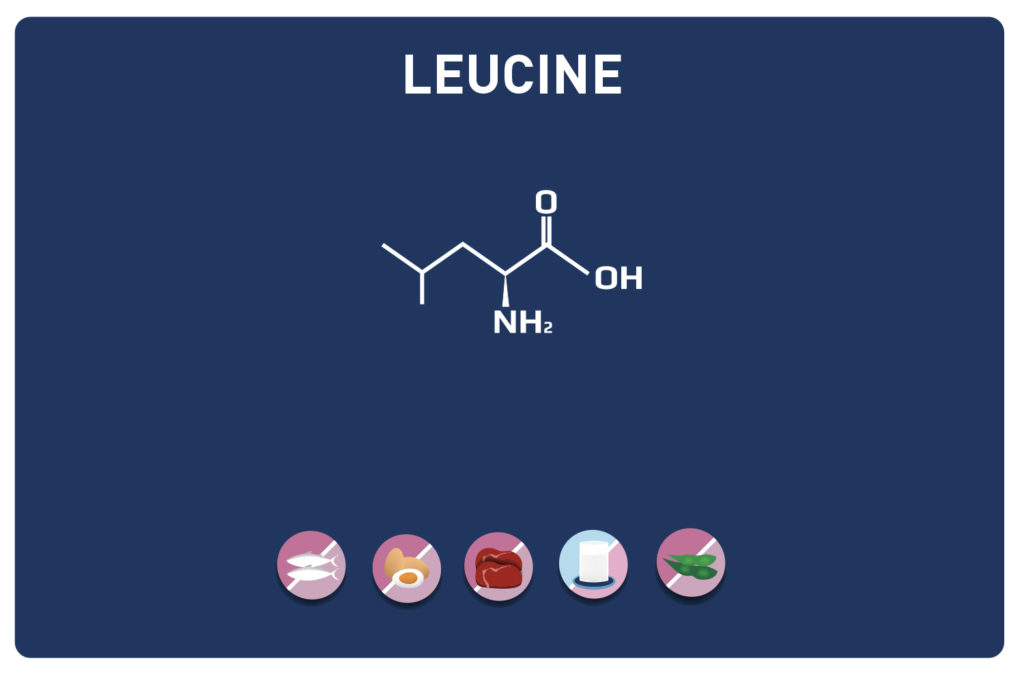
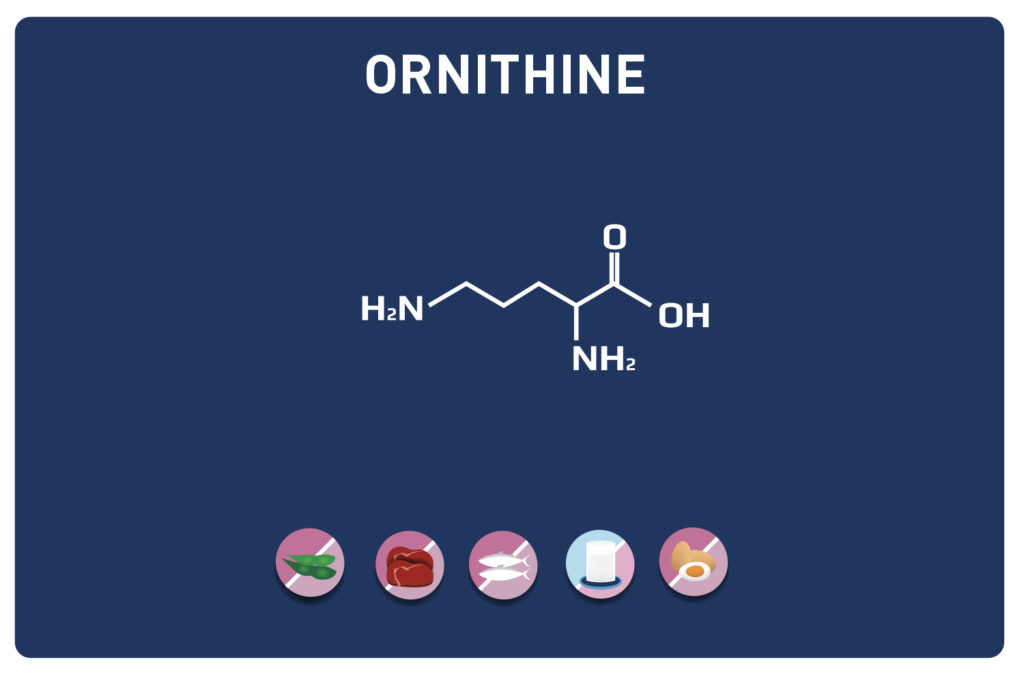
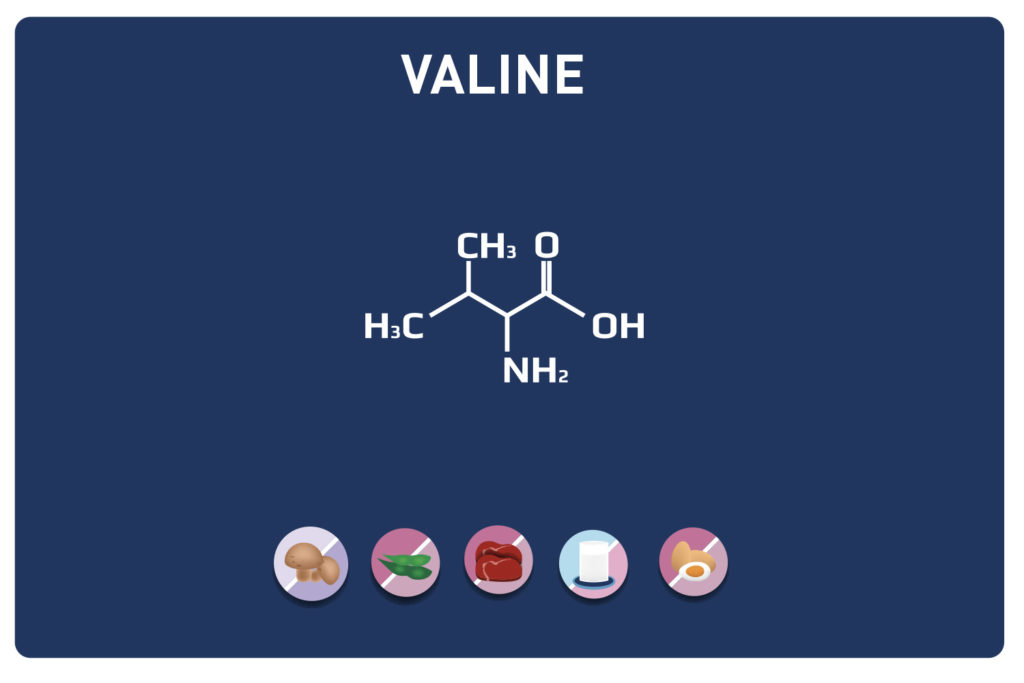
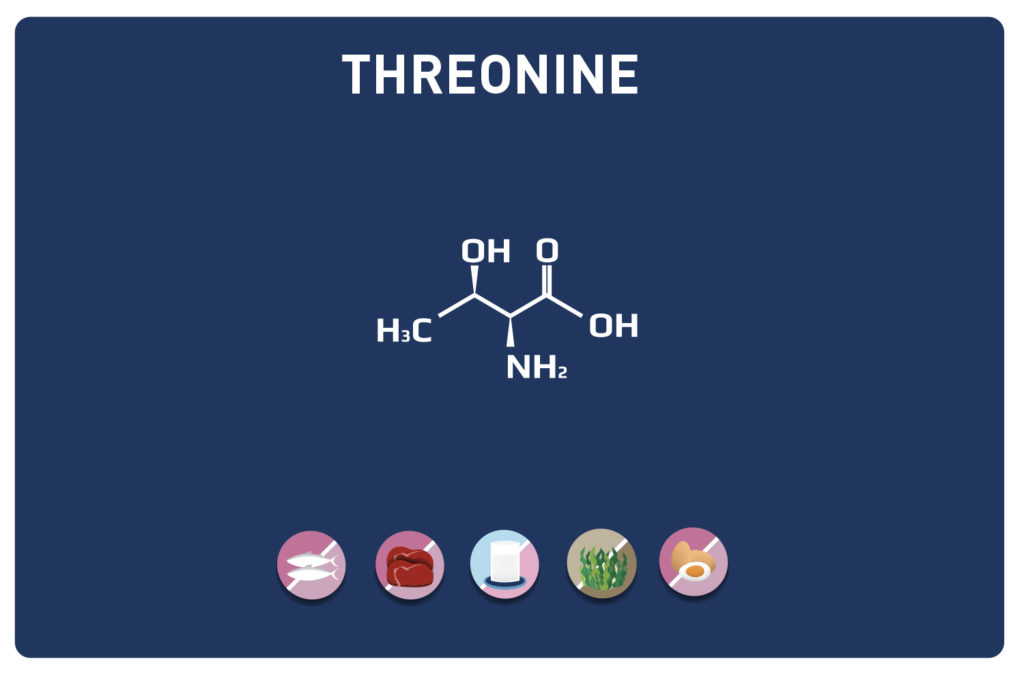
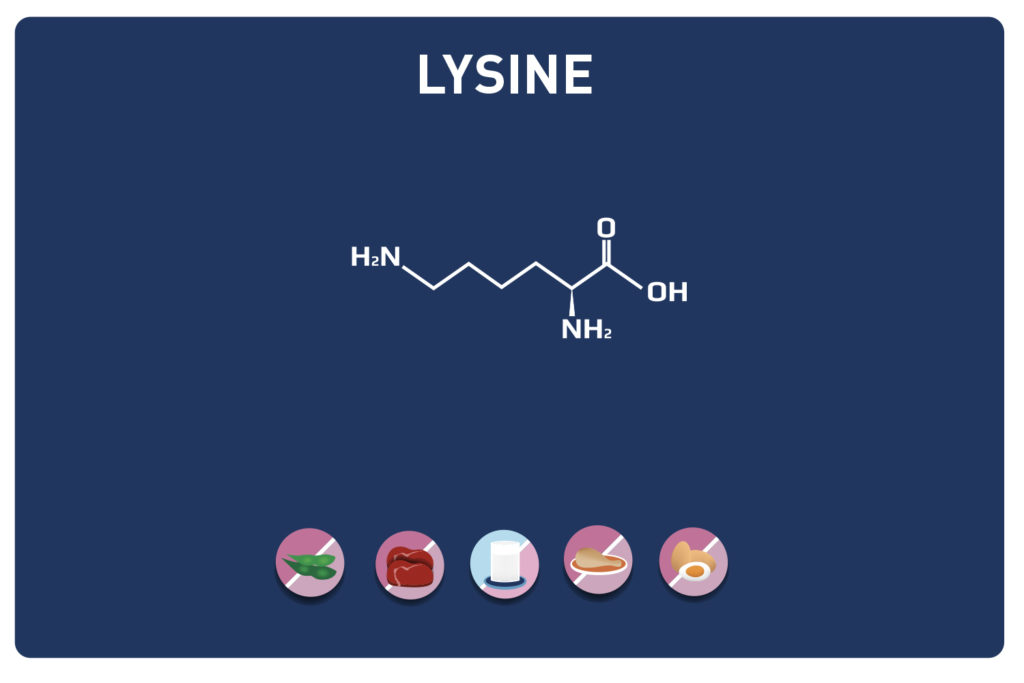
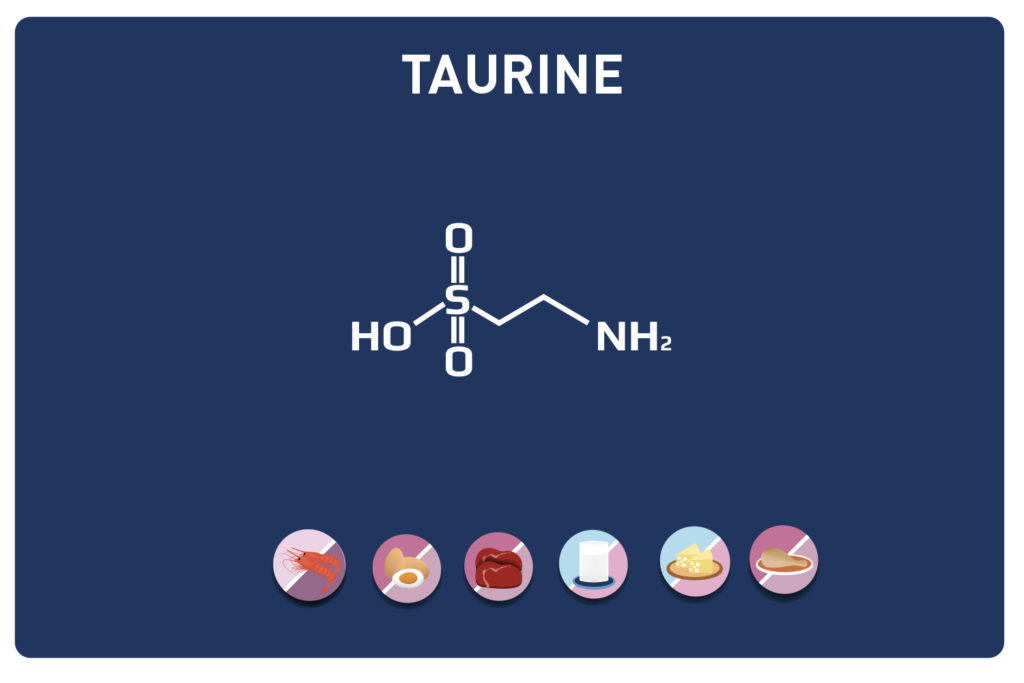
