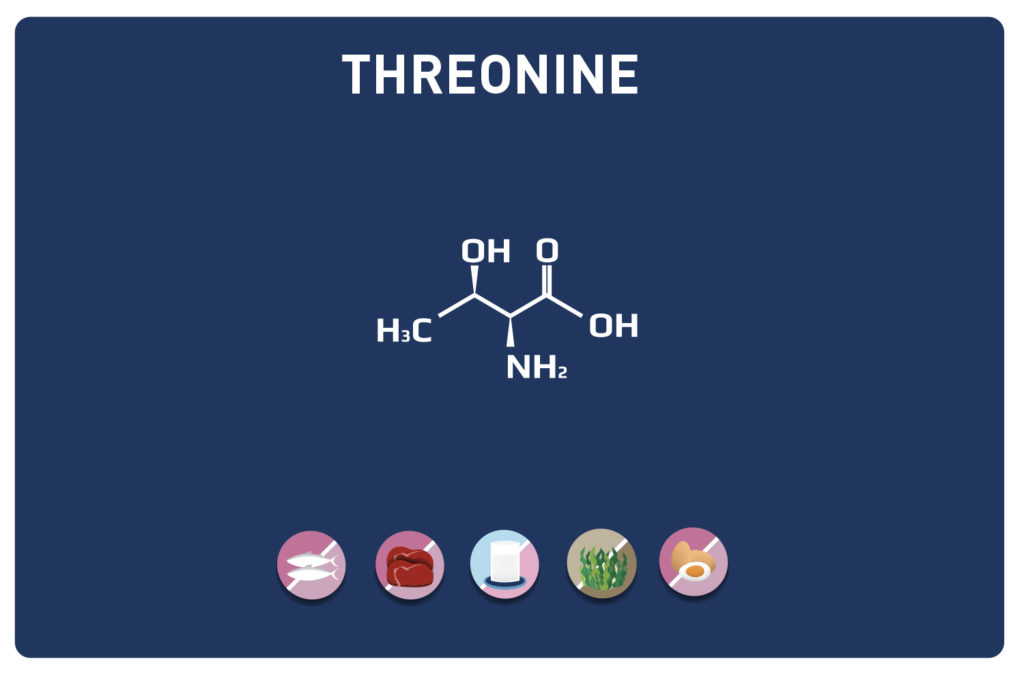
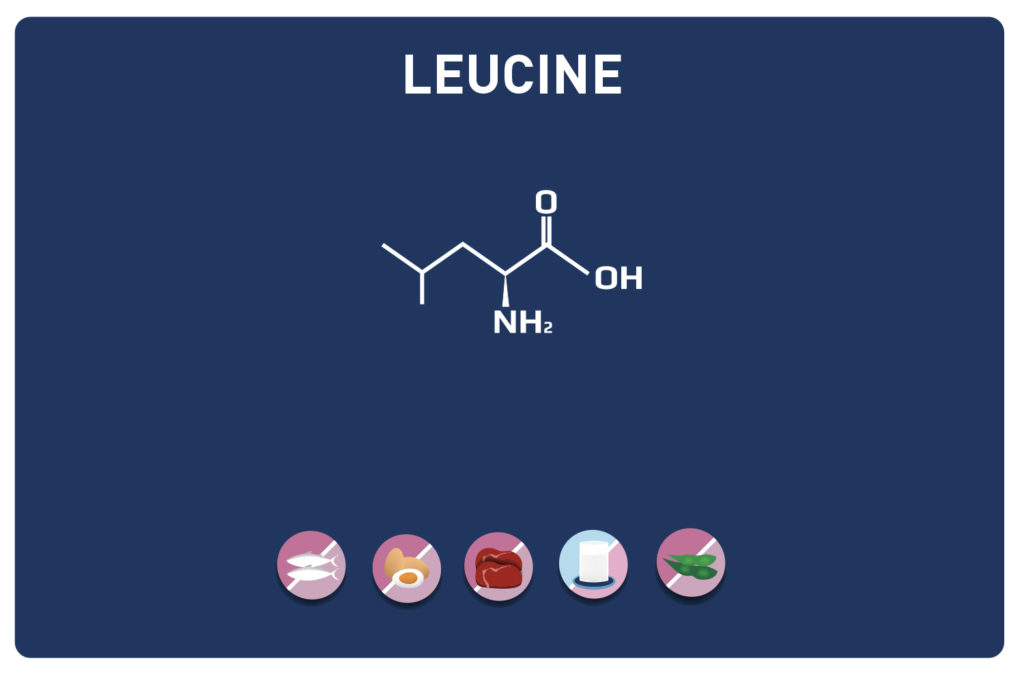
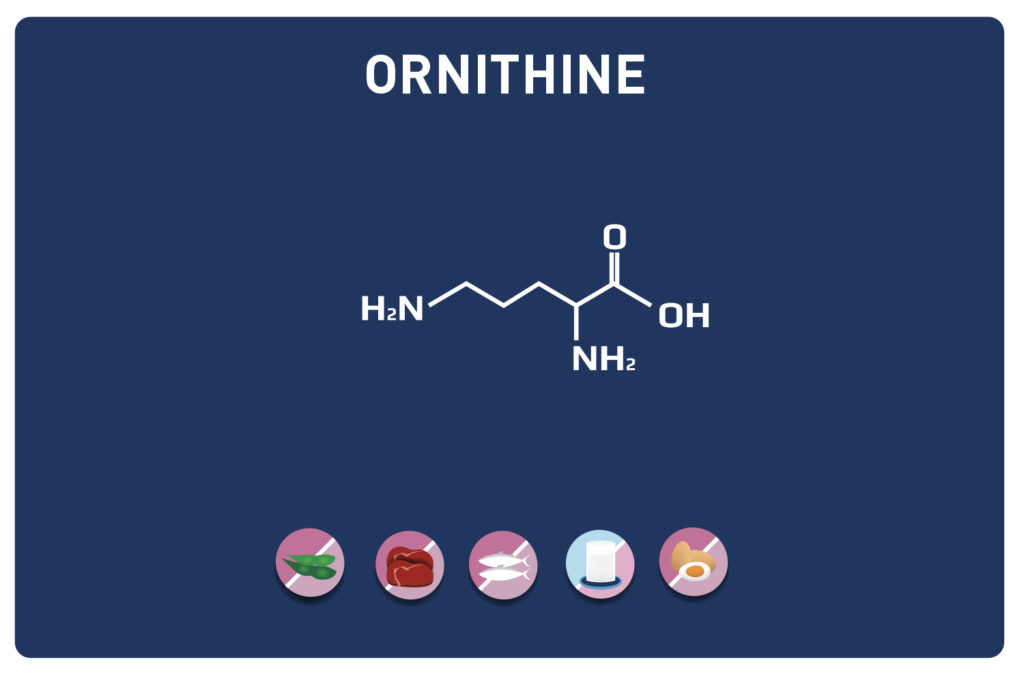
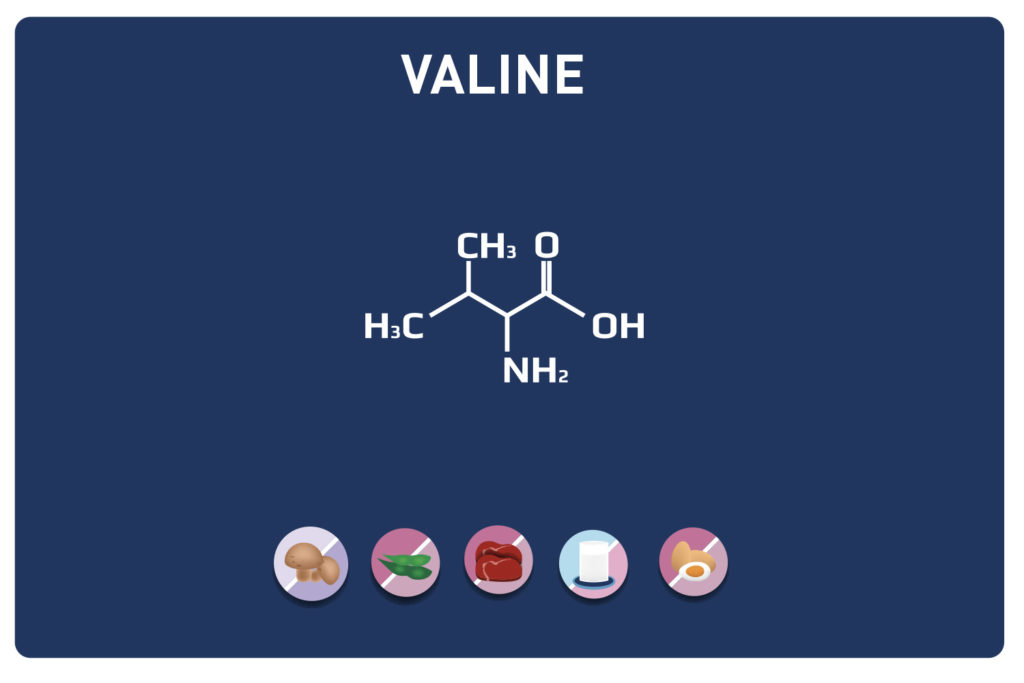
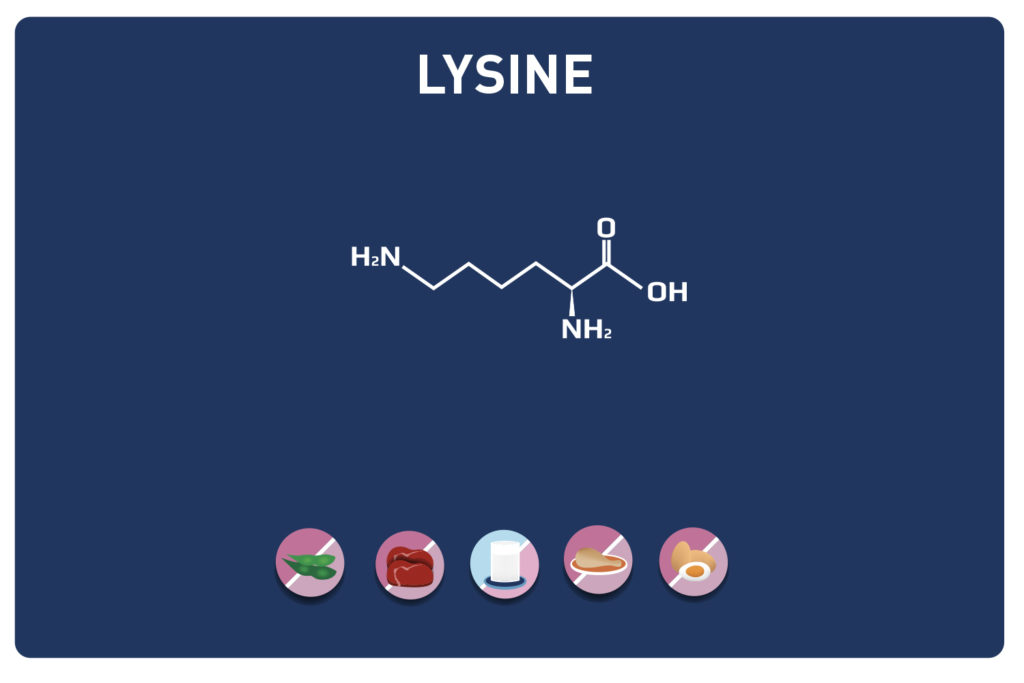
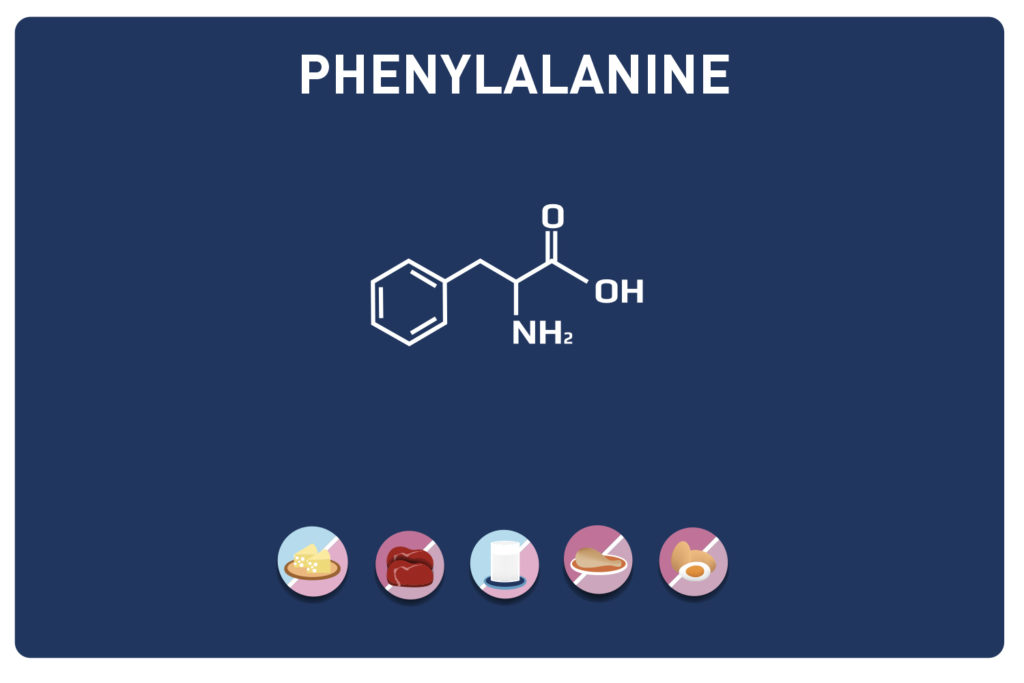
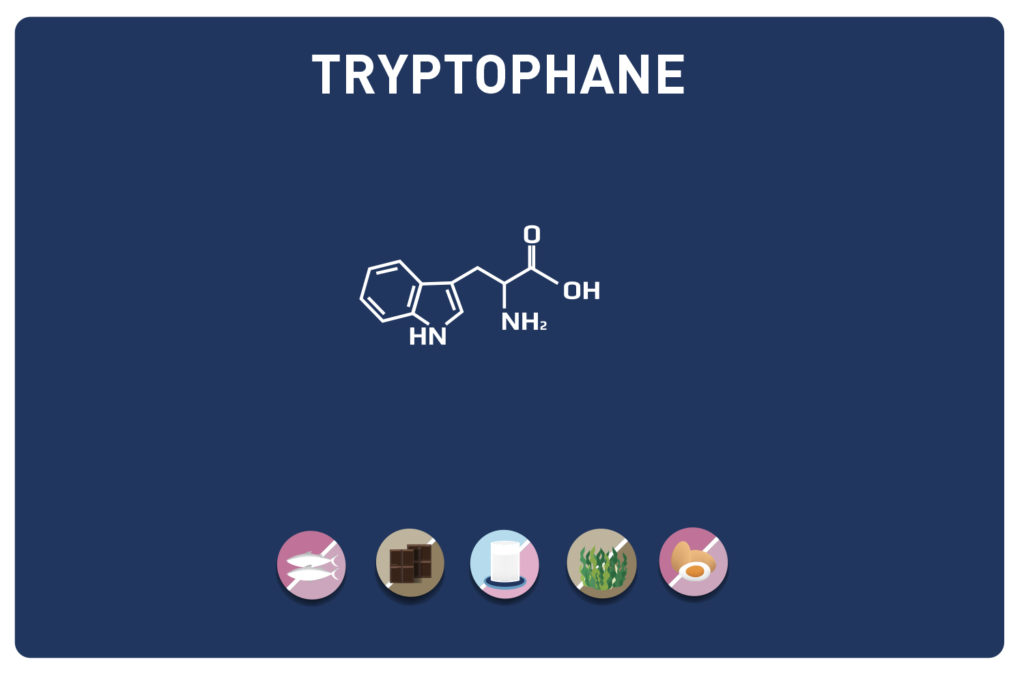
Threonine is an essential amino acid, so it cannot be synthesised by the body and must therefore necessarily be supplied by the diet. It is a key nutrient for the gut and immune function. It is found in high concentrations in the heart, skeletal muscles and central nervous system.
ITS ROLE
- Essential for proper functioning of the intestine
- Involved in the formation of collagen, elastin and tooth enamel
- Precursor to glycine, serine and glucose
- Antibody formation
- Necessary for maintaining the body's protein balance
- Necessary for the maintenance of normal function of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, liver and immune system (Immunostimulant: thymic, cellular, immunoglobulins and antibodies)
- Prevents fat accumulation in the liver
NEEDS
Requirements are estimated at 500-1500 mg per day
COACTIVE ELEMENTS
- Minerals:Zinc, copper, selenium
- Vitamins:C, A, E, B9
- Amino acids:Glycine, alanine, aspartic acid, histidine
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids:Omega-3
THERAPEUTIC USES
- Anti-inflammatory in rheumatoid arthritis (associated with histidine, copper and omega-3)
- Used in the control of epileptic seizures
- Antidepressant effect
FOOD SOURCES
- Meat & poultry
- Eggs
- Dairy products
- Lentils
- Mushrooms
- Wheat germ
- Nuts, beans, sesame seeds
- Seeds