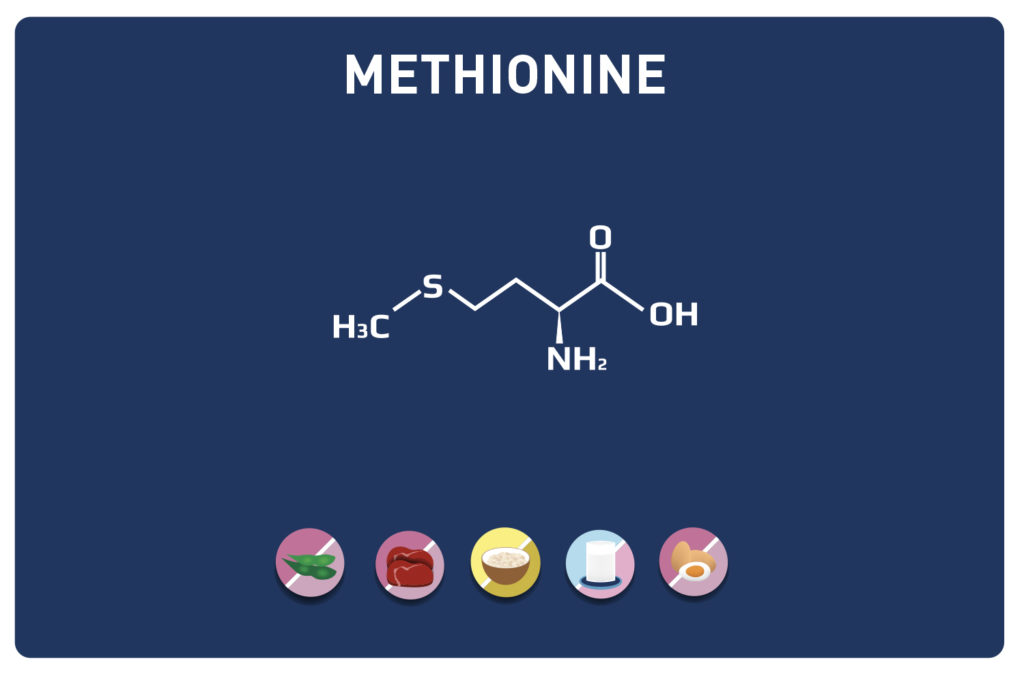
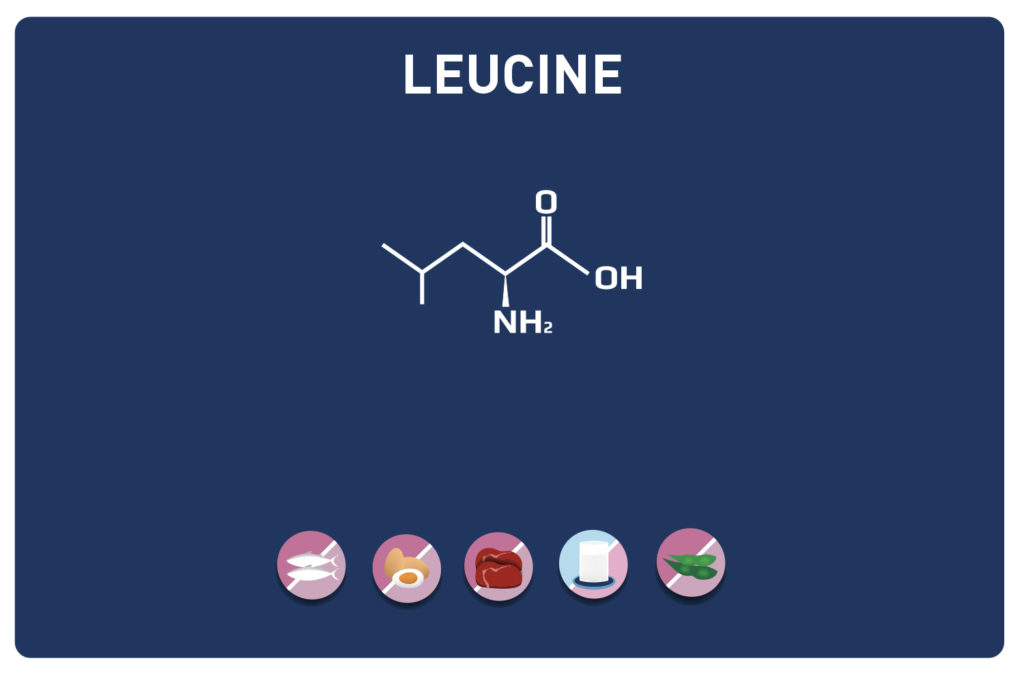
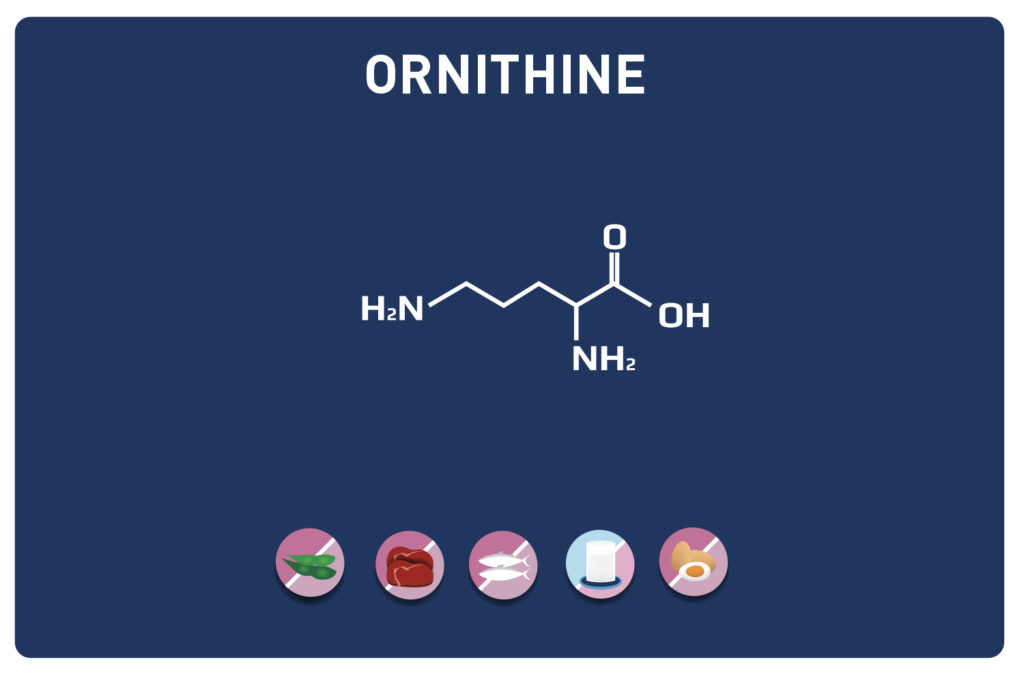
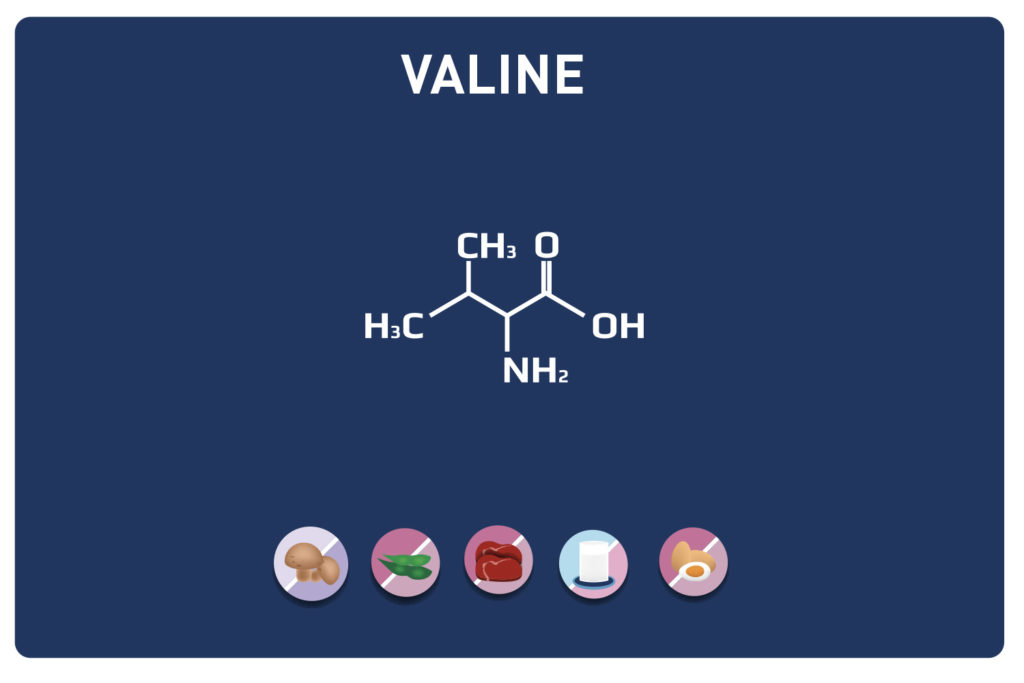
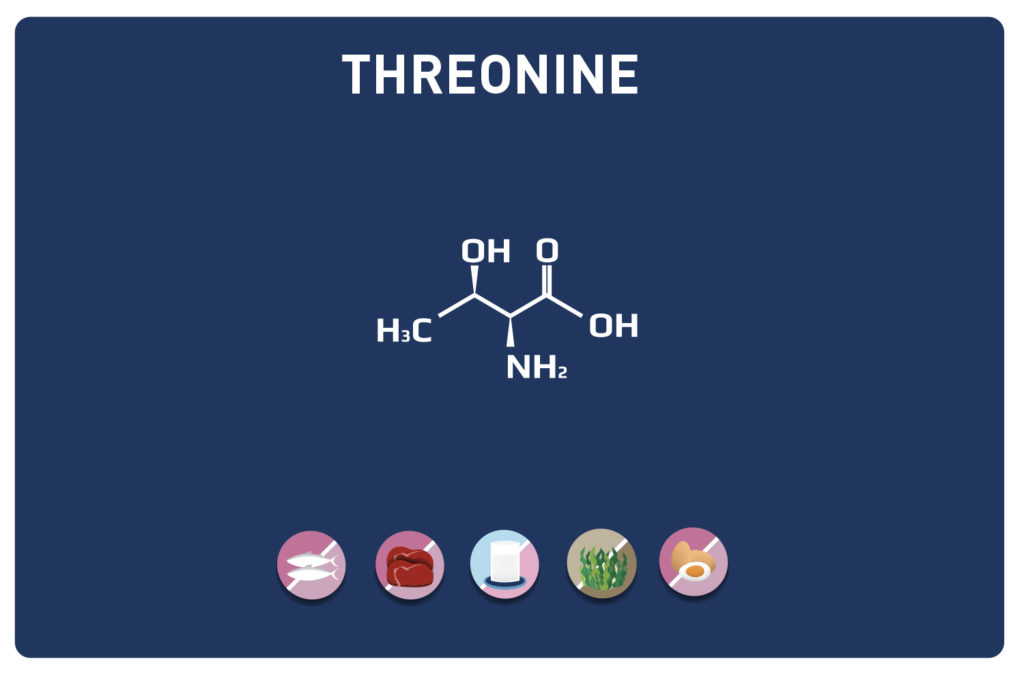
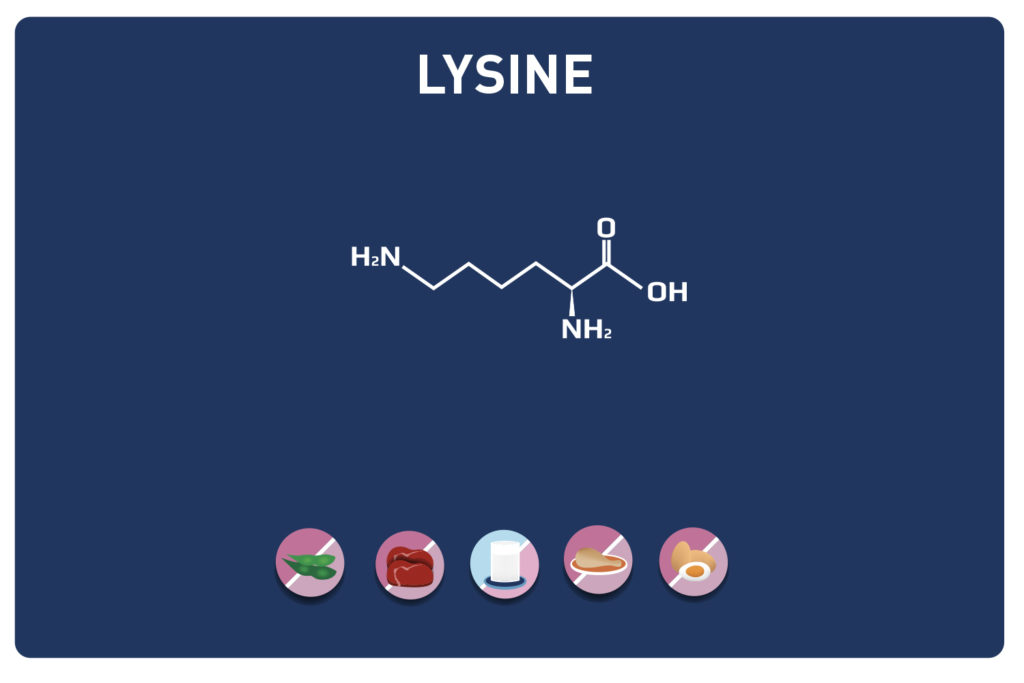
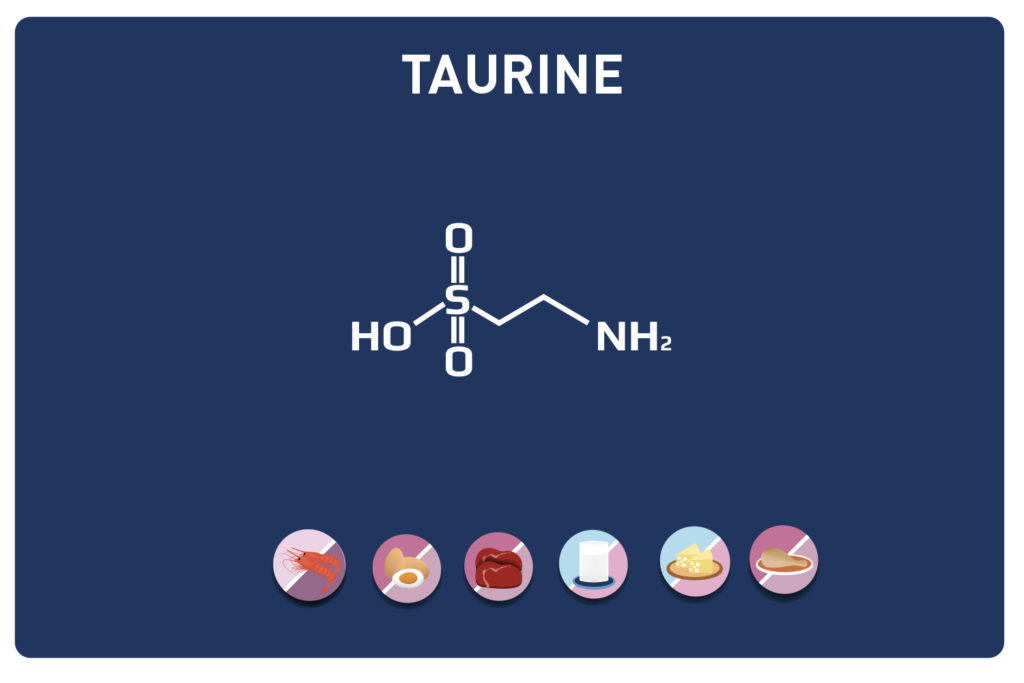