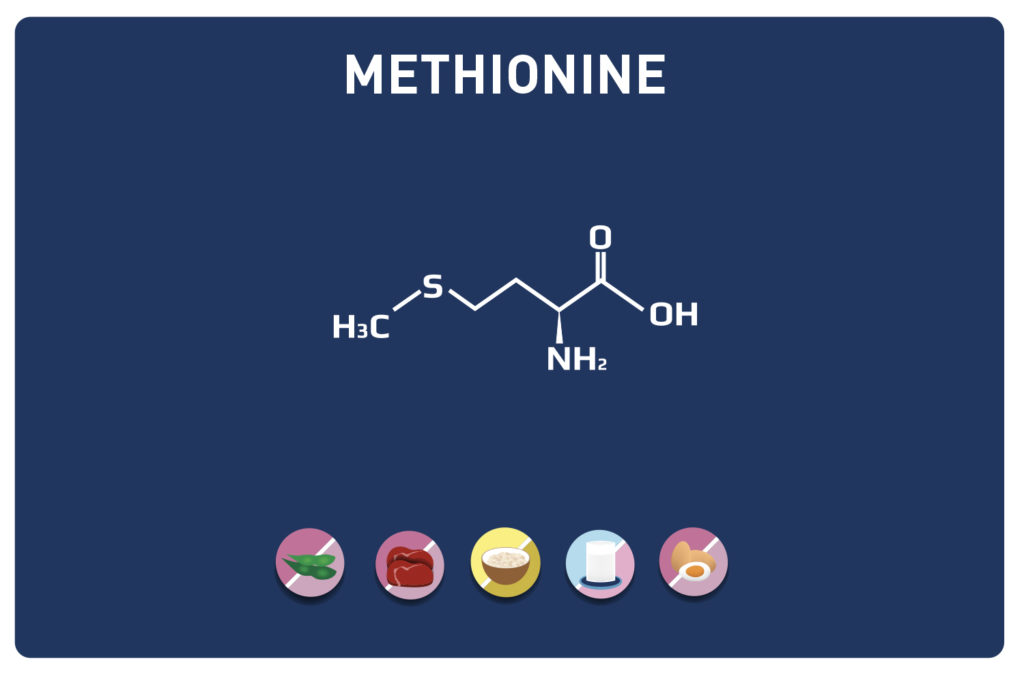
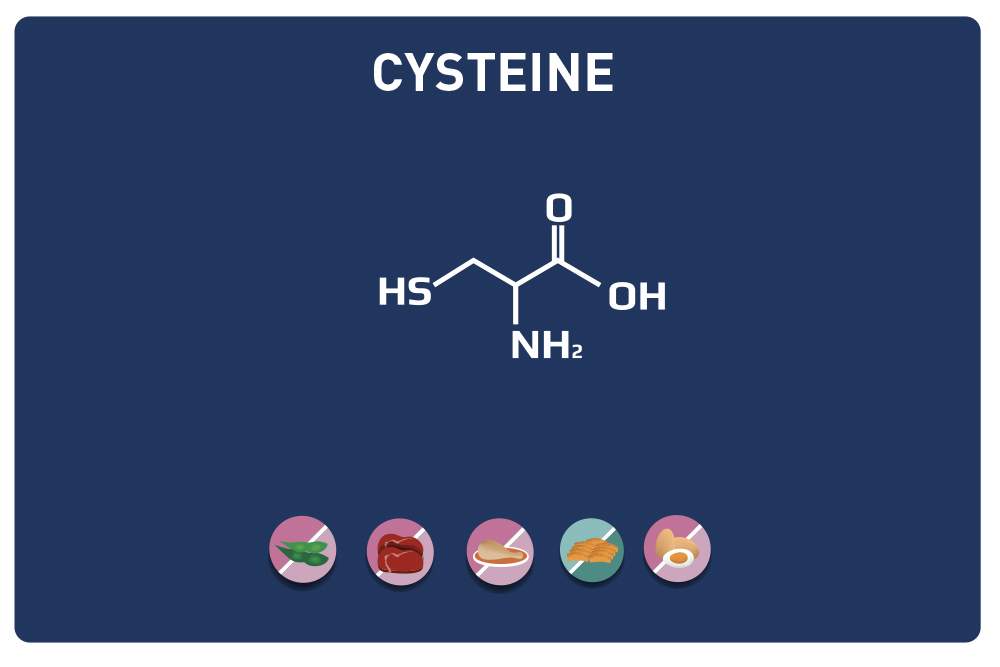
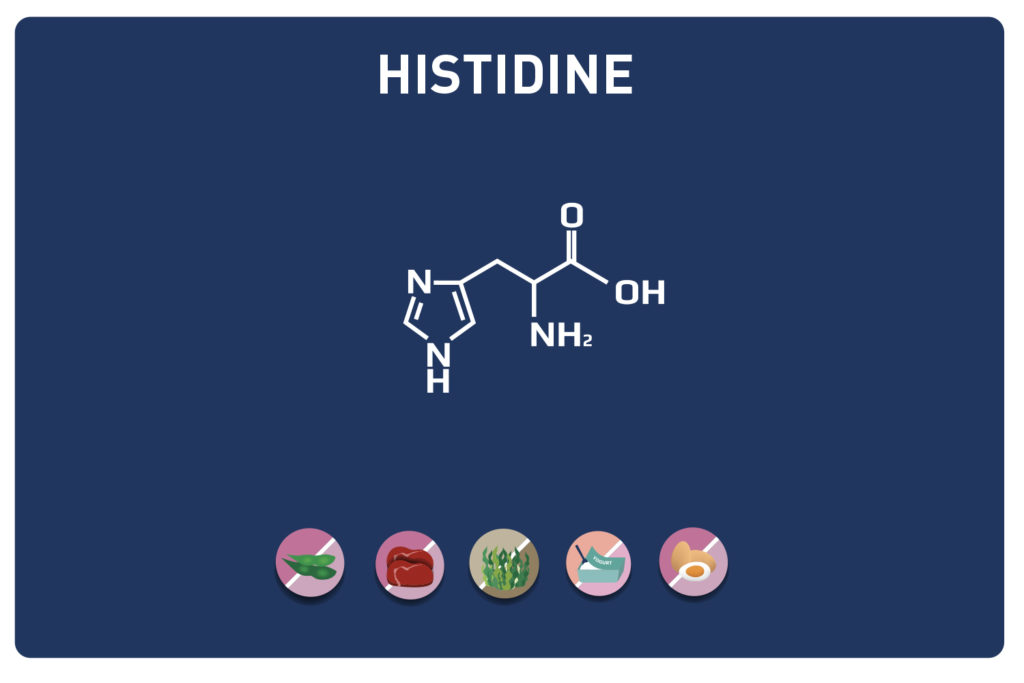
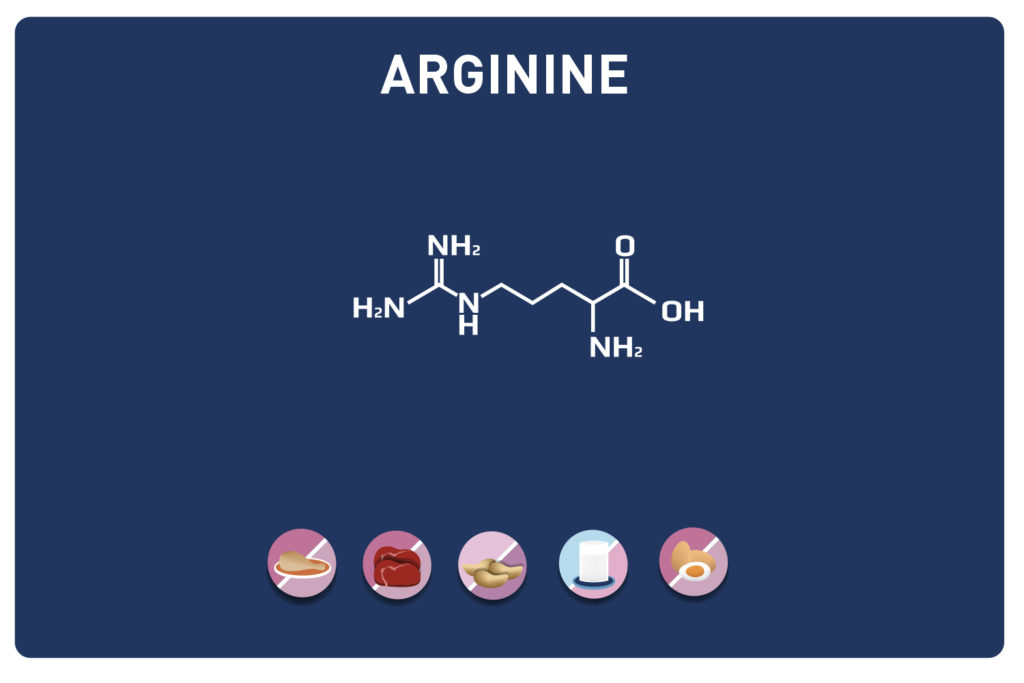
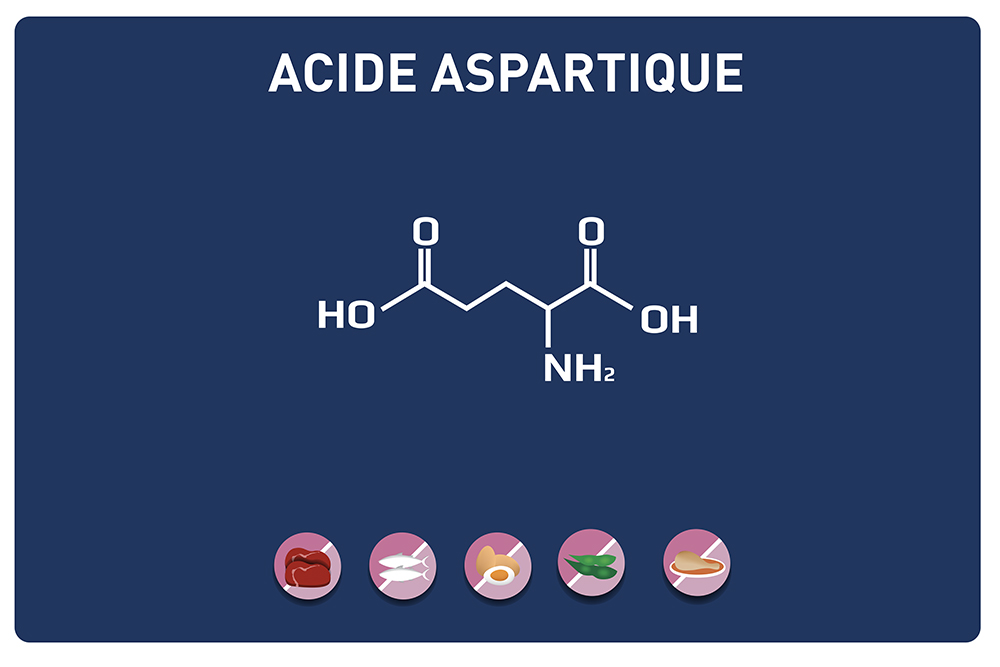
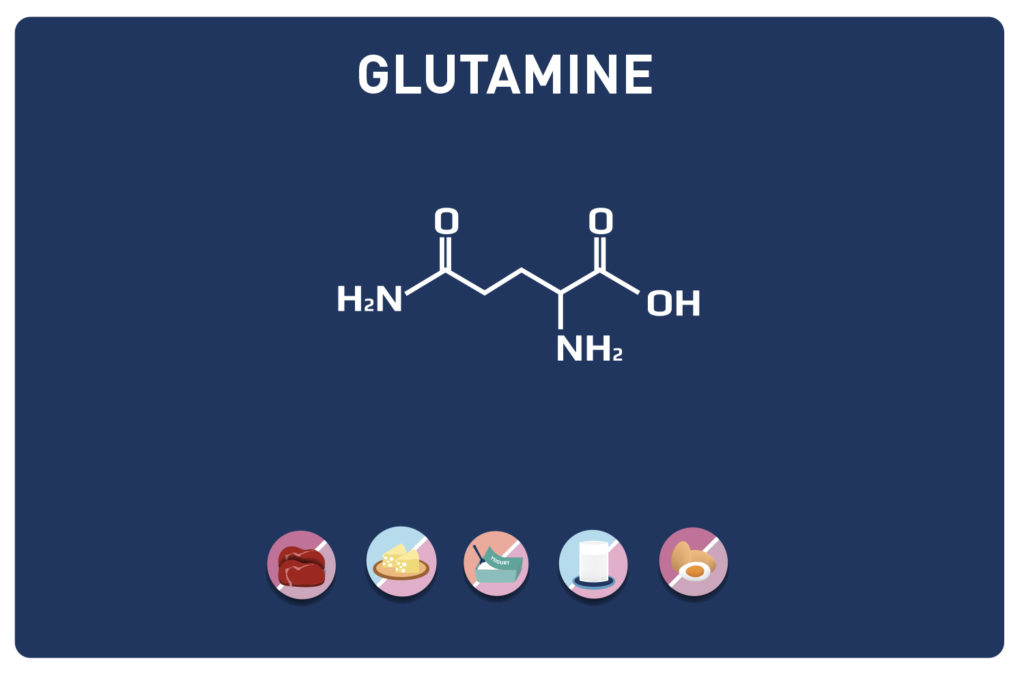
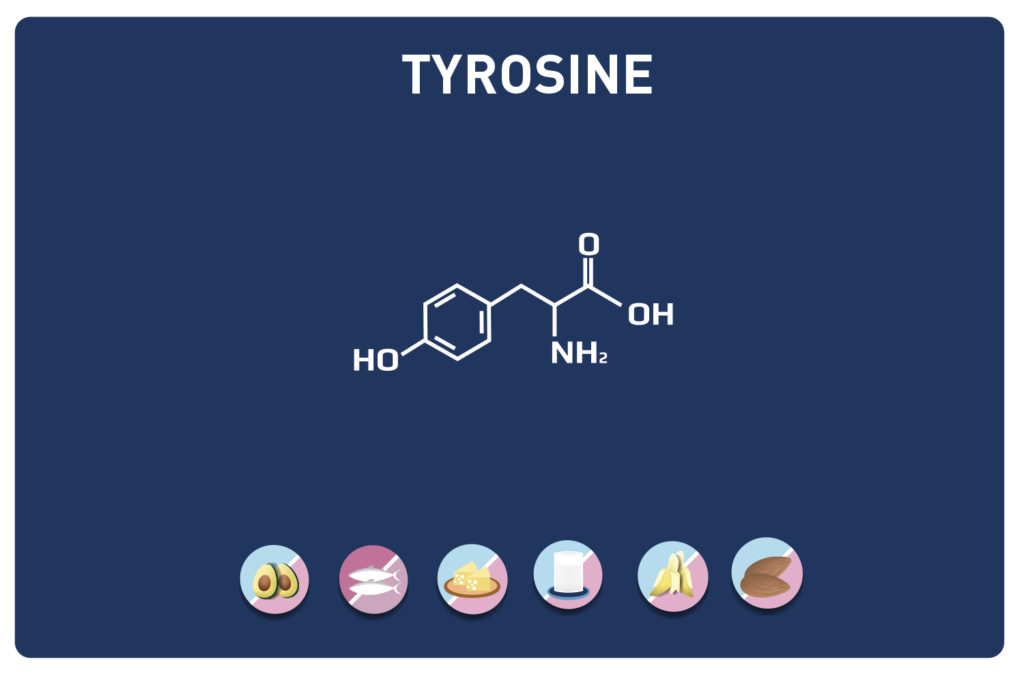
Leucine is an essential amino acid, it cannot be synthesized by the body, so it must be provided by the diet.
It is with valine and isoleucine, one of the three constituents of BCAA and certainly the most important. It is the only ketogenic amino acid and is likely to be converted during ketogenesis into ketone bodies (from the breakdown of albumin and fats in the body).
It is the most anabolic and the most anti-catabolic of all the amino acids.
Role of Leucine
- Optimises muscle recovery
- Source of Muscle Energy
- Anabolic, to boost the body's ability to build muscle by promoting protein synthesis.
- May stimulate the release of insulin and thus help stabilise or lower blood sugar levels.
- Promotes wound healing (skin, bone, muscle)
- Powerful anti-catabolic agent
- Fights sarcopenia
- Anti-stress
Leucine requirements
Daily requirements for leucine are estimated at between 12 and 16mg per kg at rest, but during endurance exercise or strength exercise that promotes protein synthesis, requirements increase to 30 to 50mg per kg per day.
Recommended doses are generally between 1 and 20g per day,depending on the strategies used.
Valine and isoleucine enhance the effects of leucine and allow for greater efficiency in both muscle development and energy production.
