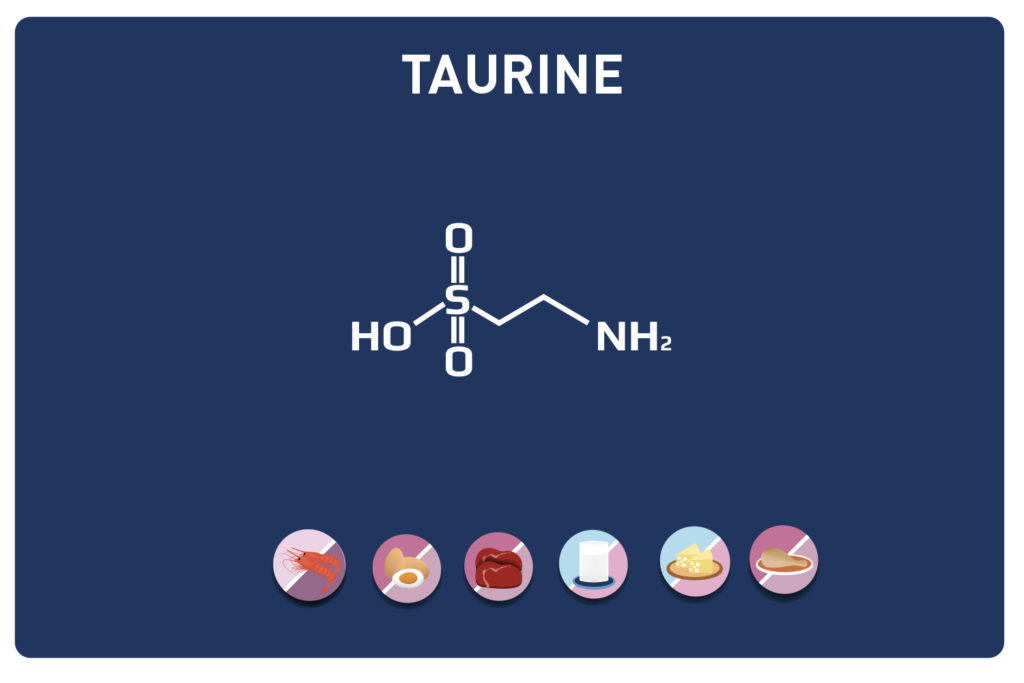
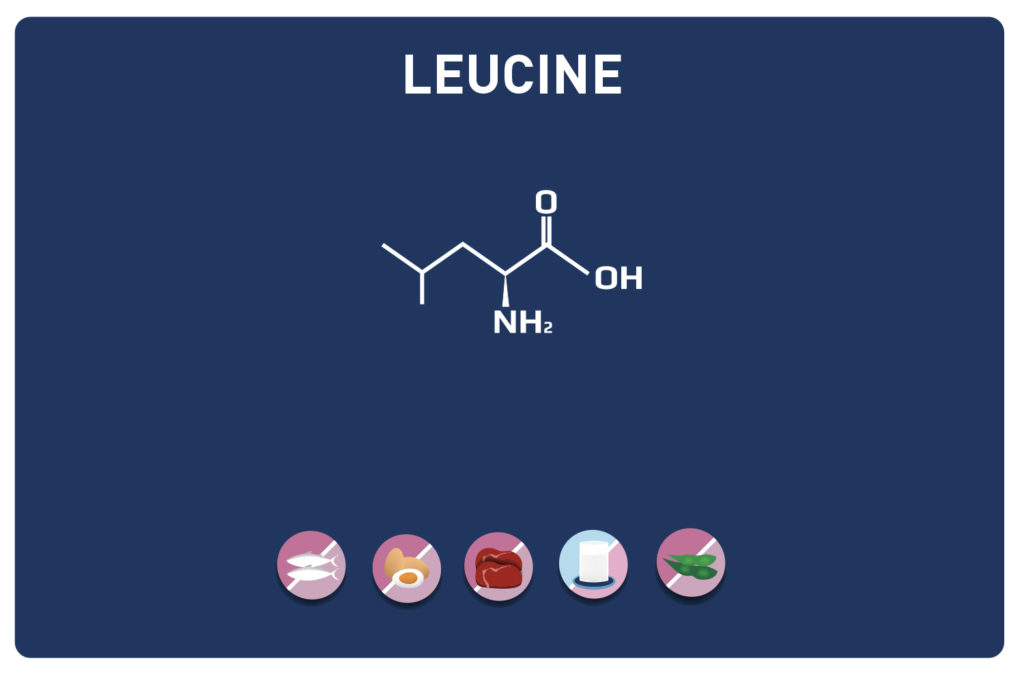
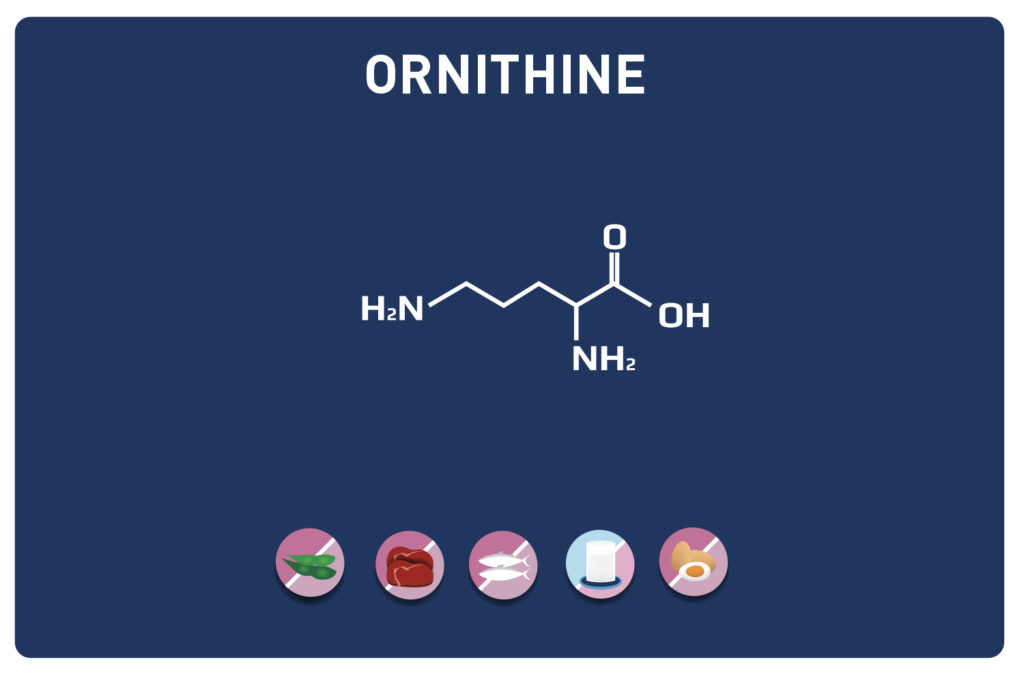
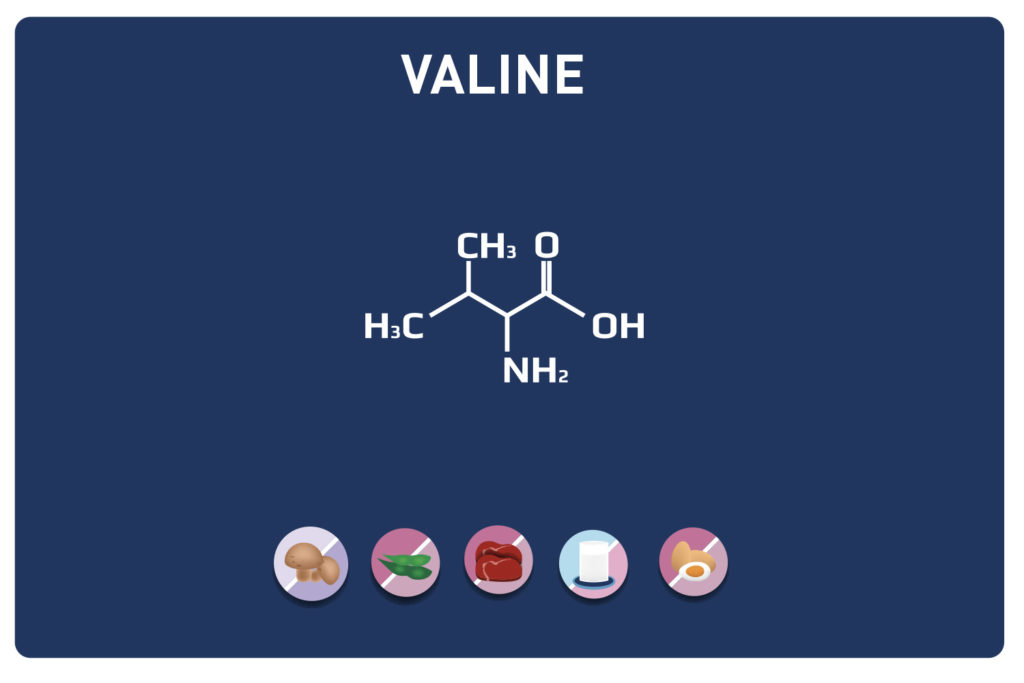
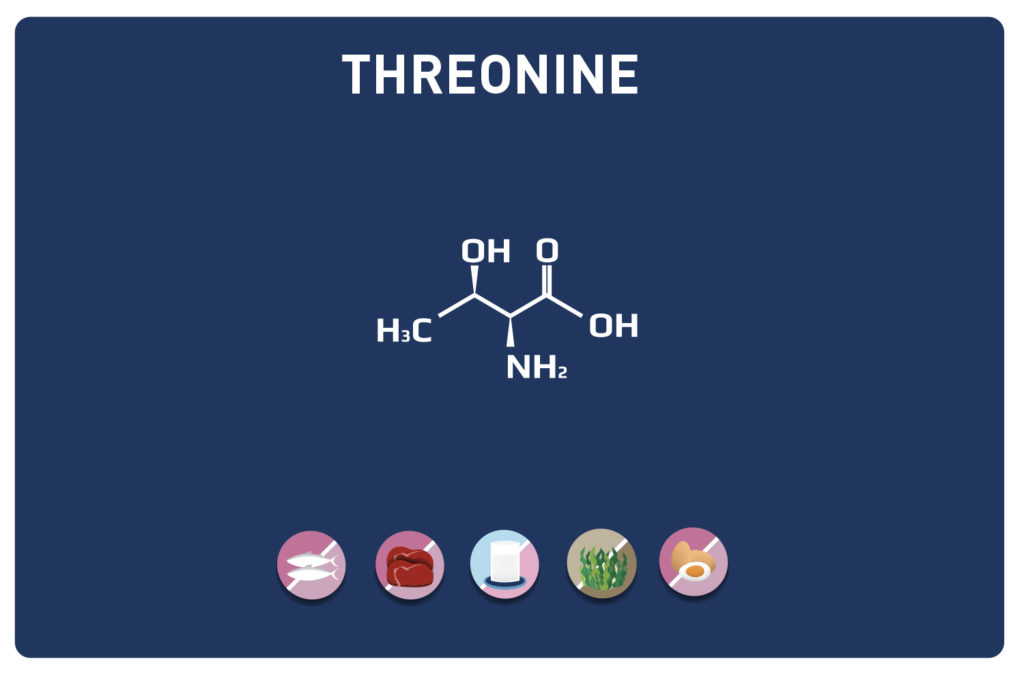
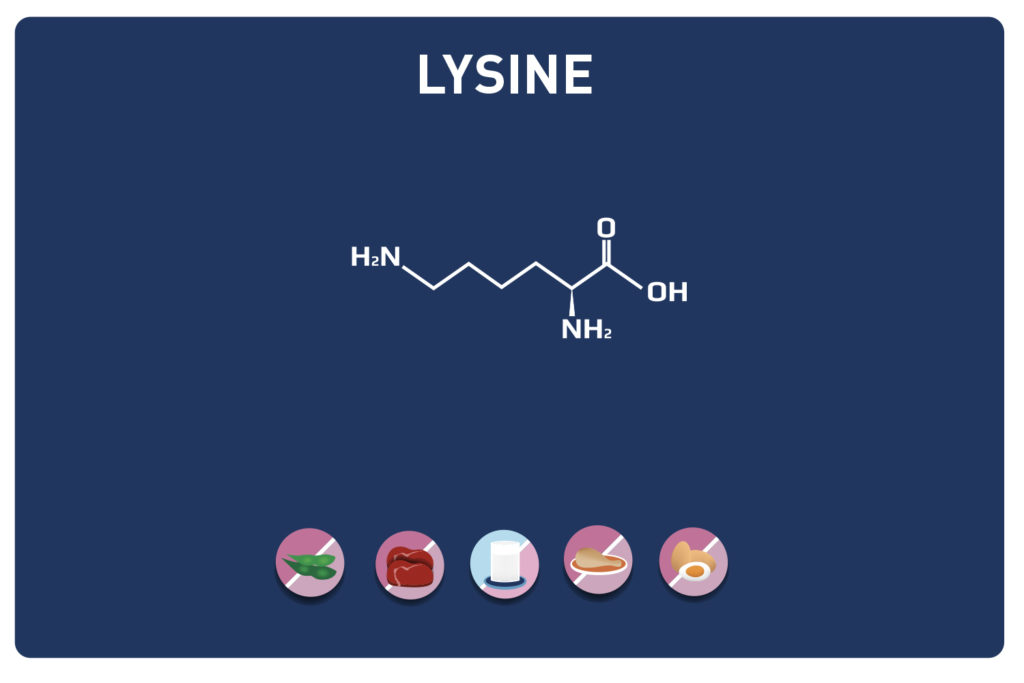
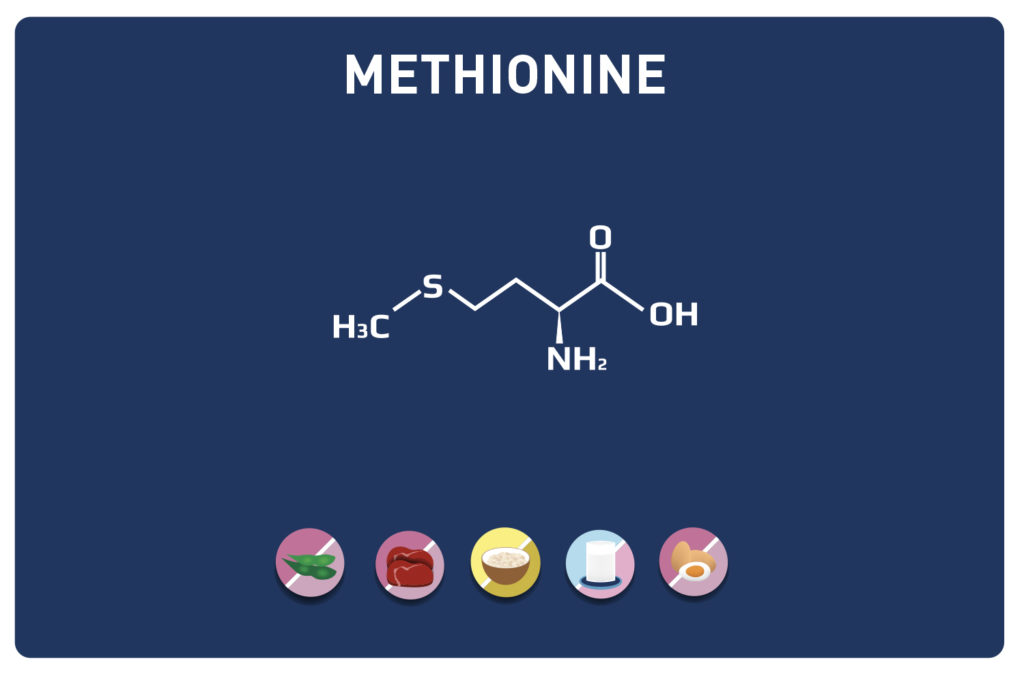
