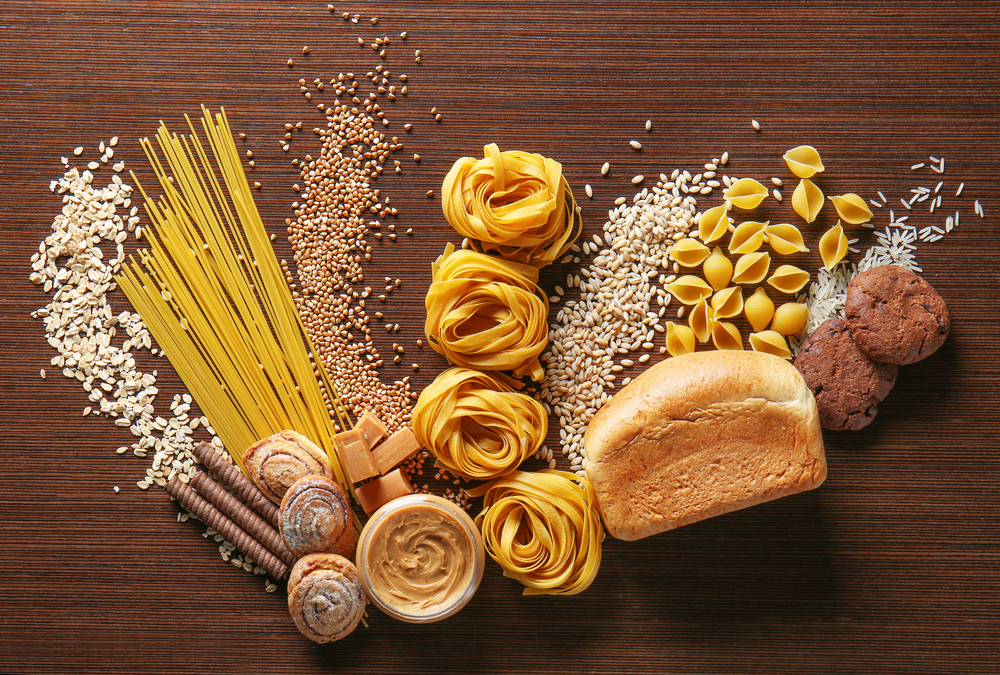
Apart from fats and proteins, carbohydrates play a very important role in providing energy to the body. They mainly deliver energy to the brain. The least you can do is to get half of your required caloric intake during a day from carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are mainly found in plant foods such as pasta, potatoes, fruit and vegetables, but also in some animal food sources such as milk.
OPT FOR POLYSACCHARIDES INSTEAD OF MONOSACCHARIDES OR DISACCHARIDES
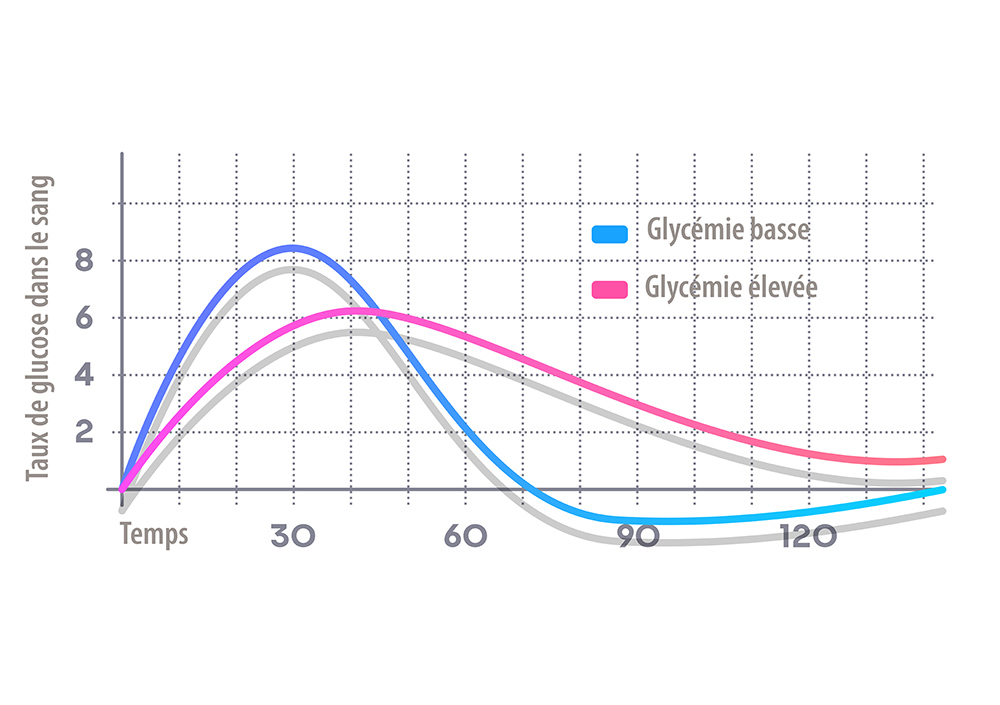
Depending on the composition as well as the effect on a person's metabolism, there are different kinds of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are easily and quickly processed by the body and go directly into the bloodstream. They are produced continuously and cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels.
