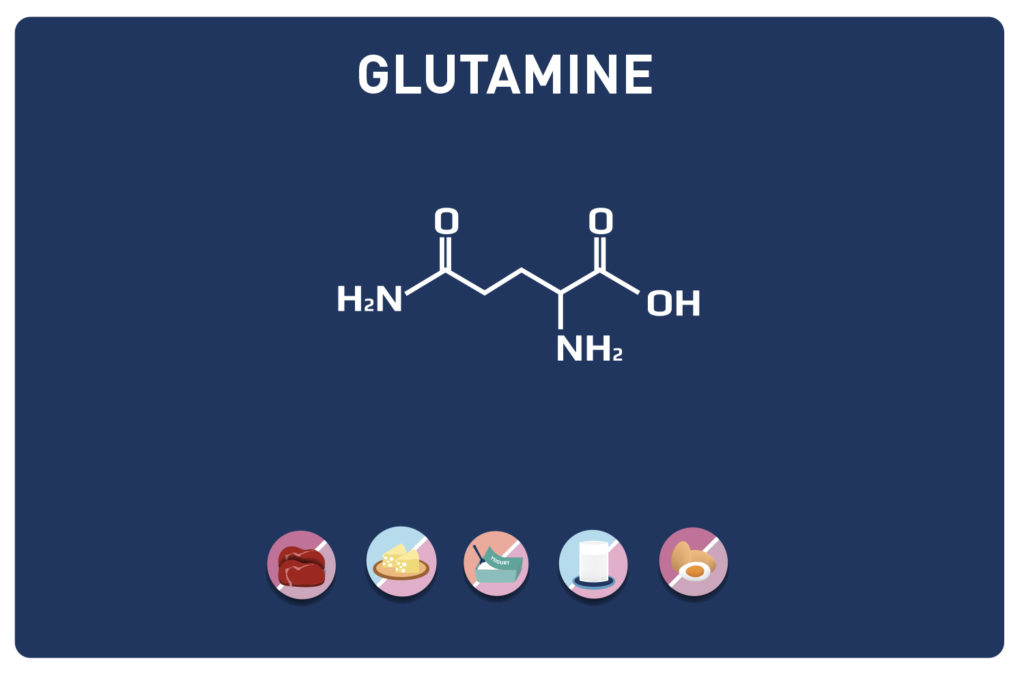
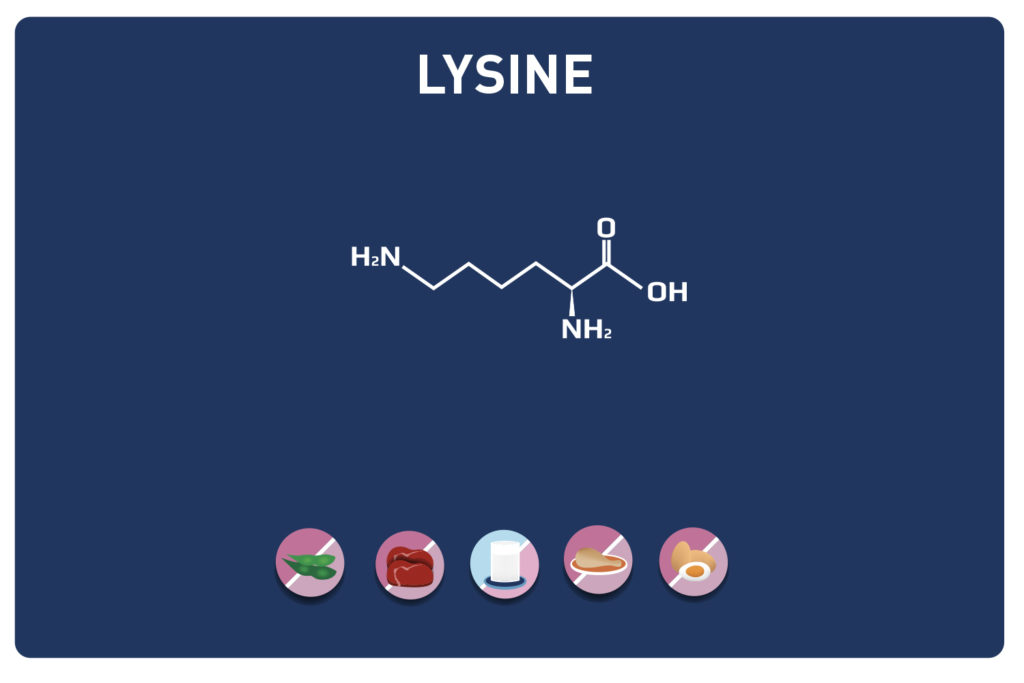
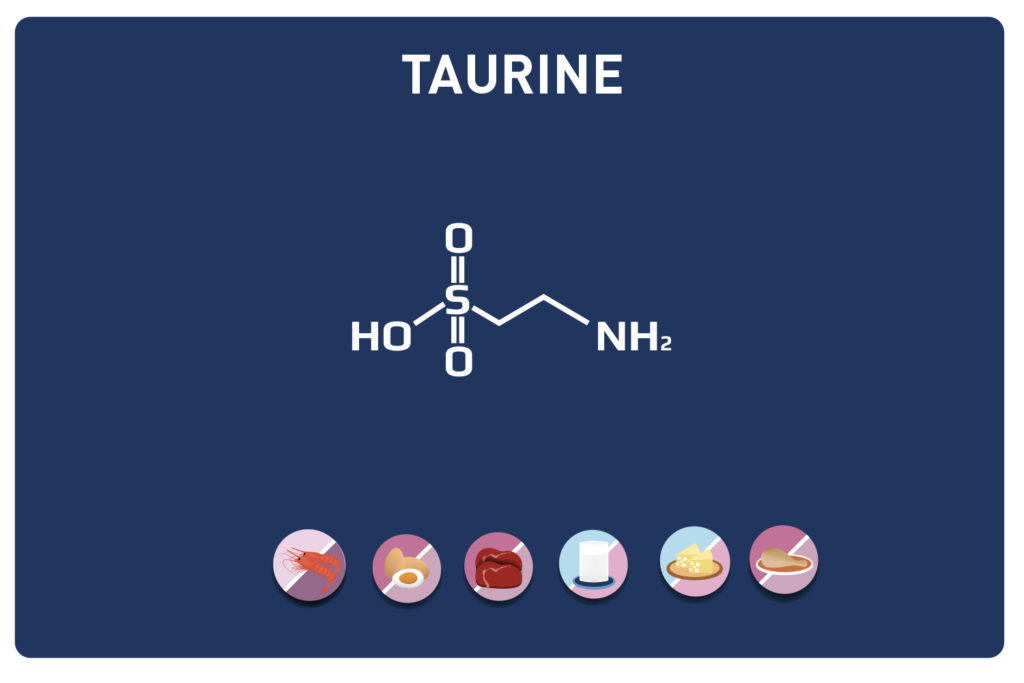
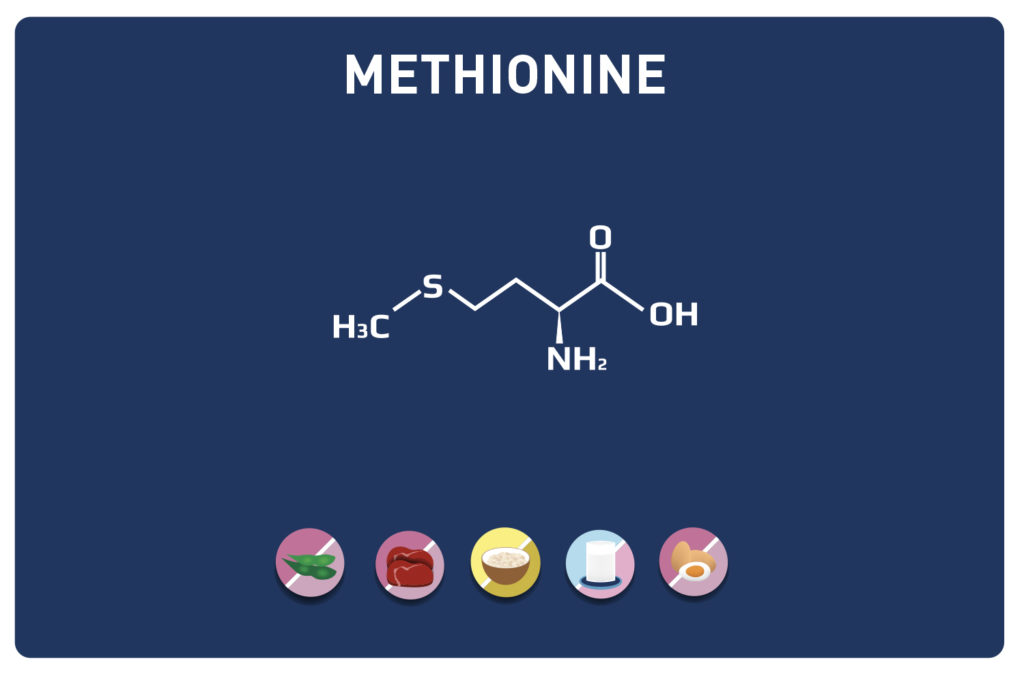
