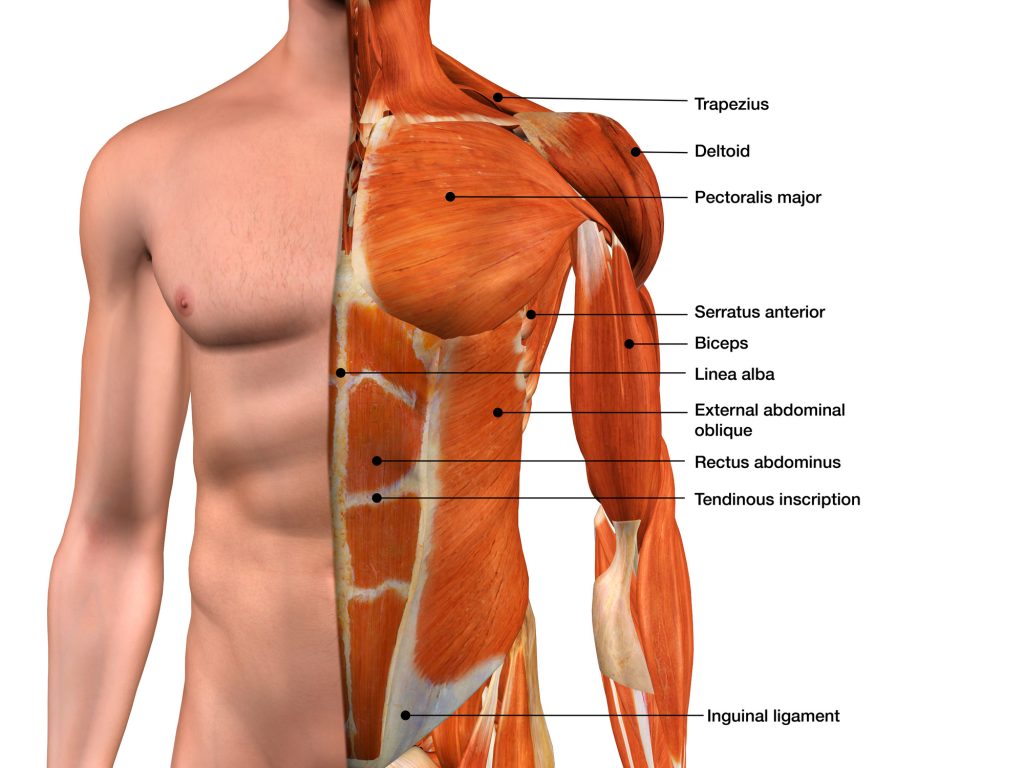
Generally speaking, only a small percentage of sportsmen and women in any field really know what the muscle groups are. They only know the most famous ones like pectorals,abdominals, biceps and even then they know them by name but not by function. This often causes frequent injuries in some people because they do not know the limits of the body nor the appropriate gestures to avoid this kind of situation.