MONOSACCHARIDES
Monosaccharides, or oses, are the simplest carbohydrates and cannot be hydrolysed. There are two types: aldoses and ketoses. They are also distinguished by the number of carbon atoms in their chemical structure, such as trioses, pentoses and hexoses. The main monosaccharides are glucose, fructose and mannose. They all have the same chemical formula (Cn(H2O)n), but different configurations.
Monosaccharides are not composed of only one sugar molecule, for example glucose and fructose. Glucose causes a rapid rise in blood sugar levels and provides an instant source of energy. Fruit, honey and sweets contain glucose.
- Sucrose
It is a white solid, crystallised in the anhydrous state and very soluble in water. Widespread in the plant kingdom, sucrose is abundant in the beet root and sugar cane stalk.
- Maltose
This is a disaccharide that is not very abundant in the free state. It exists in malt where it results from the enzymatic hydrolysis of starch.
- Lactose
Soluble in water, lactose is found in the milks of Mammals (4 to 5% in cow's milk and 5 to 7% in women's milk).
DISACCHARIDES
Disaccharides are formed by the combination of 2 monosaccharides during a synthesis reaction. Made up of two sugar molecules, for example (milk sugar) cane sugar, beet sugar and food sugar, this glycosidic bond results from the union of two hydroxyl groups with the loss of a water molecule. Dairy products, sweet foods such as chocolate, jam and biscuits contain large amounts of monosaccharides and disaccharides. The most important ones, with the formula C12H22O11, are sucrose, maltose and lactose.
POLYSACCHARIDES
These are the polymerisation products of glucose and are represented by starch, glycogen and cellulose. They are also called complex carbohydrates, because they are composed of at least 10 molecules. Because they dissolve more slowly, they promote a slower rise in blood sugar levels and prolong the feeling of fullness. Polysaccharides should therefore make up the majority of the carbohydrates a person consumes.
Polysaccharides are most common in oatmeal, rice and potatoes. They also provide essential vitamins and minerals. Dietary fibre is also found in wholemeal products and is in a special form. For a healthy stomach and intestines, dietary fibre aids digestion.
If a person is intensively involved in sports, his or her body obviously needs a somewhat higher carbohydrate content. This is because the body needs energy to perform. Carbohydrates are the ones that provide energy and power to the person. However, before competitions, during heavy use or after intensive training, it is advisable to eat a diet rich in carbohydrates in order to regenerate the energy.
THE NEGATIVE SIDE OF CARBOHYDRATES, ESPECIALLY IN TERMS OF BODY FAT
If a person's diet provides more carbohydrates than they burn, the muscles store the remaining sugar as glycogen. In this way, the body can draw on this energy reserve when it is needed more and the person is not taking in more through nutrition.
If the glycogen reserves in the muscles are always full because a person consumes too many carbohydrates, the extra energy is converted into fat and the person gains weight.
Excessive carbohydrate intake (especially refined sugars) has been shown to have harmful effects including increasing the risk of dental caries, certain types of cancer, overweight and obesity and high blood triglyceride levels. In the long term, excess sugar can cause hyperinsulinism and then type 2 diabetes.
WHEN TO EAT CARBOHYDRATES AND IN WHAT AMOUNTS?
To lose weight easily, it is advisable to keep your diet low in carbohydrates. It is best to replace high-calorie carbohydrates with high-nutrient proteins. When consuming carbohydrates, it is best not to focus too much on monosaccharides and disaccharides in favour of complex carbohydrates.
Carbohydrate requirements are based on the average minimum amount used by the brain. There is no tolerable maximum intake of carbohydrates because there is insufficient scientific data. However, it is advisable to limit the intake of added sugar to less than 15g per day because beyond this amount, individuals tend to consume fewer essential nutrients. In addition, the consumption of added sugar promotes overweight and civilisation diseases such as diabetes. Soft drinks, sweets, cakes, biscuits, fruit drinks, sweetened dairy products and breakfast cereals are the main sources of added sugars in the population.
The glycaemic index shows how quickly a food can raise blood sugar levels. Fish, meat, vegetables, salad, nuts, legumes and wholemeal products have a low glycaemic index, prolong the satiety effect and provide energy even during a diet.

![shutterstock_1151142092 [Converti]](https://www.ericfavre.com/lifestyle/uk/wp-content/uploads/sites/15/2021/09/que-sont-les-glucides.jpg)