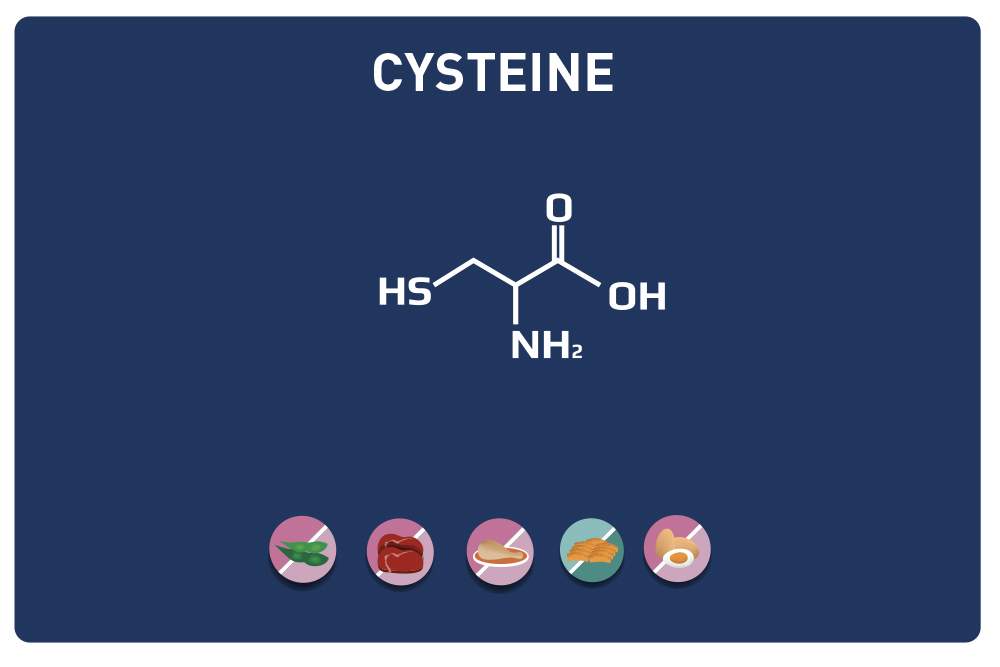
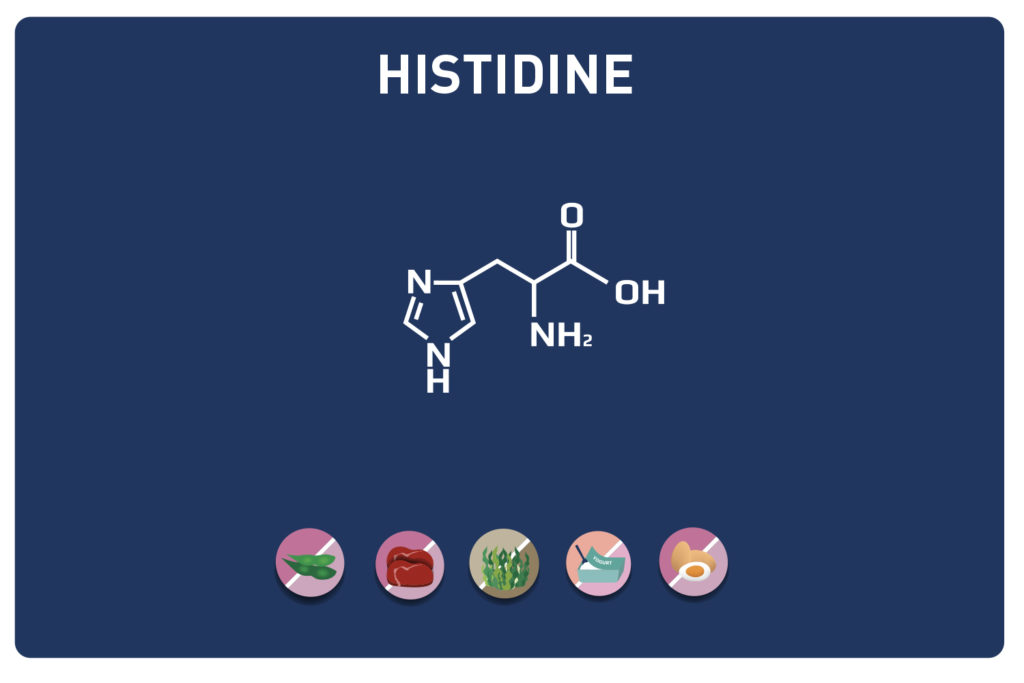
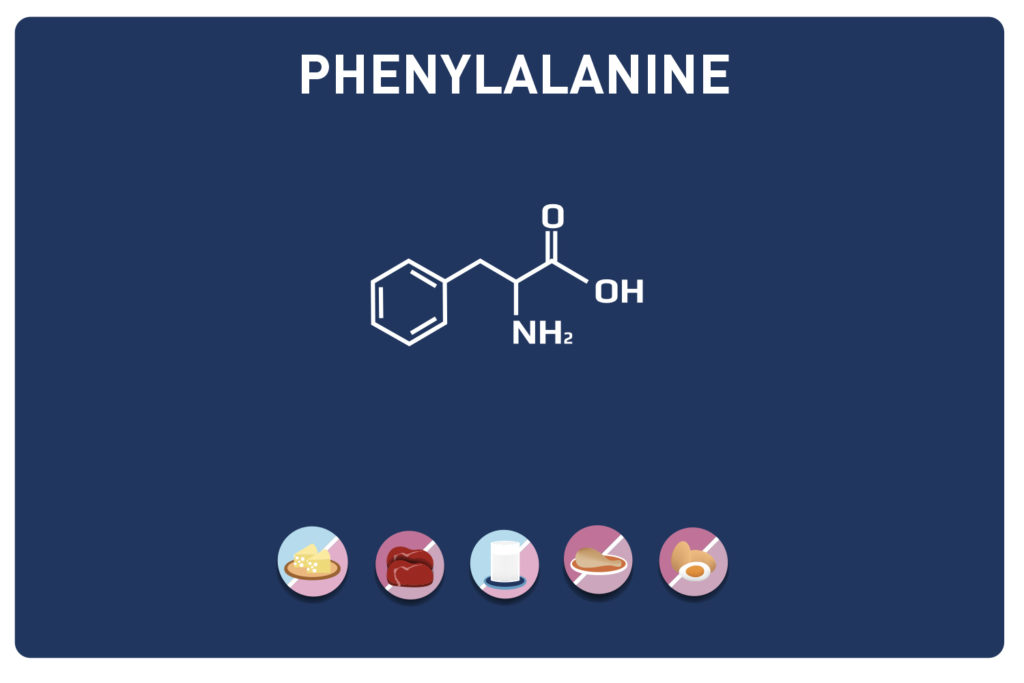
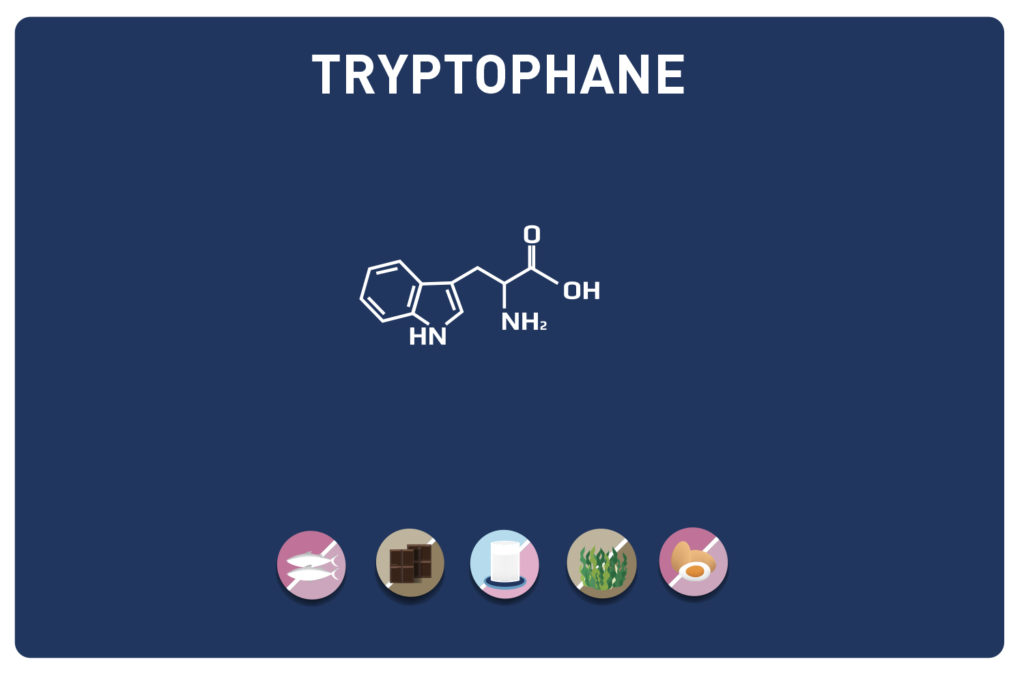
A non-essential amino acid, derived from cysteine, TAURINE is a member of the amino acids sulfur.