Muscle groups of the arm
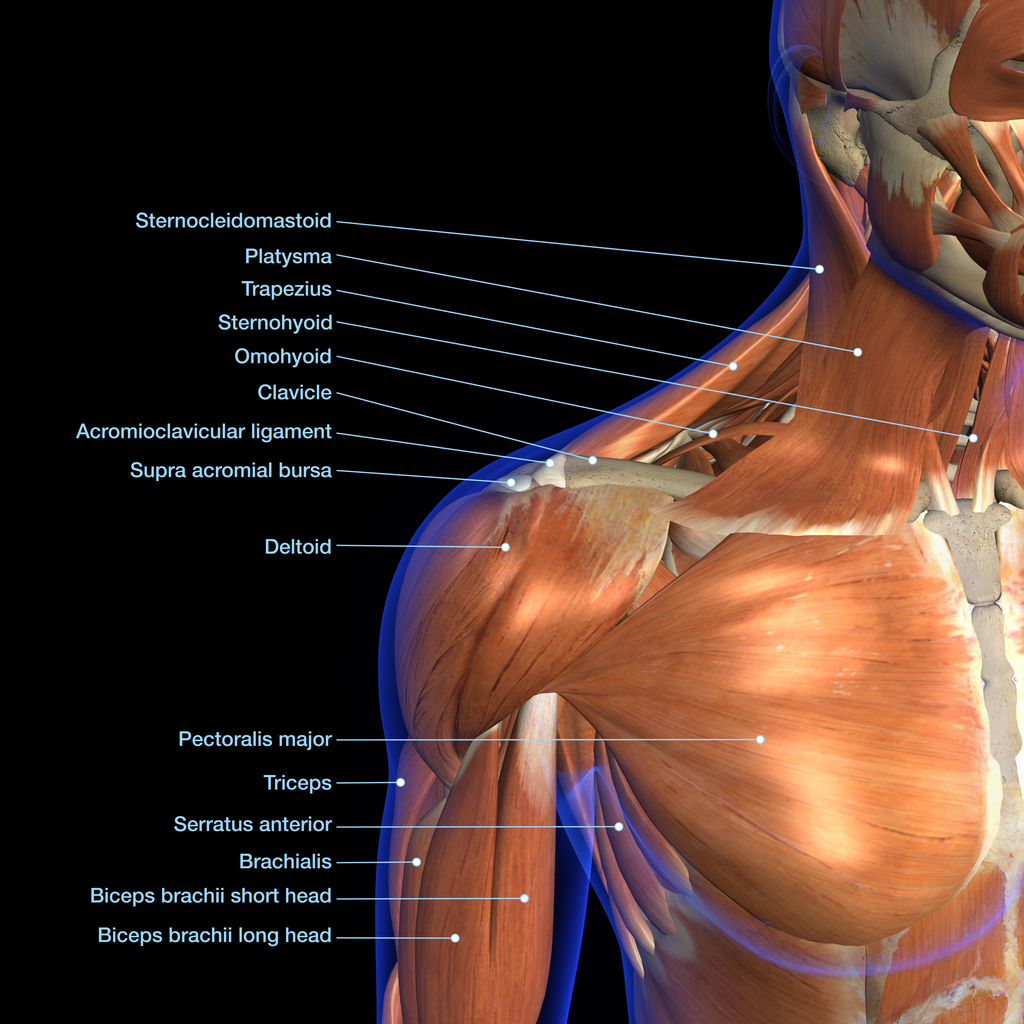
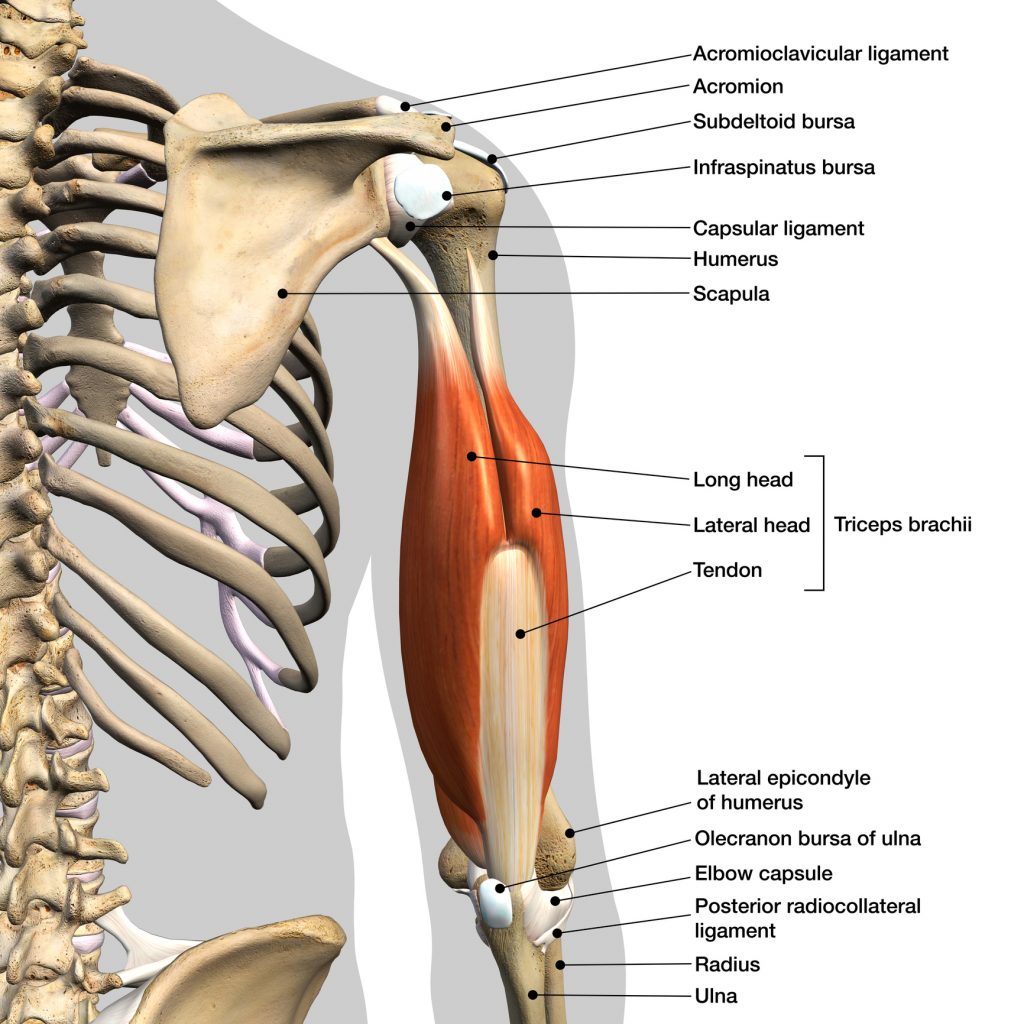
For a bodybuilding enthusiast, having a wide circumference of the arms is one of the most important things. It includes the biceps, which provides rotational movements of the forearm and is made up of a front part, the biceps brachii, and an outer part, the brachialis. The latter constitutes 1/3 of the total volume in opposition to the triceps 2/3 of the volume, in the posterior part of the arm ensuring the movements of extensions and subdivided into 3 parts: vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, the long head.
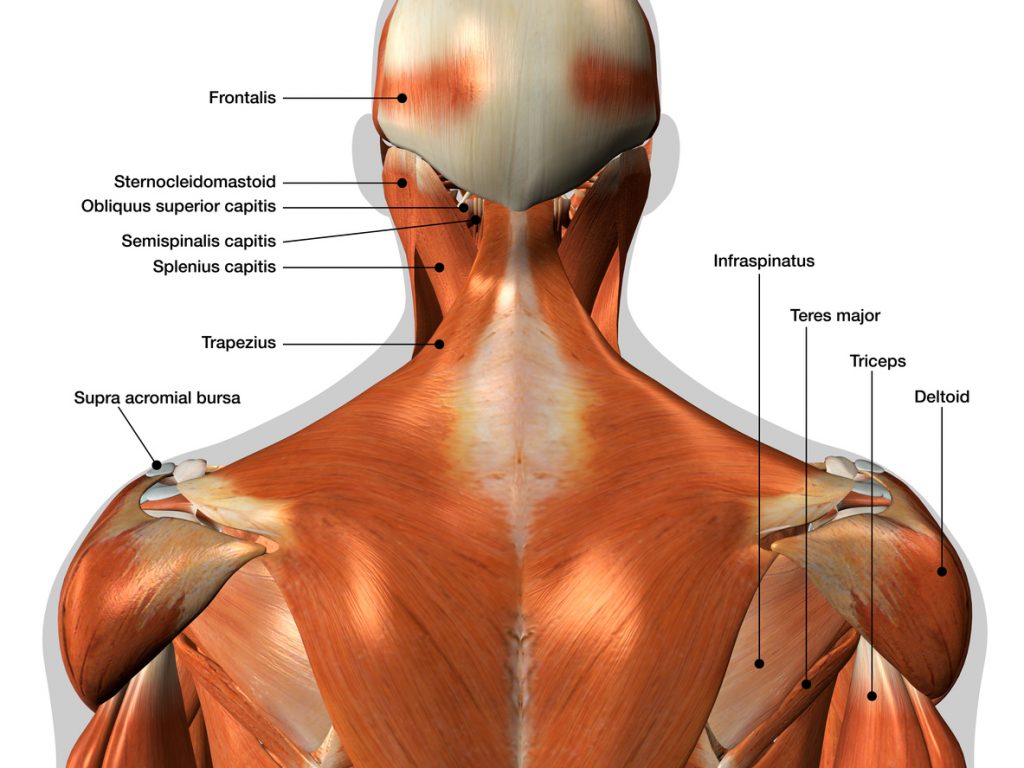
