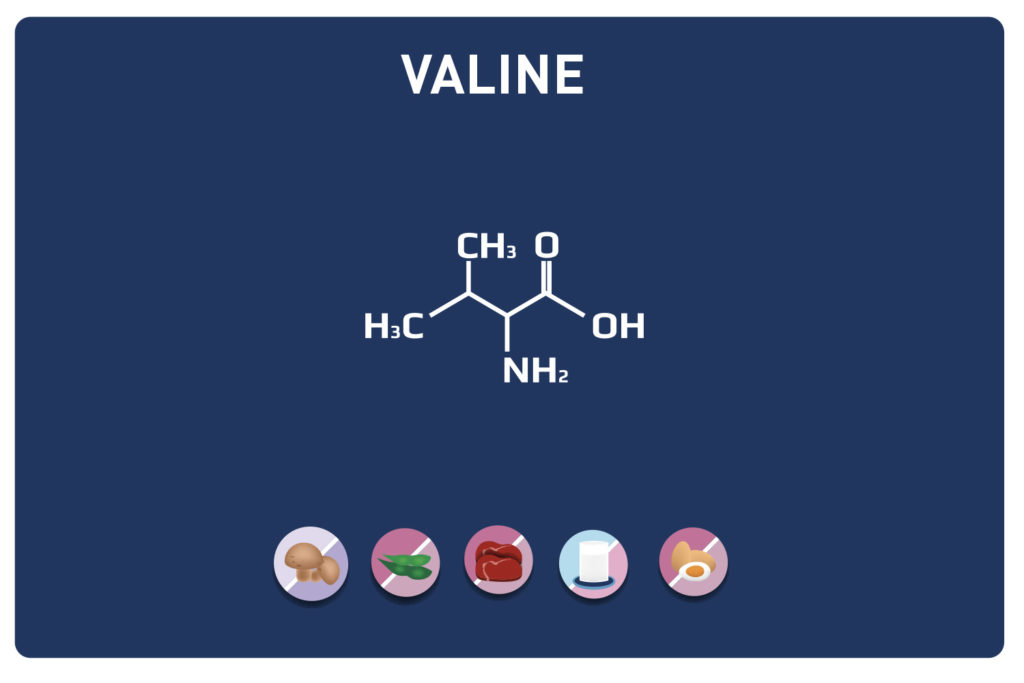
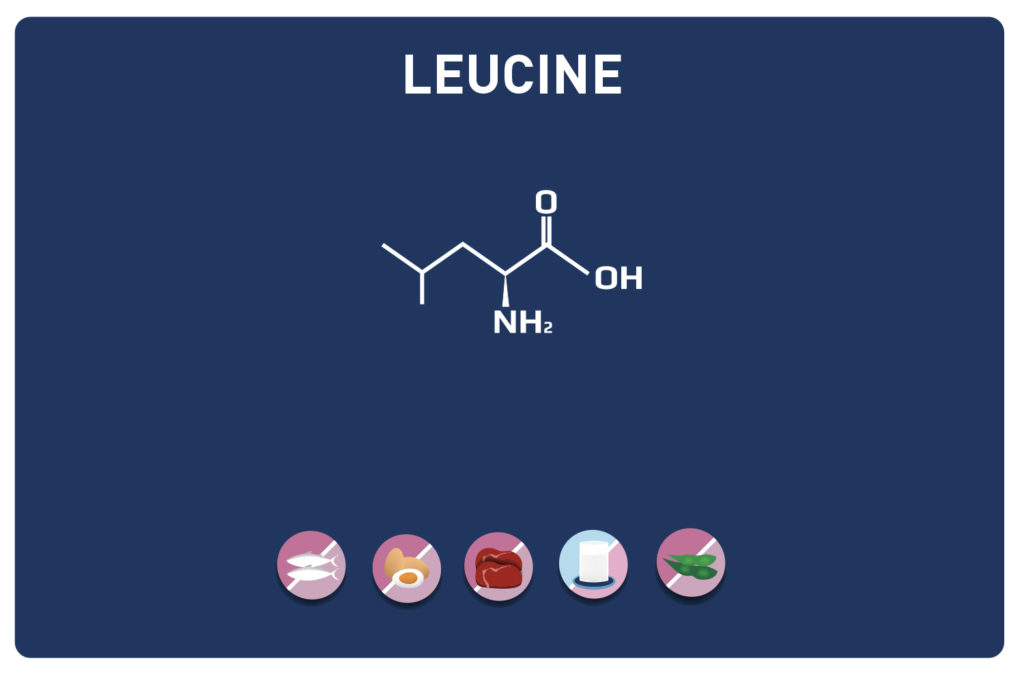
