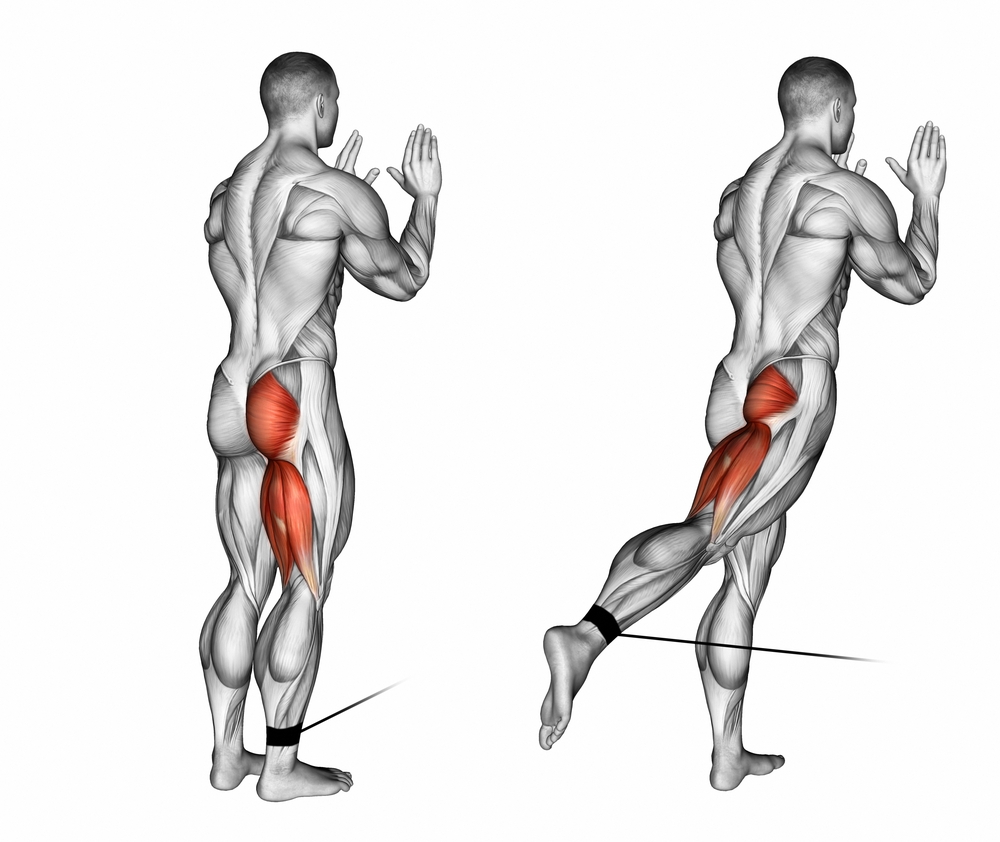
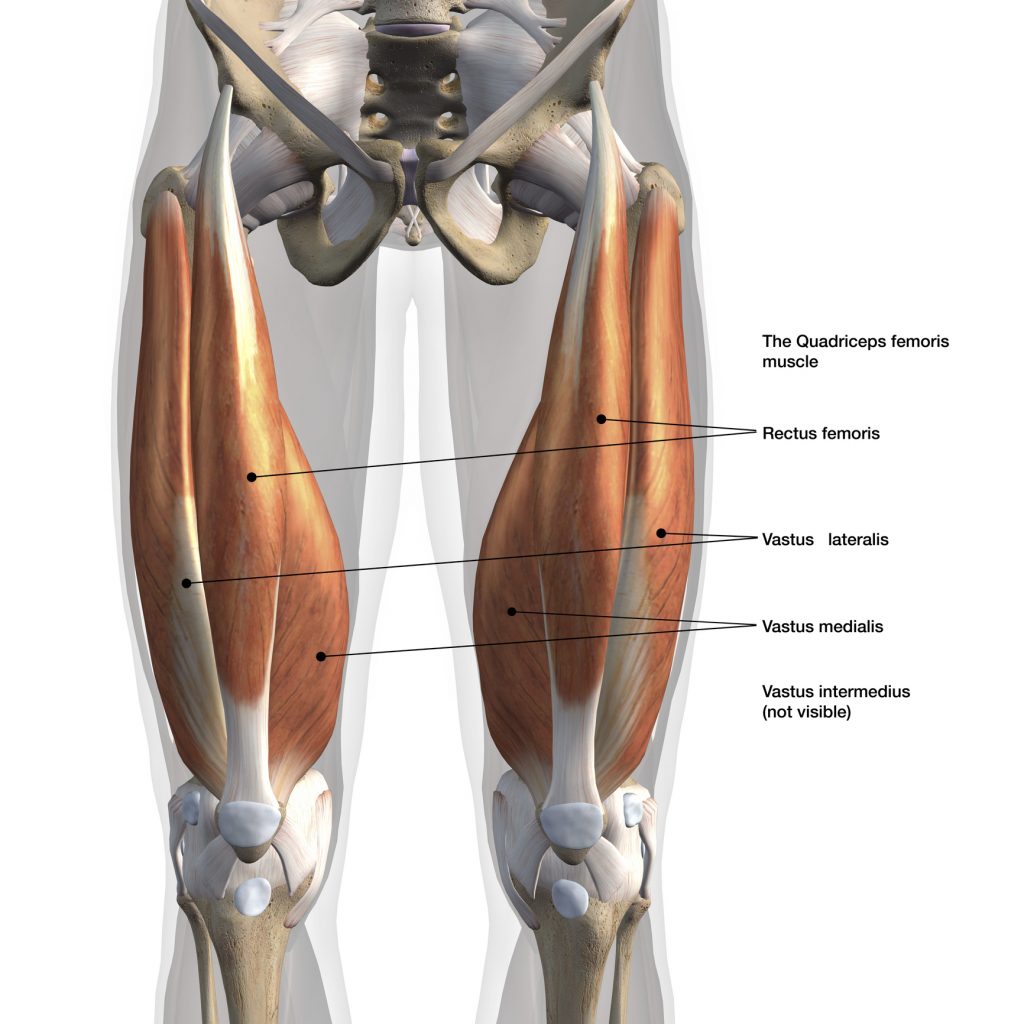
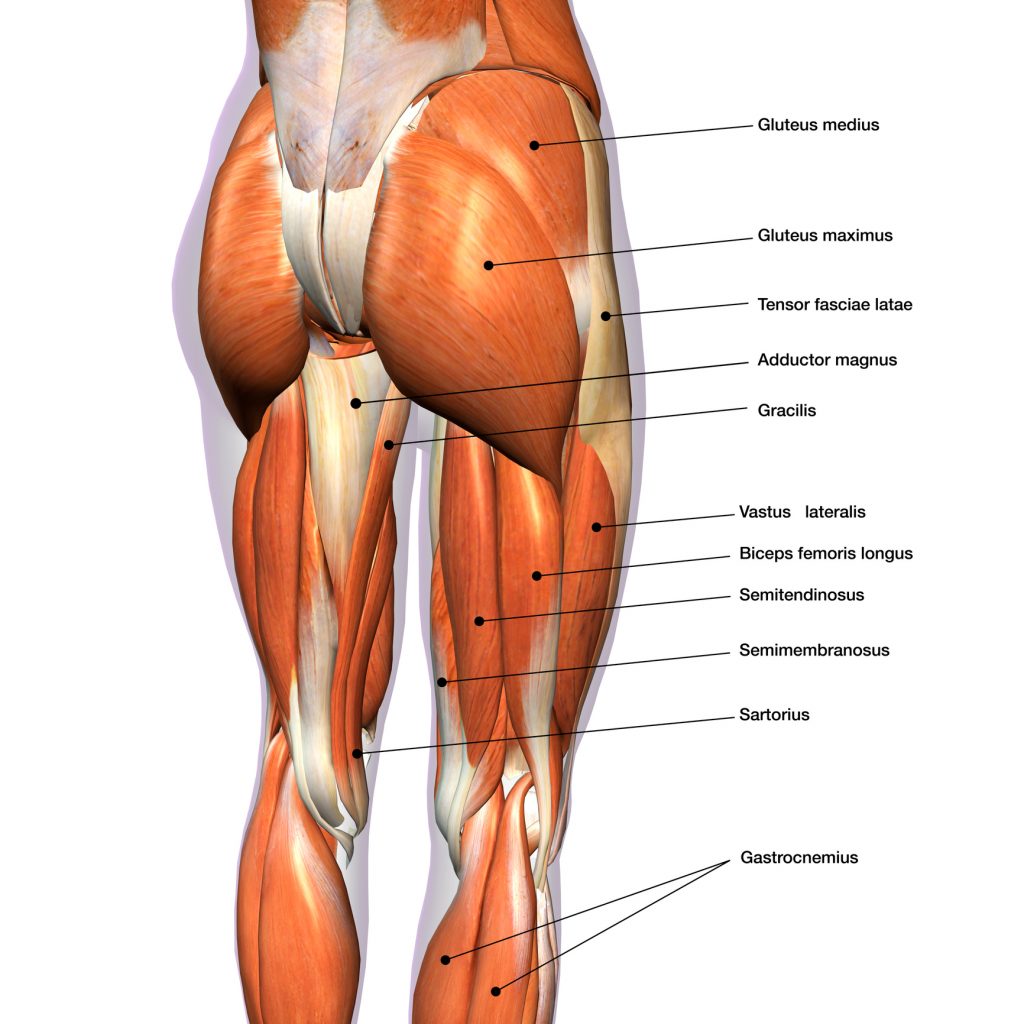
The quadriceps is the largest muscle in the human body, located in the inner thigh (leg). It is the largest muscle in the human body and is used for movement and to carry the body weight.
In 1880, Krause's research on the musculoskeletal system of the quadriceps led to the development of knowledge about this muscle group, which is used in bodybuilding competitions.
Continuous research into human anatomy provides new information about the quadriceps and its biomechanical functions. Thus, since 2016, a group of researchers ,including surgeon Grob K, has been looking again at a new muscle that is part of the quadriceps: the Tensor Vastus Intermedius or TVI.
As described in anatomy textbooks, the quadriceps is composed of an
iliotibial tract as well as 3 vastus muscles (medial, intermediate,
lateral). However, researchers have discovered a new tensor muscle
between the vastus lateralis and the vastus intermedius. It has been
named the ITV, and is therefore the fifth muscle of the quadriceps.
For this reason, researchers refer to it as the quintriceps. The initial aim of the research was to clarify whether this tensor was a variation of the vastus lateralis or the vastus intermedius, or whether it was separate from the extensor apparatus.
The attributes of the Tensor Vastus Intermedius
The main element that proved the proper integrity of the TVI was to study the motor plates, its innervation, and its nourishing source. It was found to be completely independent, innervated by the femoral nerve, and nourished by the lateral circumflex femoral artery.
Distally, the TVI attaches with a separately fused aponeurosis in the quadriceps tendon, and insertion on the medial aspect of the patella. This therefore confirms its own muscular integrity.
This muscle is referred to as the tensor muscle because it has the same function as the tensor fascia lata whose main role is the stabilisation of the knee complex. Thus, during these studies, no less than 4 different chiefs were discovered, defining the properties of this muscle:
- Independent type
- Intermediate vastus type
- Vast lateral type
- Common type