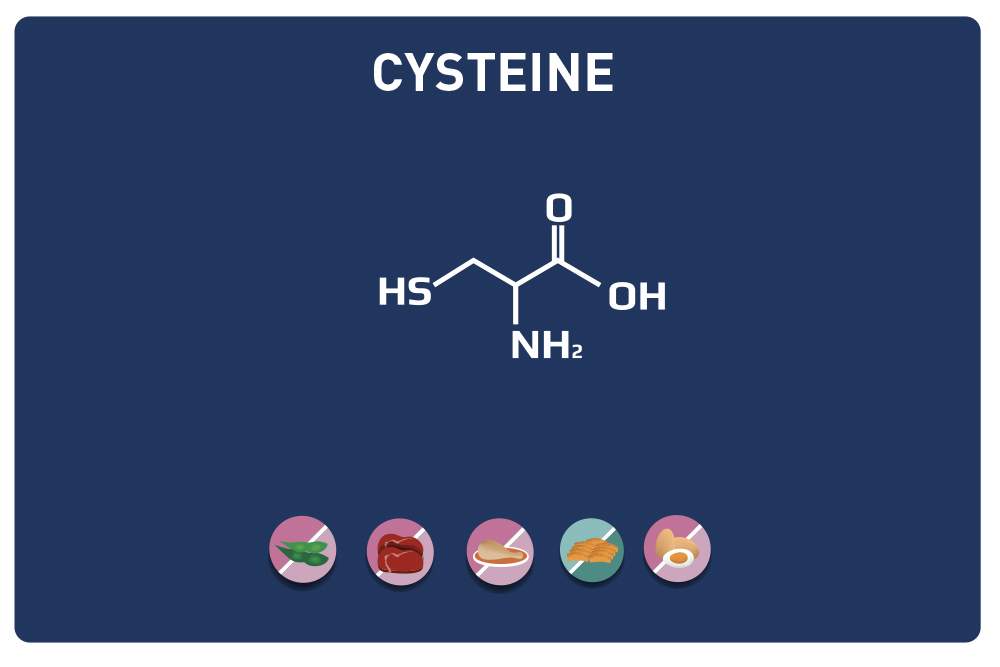
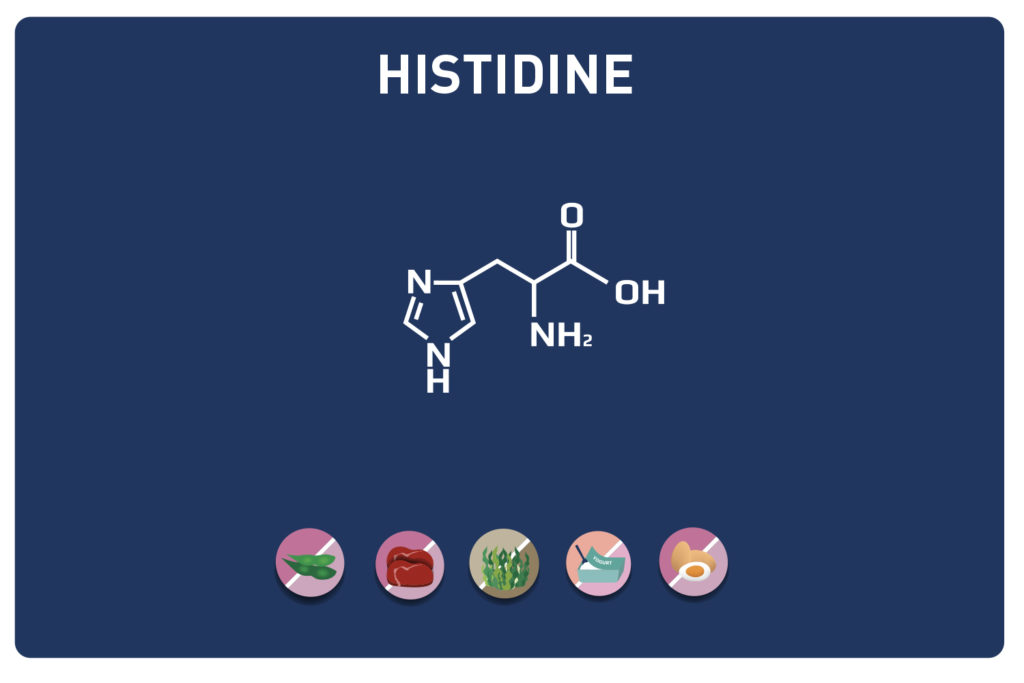
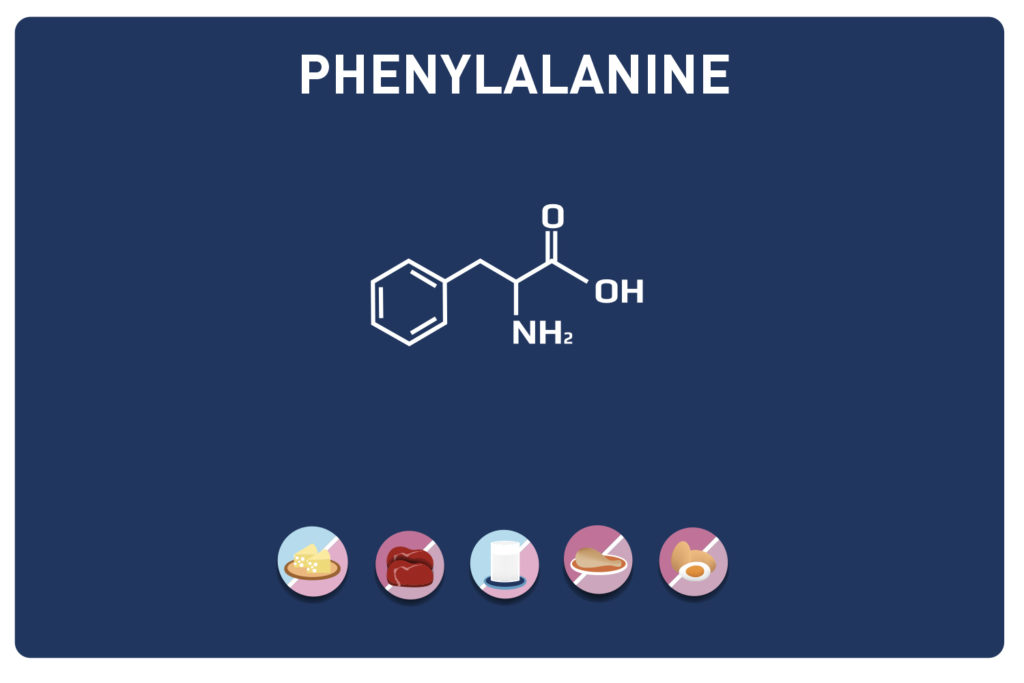
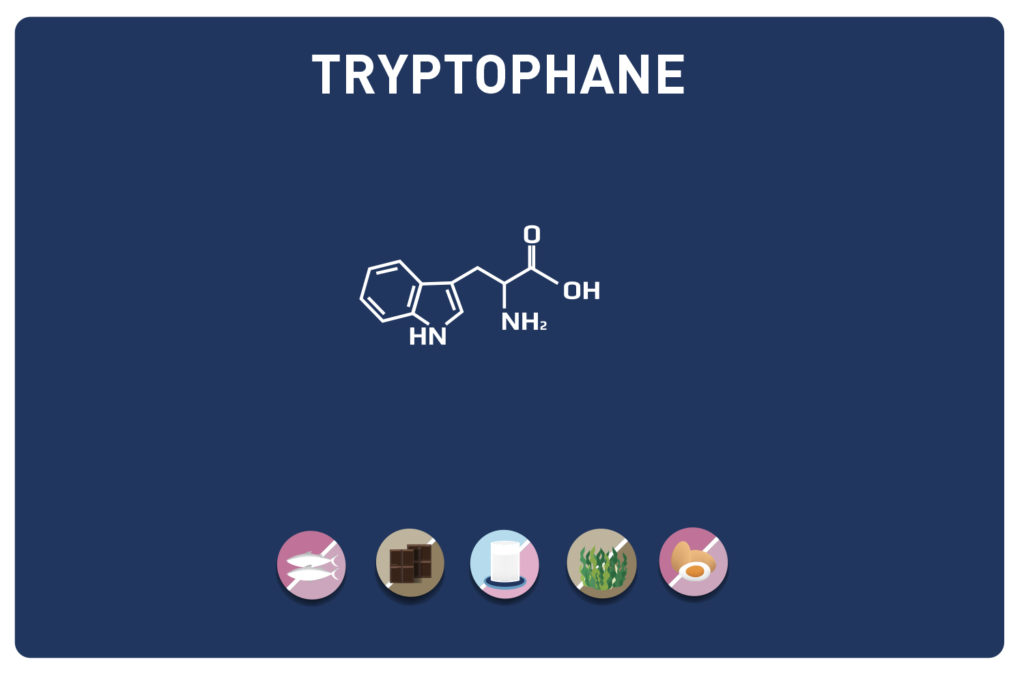
This sulphur amino acid is one of the 9 essential amino acids, so it must be provided by the diet as our body cannot manufacture it. It is used by the body in the biosynthesis of proteins and other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, hence its qualification as proteinogenic.
ROLES
- Antioxidant- participates in the production of glutathione, a highly antioxidant substance. Neutralises heavy metals
- Limits fat deposits in the liver
- Improves the assimilation of zinc
- Antidepressant when associated with ATP in adenosyl L. methionine
- Plays an essential role in the metabolism of depressed people
- In combination with B vitamins, methionine reduces inflammation, strengthens hair structure, relieves pain.
- Stimulates the formation of cartilage tissue
DOSES
Doses between 500mg and 3g/day are recommended. However, this amino acid becomes toxic at higher doses.
Note: Studies suggest that a diet very rich in methionine may promote stomach and intestinal cancers.
For this reason, the World Health Organization recommends that the daily intake of methionine should not exceed 1g/day.
FOOD SOURCES
Cheeses (parmesan and gruyere), eggs, fish, meat and poultry, garlic, lentils, onions, wheat germ, soya.