Free radicals are unstable molecules created by the body during the process of changing nutrients into energy. And thanks to antioxidants, the body has the possibility to neutralize them.
However, this defence is useless if their production is in excess
This phenomenon will cause several harmful effects on the body. While sport, thanks to the increase in energy needs, increases the production of free radicals.
To stay healthy in this way, it is advisable to know this basic in nutrition and to follow the following guidelines.
A free radical, what is it?
It is a molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons on its outer layer. These electrons cause instability. In order to be in equilibrium, it is necessary for atoms to have an even number of electrons to gravitate around the nucleus. In this case, the electrons are said to be paired.
It is also possible for an atom to lose or gain an electron during oxidation reactions. This system makes these electrons single and thus becomes unstable. This is called a free radical.
Free radicals, necessary in sports
Free radicals are essential for the body's defence. These are necessary in endurance sports. During cycle races, marathons and triathlons, the body needs a high level of oxygen consumption to provide sufficient energy for the effort. In other words, these types of sports are largely the sources of free radicals.
According to the conventional wisdom, sport movement actually increases the multiplication of free radicals. This actually increases the body's ability to defend itself against them. In addition, physical movement develops the antioxidant defence system to effectively avoid oxidative stress.
To protect against free radicals, it is best to carry out daily physical activity. It has been proven that the multiplication of free radicals damages organs and tissues. To fight against oxidative stress (ORAC index), sport is a better solution.
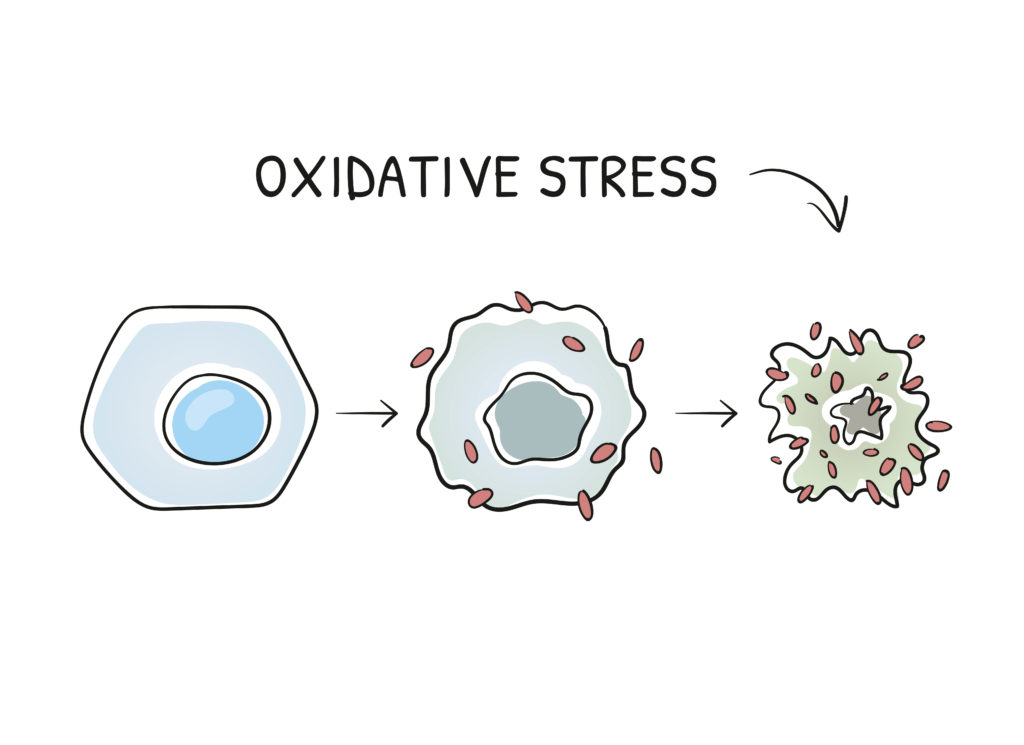
Focus on oxidative stress
When free radicals come from a low amount, the body manages it closely to protect itself from antioxidants. The novel molecules become neutralised and do not damage the cell. In the normal case, the production of free radicals and antioxidants will be balanced.
On the other hand, if free radicals are present in large quantities, the body will not be able to cope with this situation. The antioxidants and free radicals become unstable. And the unstable molecules balance each other to get an electron from the oxidant. In turn, the oxidant will be unstable and become a free radical.
The sequence of this reaction changes the structure of the molecules and also causes them to deteriorate. This is called oxidative stress. There are rusty cells, as it were, because the mitochondria are directly attacked.