Discovered in 1827 in bull bile by two Austrian researchers F. Tiedermann and L. Gmelin, it plays a major role in the brain (neurotransmitter) and other electrically excitable tissues (heart, muscles, bladder, retina, vascular system).
It is therefore found in large quantities in the brain (olfactory bulb and hippocampus), heart, muscles and retina.
It is also involved in lipid digestion by increasing hepatic fat metabolism. It stimulates the formation of taurocholate (bile acid) which increases the excretion of cholesterol by the bile.
MAIN EFFECTS
- Protects the retina
- Fights macular degeneration and other serious eye diseases
- Strengthens the heart muscle(contractility)
- Decreases blood pressure
- Antiarrhythmic
- Strengthens the detoxification function of the liver
- Enhances the elimination of cholesterol
- Indispensable for the absorption of fats
- Antioxidant
- Tranquilizer
- Anti-epileptic effect
- Decreases lactic acid accumulation
- Enhances sperm mobility
COACTIVE AND METABOLICALLY USEFUL ELEMENTS
Minerals:Zinc - Manganese
Vitamins:B6 - A
Amino acids:Cysteine
AGPI(Polyunsaturated fatty acids): DHA or cervonic acid - EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid).
EXCESS
Risks of ulcers by stimulating the secretion of gastric acids and in particular by increasing the ulcerogenic effect of aspirin.
FOOD SOURCES
Red meat, eggs, milk and dairy products, seaweed, mushrooms, oysters, fish.