Then there are the shoulders or deltoids which are considered a large muscle and are essential for performing any type of movement involving the upper part. Each is subdivided into 3 muscle groups: anterior, lateral and posterior. These work together to allow flexion and abduction movements and also extensions. But the shoulders are essential, allowing the arms to perform rotational movements. The forearms complete the action, and they are made up of several muscle fibres whose roles are to allow finger and hand movements but also to be in osmosis with the movements of the biceps. The muscles are the brachioradialis, the ulnar flexor carpi and the palmaris longus.
The muscle groups of the shoulder girdle
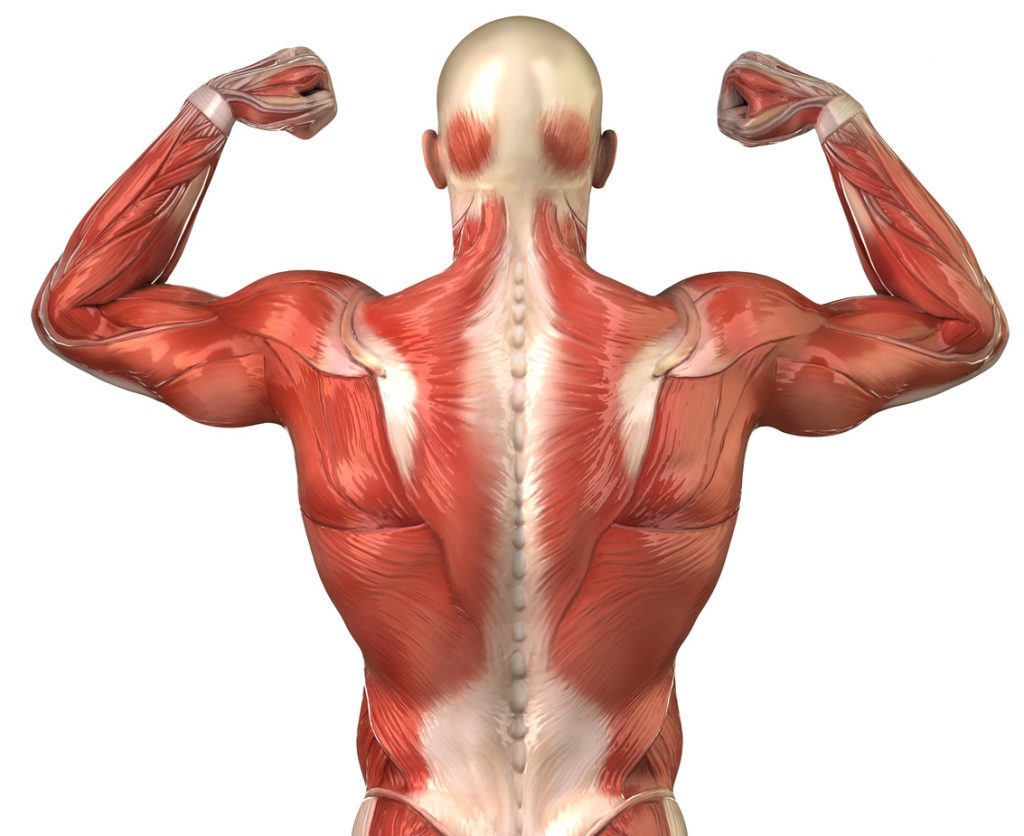
A distinction is made between the trapezius muscles, each of which is subdivided into upper, middle and lower parts. They can be combined with shoulder movements during training because they are connected. And their role is to allow movements of the shoulders as well as a movement of the head on three sides. Secondly, there are the pectoral muscles, which are subdivided into two. They are among the largest muscles used by many athletes because of their morphology, plus they give such a nice shape to the chest. Then there is the pectoralis minor which is a deeper muscle. The pectoral is essential for the movement of the arm. Its development can be carried out in particular by push-ups or bench presses.