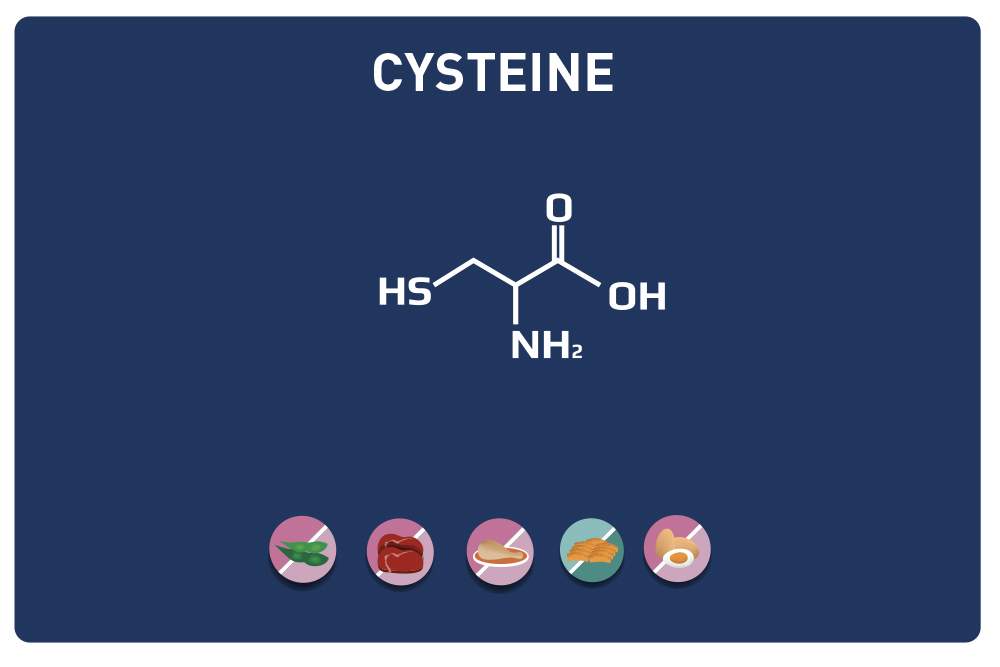
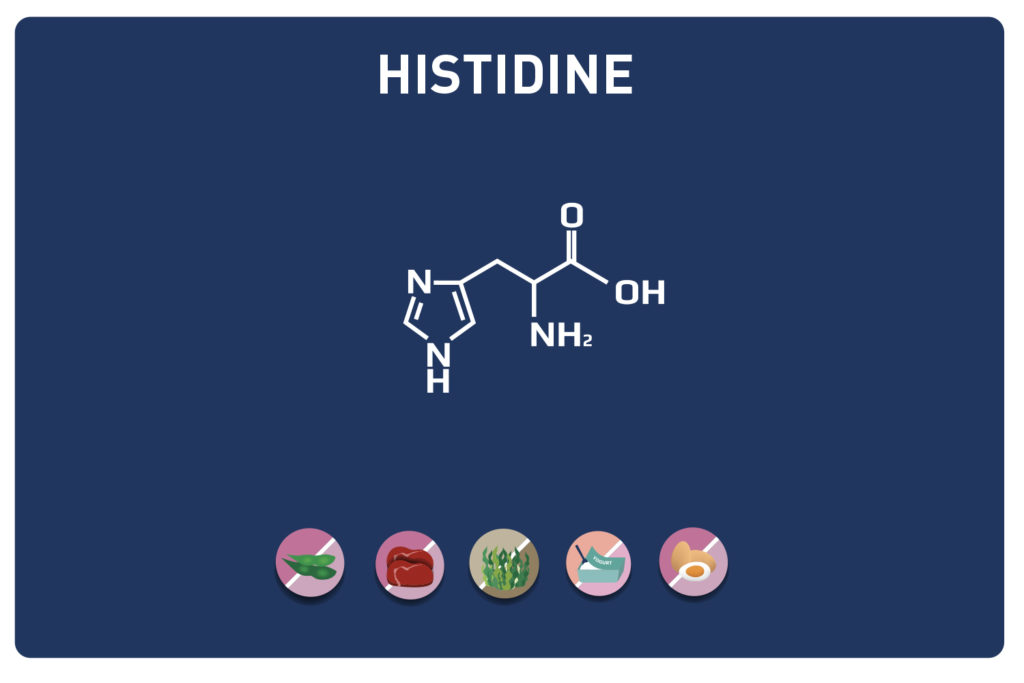
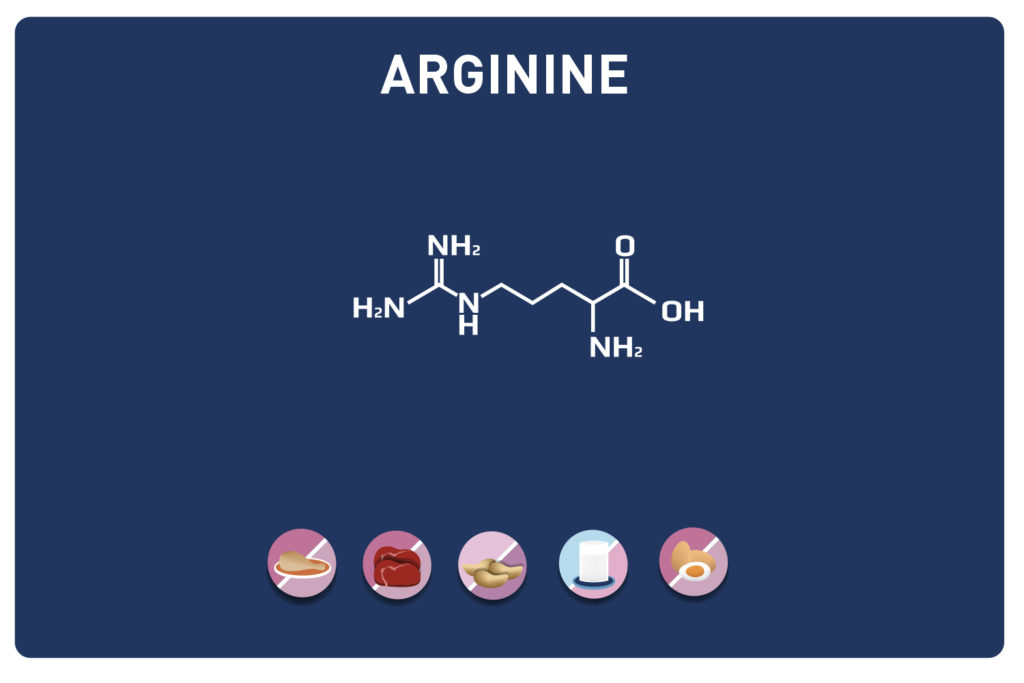
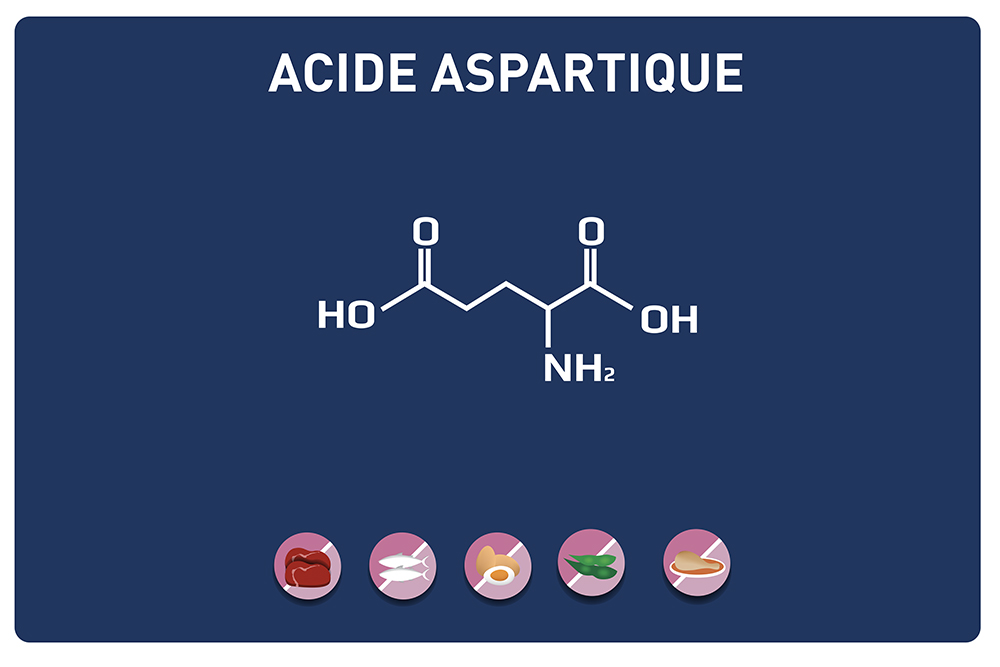