Co-active elements
- Vitamins:B1, B2, B6, B8
- Minerals:Copper, magnesium
- Glutamic acid
Interactions
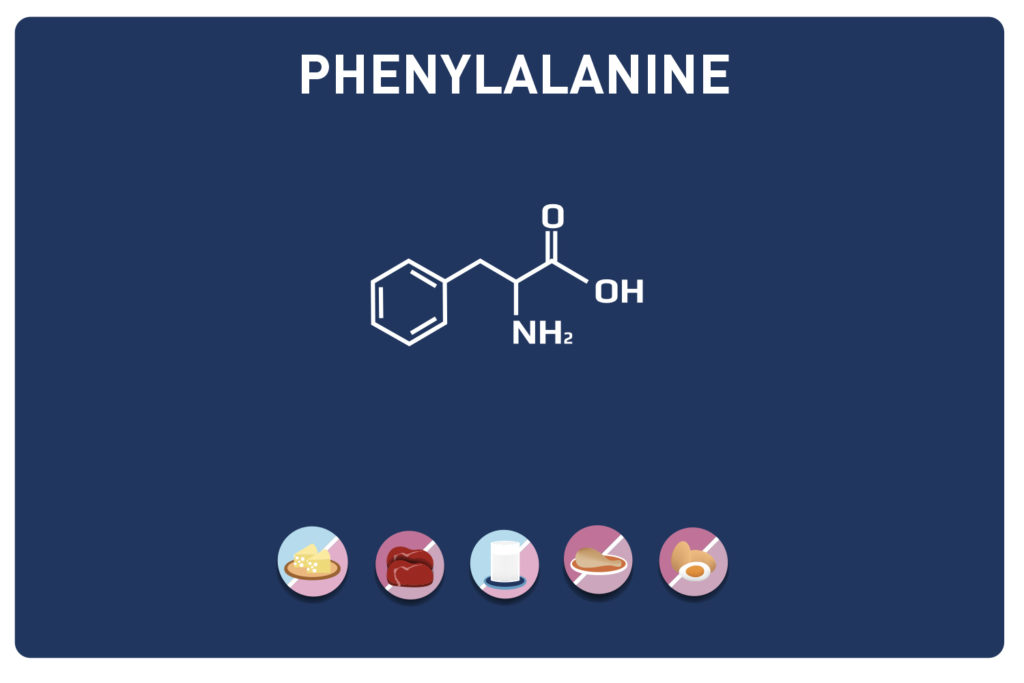
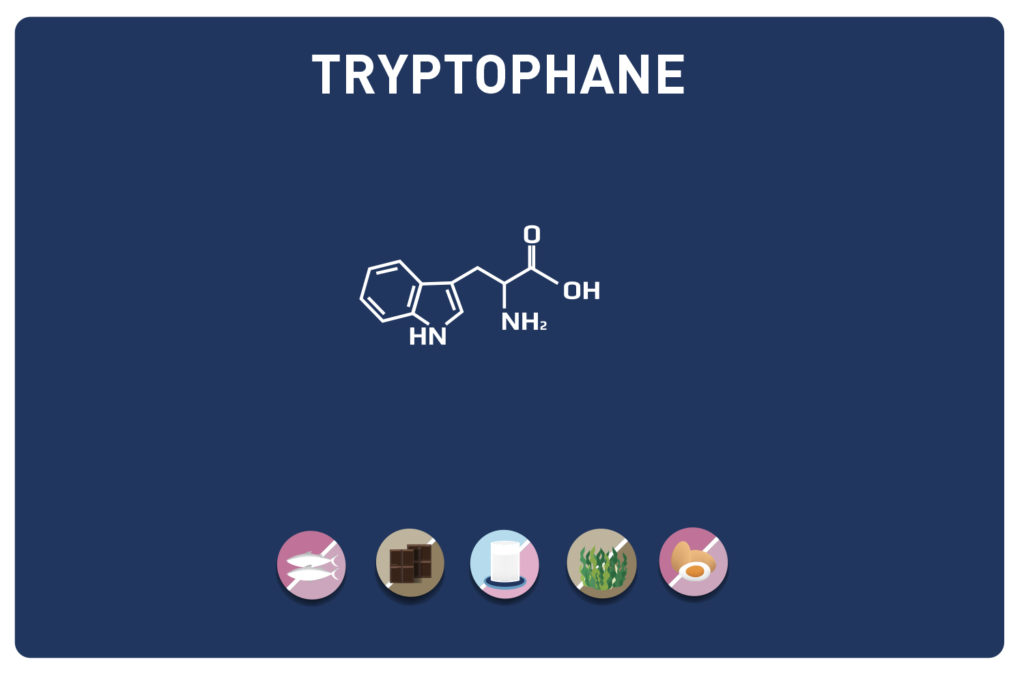
Leucine competes with aromatic amino acids (tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan) and a sulphur amino acid (methionine).
Very high doses can decrease serotonin and dopamine concentrations in the brain.