The Latissimus dorsi is a large muscle or even the largest muscle in the human body. Its surface area surrounds a large part of the rib cage, extending from one end of the pectoral muscles to the bottom of the back. Its development is done by climbing movements relying on the sole strength of the arms. It therefore allows free movement of the trunk and arms.
The muscles of the abdominal wall
This part is one of the most complex to work because it uses the movement of a group of muscles. It is composed of 3 parts which are the obliques located on the extremities and allow movements of rotation, inclination of the trunk and the pelvis. Then, the rectus abdominis is located on the surface and above the obliques and transversus muscles. The difficulty in the appearance of the chocolate bars is that they are all muscles located in depth and therefore very difficult to target.
Lower limb muscles
Adductor muscles
As the name suggests, these are the muscles that oppose the abductors. They allow a return movement of a limb towards the body. They are found on the inside of the thigh. These muscles play an important role in standing upright, but also in maintaining balance, even when standing on one leg, by locking the pelvis. The adductors extend from the pubis to the posterior vertical crest of the femur but are made up of several muscles including: the adductor magnus, adductor longus, pectineus and gracilis. But in addition to playing a role in standing, they allow flexion or rotation, this is perfectly felt in the legs when climbing stairs. They are therefore the most worked by footballers. In the field of bodybuilding, their first work guarantees soreness the next day.
Buttocks
The buttocks are without context very appreciated muscles of the glance, at the two sexes, they are thus very worked currently. But they don't just adorn the body, they are the most voluminous and the most powerful. Indeed, these muscles stabilise the pelvis and allow the movement of the thighs. They are a group formed by: the gluteus maximus, which gives them their much-prized curved shape, the gluteus minimus and the gluteus medius.
The ischio-leg muscles
More commonly known as the muscles at the back of the thigh. They play an important role in knee and leg flexion, but also in hip extension. They are also used extensively in walking and standing. Working them in a run is very common. The hamstrings are made up of 3 muscles: the biceps femoris, the semitendinosus and the semimembranosus. These muscles extend to the pelvis (part used for sitting) below the knee. The semitendinosus is medial, followed by the semimembranosus and externally, the biceps femoris.
Plyometric, polarity and other exercises
In bodybuilding, there are two types of exercises, the first one groups isolation exercises and the second one constitutes polyarticular exercises. Particularly, these last ones are work of joints and different muscle groups. For example, the deadlift and the bench press are part of the polyarticular exercises. In particular, the deadlift mobilises several joints including the hips, knees, calves, quadriceps, hamstrings, trapezius, lumbar, lower back, lats, abs, gluteus maximus and medius, forearm muscles, in short a whole host of joints. Discover the benefits of multi-joint exercises.
Sometimes to perfect trainings it is essential to do plyometric exercises and regularly do the best basic strength training exercises.