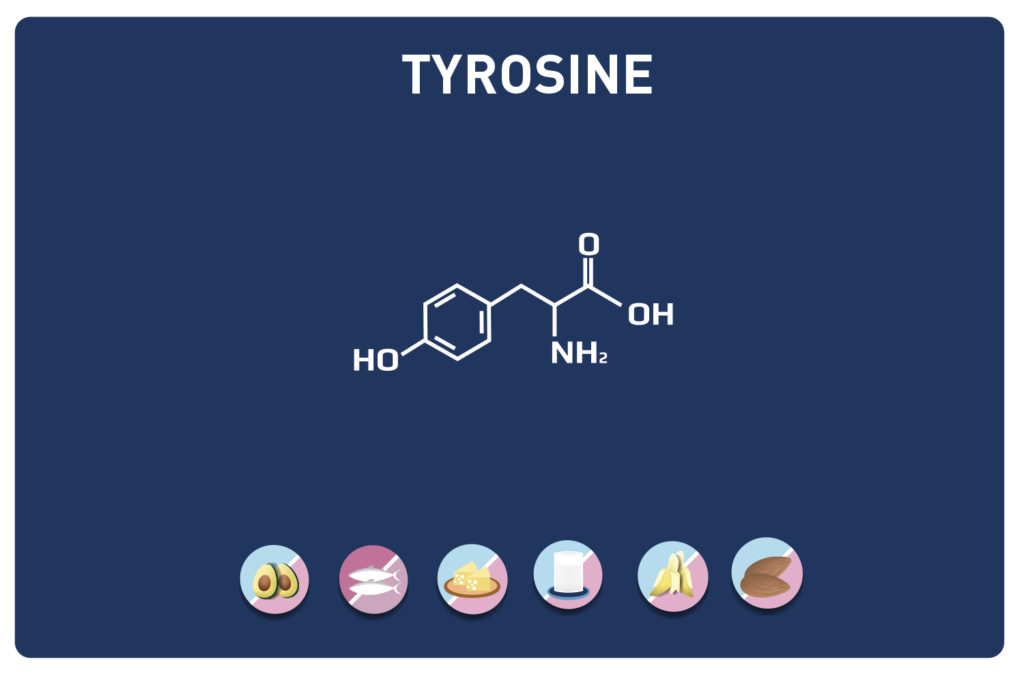
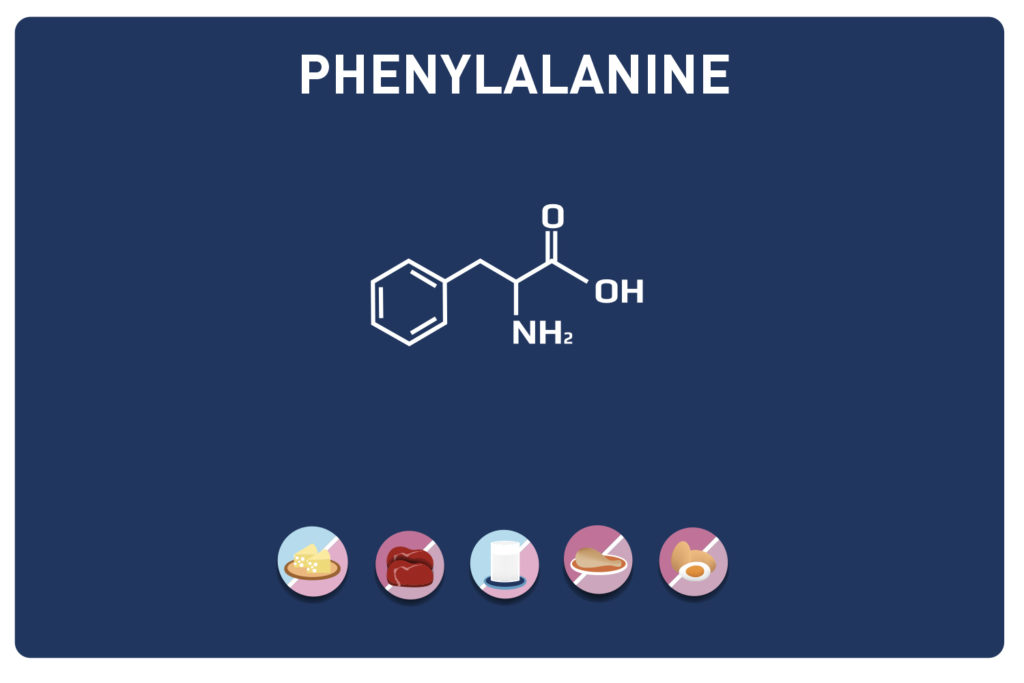
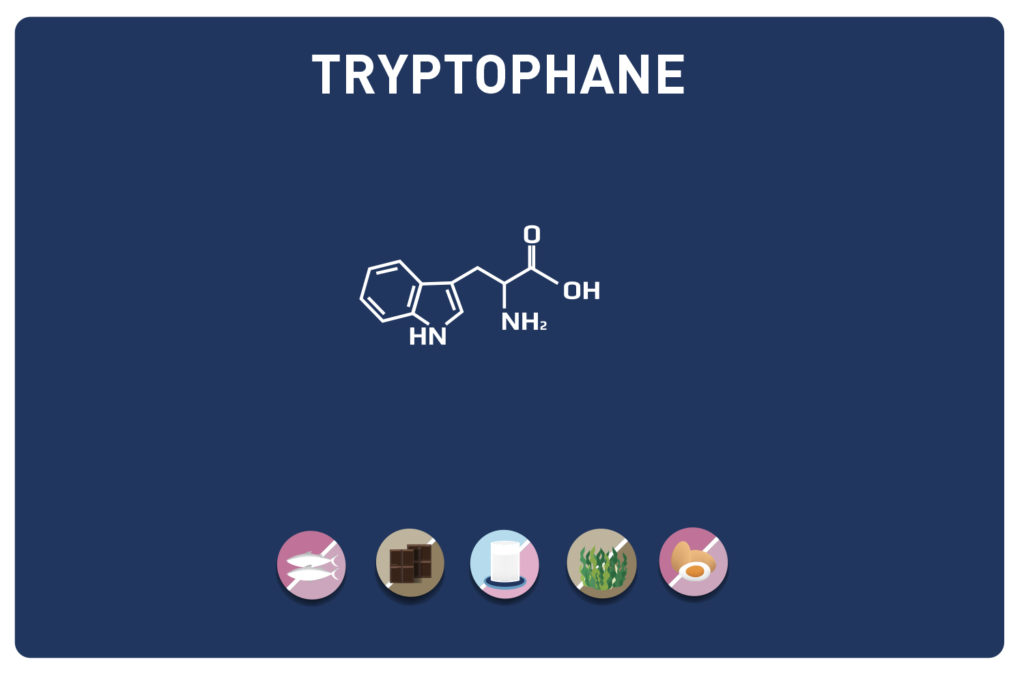
Glutamic acid and its derivatives glutamine and 2-oxo-glutaric acid (alpha-ketoglutarate) are amino acids.
L-glutamine, initially classified as a non-essential amino acid because it can be synthesised from food and other amino acids, is currently considered semi-essential because in certain situations, such as intensive training, its synthesis by our tissues may not be sufficient.
It is the most abundant amino acid in blood and muscles (0. 5 to 0. 8 mmol/l in plasma and more than 50% of free intracellular amino acids).
