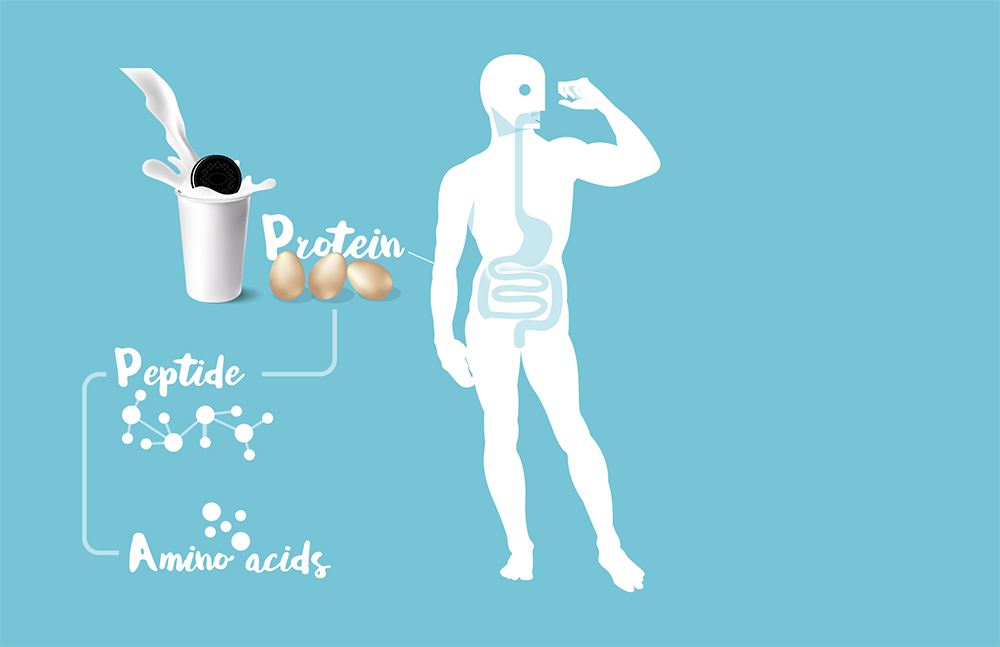
Amino acids are molecules that make up proteins. They are fundamental to the functioning of the human body. This is why they are often an ideal dietary supplement for athletes. Overall, their role is to transport and store all nutrients such as water, lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
Before listing the different types of amino acids, a clarification is necessary. Amino acids are divided into two groups: non-essential and essential.
Essential amino acids
There are a total of 9 essential amino acids. They are called essential because the body is unable to produce them itself. It is therefore essential to find them through the diet.
- Leucine:Leucine plays a very important role in muscle building, as it is involved in muscle reconstruction. It is also involved in tissue and bone regeneration. It is mainly found in red meat, turkey and tuna.
- Isoleucine:Isoleucine helps the muscles to recover after physical effort. Isoleucine also promotes the transport of red blood cells, and therefore oxygen, in the body. It is found in dried vegetables and fruit and in wholemeal cereals.
- Valine: This is a source of energy for the muscles, it improves their recovery, but it is also a stimulant for the nervous system. It is found in meat and dairy products in particular.
- Lysine:Lysine is involved in the development of bones and in the secretion of antibodies and collagen. Lysine is found in meat, milk, eggs and legumes, among other things.
- Methionine: Methionine is involved in protein synthesis and plays a role in cell survival. Methionine is present in eggs, meat, soya. . . (it also formstaurine).
- Tryptophan: It is involved in the secretion of serotonin and melatonin. Thus, a deficiency can lead to a dangerous problem with mood (serotonin) and/or sleep (melatonin). Fish or nuts are foods rich in tryptophan.
- Threonine:Threonine is an amino acid that is essential for the regulation of cholesterol in the blood. Threonine is found in abundance in trout, veal and octopus.
- La phenylalanine:Phenylalanine plays a role in the nervous system, by reducing pain and participating in the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters. Phenylalanine is also an intellectual stimulant. It is found in fish, meat and some dairy products.
- Tyrosine:Tyrosine is involved in stress management: it stimulates the production of dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline. Tyrosine is found in many foods such as poultry, almonds, bananas, avocados. . .
Amino acids in children
- Histidine:Essential only for infants, who find it in their mother's milk, histidine enables copper and zinc to be fixed and is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. It is involved in the production of red and white blood cells, protects the nerves and limits the risk of allergies.
Non-essential amino acids
In contrast to those mentioned above, non-essential amino acids are synthesised by the human body. However, in the event of insufficient production, it is possible to find them in the diet.
- Arginine: It plays a role in the immune system, but above all it promotes the secretion of growth hormones. In addition, it is a natural vasodilator: it dilates the blood vessel walls and increases blood flow.
- Cysteine: Although present in small quantities in proteins, cysteine plays an important role in the synthesis of melanin (skin and hair), but it also has an anti-inflammatory role.
- Alanine:It is a neurotransmitter that provides the energy necessary for the liver to function.
- Asparagine:Asparagine is involved in the proper functioning of the nervous system.
- Glutamine:Very useful in bodybuilding, it plays a role in protein synthesis, which means that it is used during muscle contraction. It has an anabolic effect leading to the increase and expansion of muscle cells. In addition, it maintains the intestinal barrier.
- Glycine:Glycine has many roles in the body (neuromediators, detoxifying, antioxidant. . . )
- Proline:Proline allows the synthesis of collagen, a protein that gives strength to the skin, tendons and joints.
- Aspartic acid:This amino acid is involved in what is known as the urea cycle. This means that it enables the protein waste produced by the liver to be "sorted" so that it can be filtered by the kidneys and finally eliminated in the urine.
- Glutamic acid: This is a neurotransmitter that stimulates the central nervous system. Too much glutamic acid in the blood can damage neurons and lead to epileptic seizures.
- Serine: This is a common amino acid in proteins that has an important role in the nervous and immune systems.
Amino acids in bodybuilding
Of course you should not focus on all these amino acids; for the most part you will find them in your daily meals. In bodybuilding, the most important amino acids are leucine, isoleucine and valine which are the amino acids that mostly make up the food supplements called BCAA.
Indeed, from these three amino acids, the human body can synthesise glucose. The glutamine and arginine are also regularly used. And others such as theanine,HMB, or aspartic acid.