Then, this attack continues through the whole cell, even the DNA. If more cells are destroyed than are produced by the organism, the dead cells accumulate. In the long run, they destroy the body and can even cause death. The destruction of DNA leads to the formation of defective cells. This will in effect create dangerous diseases such as cancer.
Free radicals, the source of ageing
According to studies by scientific researchers, free radicals are the source of skin ageing.
They attack the cells and subsequently cause premature wear and tear. It is then possible to die younger instead of living to be 100 years old for example,antioxidant the future of health.
The solution is therefore the reduction of oxidative stress to extend the life expectancy of cells and organs i. e. life, such asubiquinol(a newantioxidant coenzyme Q10). In addition, ageing caused by free radicals will also have an effect on the skin. The sagging of the skin and wrinkles is caused by the oxidation of collagen.
What is an antioxidant?
An antioxidant is a molecule that reduces and even prevents the oxidation process. Previously, it was used to protect metals from corrosion. It is also used as a preservative for food.
But in biology, antioxidants are molecules that control free radicals in the oxidation reaction. They even make them harmless. It is in a way an ideal antidote to counter the harmful consequences of free radicals.
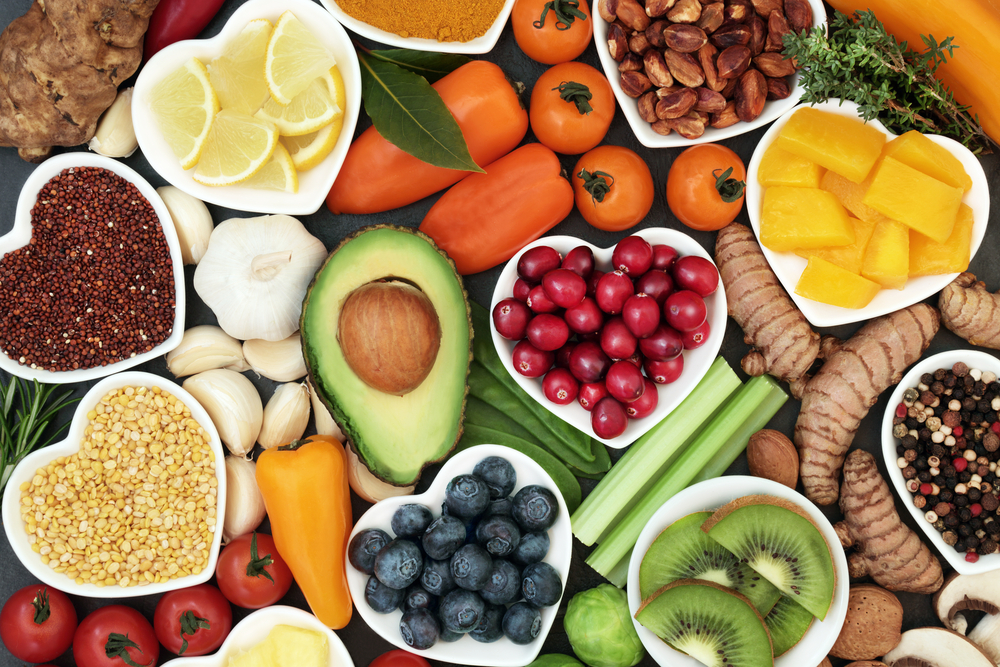
These antioxidants are found in plant foods such as fruit and vegetables. They can also be found in food supplements and the body manufactures them itself.
The Orac Index, a parameter for assessing the antioxidant content of foods
The Orac index is a parameter that measures the capacity of a food to control free radicals. It is an indicator of antioxidant power. The food will be antioxidant when there is more Orac index. In France, the demand for Orac units is increasing especially among sportsmen and women who are often exposed to stress, tobacco and pollution.
Due to misinterpretations and health consequences, the Orac index is currently subject to discussion. It is possible that it can show different effects for the same food because of the number of factors, including food preparation. Within a living organism, the properties of antioxidants do not show the methods of measurement.
Antioxidants, found in many foods
In order to enjoy the benefits of antioxidants (orfighting chronic fatigue syndrome), it is important to know that they are perceivable in anything that contains carotenoids, vitamins A, C and E.
They are also present in certain trace elements and polyphenols. They can also be found in plants such as ripe blackcurrants and cranberries. To benefit from them, it is best to adopt a healthy and balanced diet. Coenzyme Q10, for example, is a powerful antioxidant.
It is present in meat, more specifically in offal, fatty fish, and soybean oils in lower concentrations. It can also be found in whole grains, beef and spinach, allowing you to naturally boost your immune system.