EFFECT OF EXERCISE
During high intensity exercise, glutamine production by the muscle increases and during low intensity but very long duration exercise, the intramuscular glutamine concentration collapses to half the resting concentration.
In the hours following training, glutamine plays an essential role in protein anabolism and ATP synthesis. At rest, it is responsible for the transport of NH3 from protein breakdown and serves as an energy substrate for intestinal cells.
Why take L-Carnitine?
As L-Carnitine acts as a mobiliser of fatty acids in the body so that they can be burnt properly by the mitochondria and converted into energy, it is suggested that it be consumed before exercise so that it can be effective and have positive effects. Whether in powder, capsule or drinkable solution, 1 to 2 g is enough to be taken about 45 minutes before physical effort.
In any case, the positive effects of L-Carnitine on the muscle are considerable. It is also interesting to take it in post-training to improve muscle recovery, but also to maintain anabolism.
Muscle pain and soreness are much less felt when taking supplements. However, in order to have visible results at the muscle level, L-Carnitine must be taken regularly for at least 6 months. During this period, it is possible to see a reduction in muscle pain.
It should be noted that L-Carnitine supplementation alone cannot claim to burn fat, but should always be combined with physical effort. On the other hand, its contribution to sports performance is undeniable.
L-GLUTAMINE AND OVERTRAINING
Overtraining is a form of exhaustion which, in addition to a drop in performance, leads to a weakening of the immune system, which can make athletes more vulnerable to infections. Various studies have shown that taking 5 g immediately after exercise and 5 g two hours later reduces the risk of infection. (1)
At the intestinal level, glutamine is said to have beneficial effects by improving the functions of the intestinal wall and the proliferation of the flora. (2)
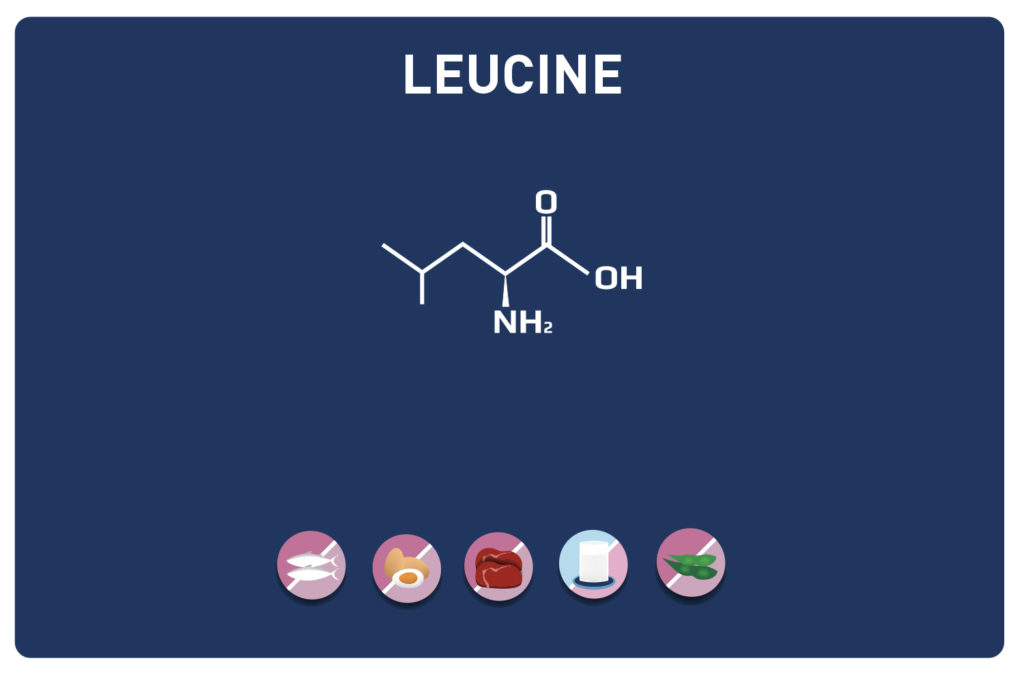
In summary, glutamine promotes muscle development by increasing the leucine level in the muscle and by combating catabolism (degradation of muscle tissue). Taking it after exercise increases the level of GH (growth hormone)(3). It also helps to burn fat and thus facilitate weight loss.
It is known to have a beneficial effect on the immune system, but requires a daily intake of 30g.