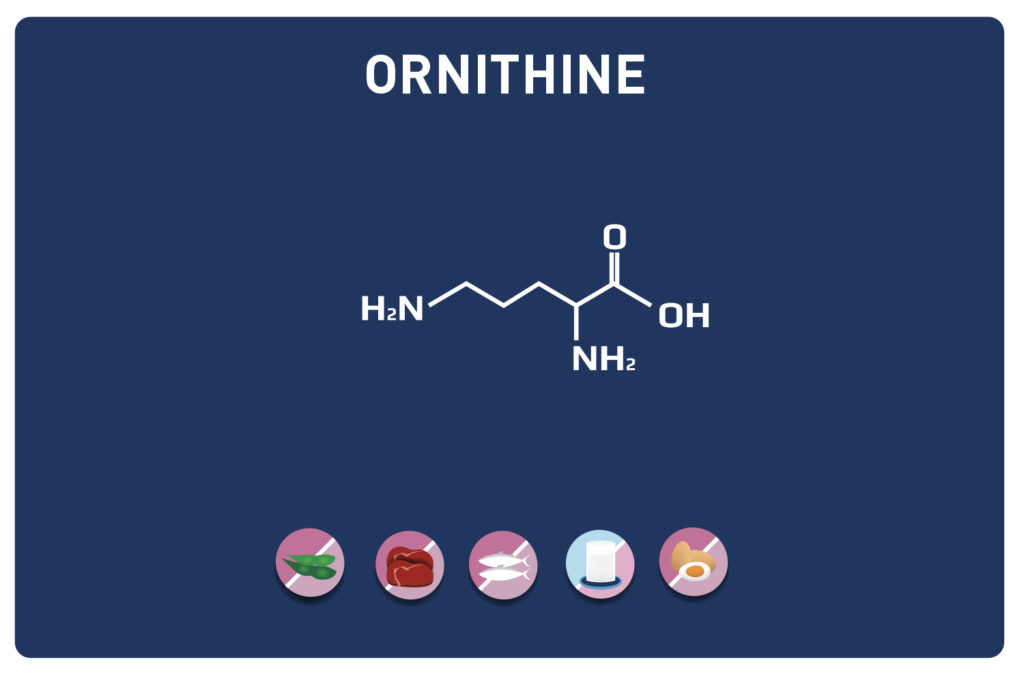
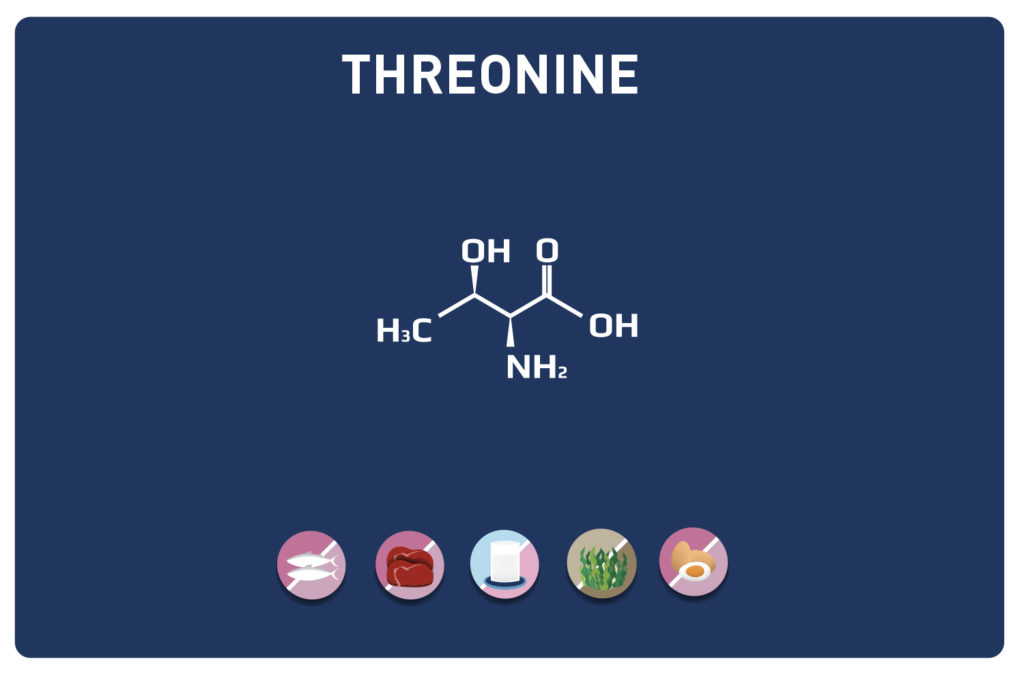
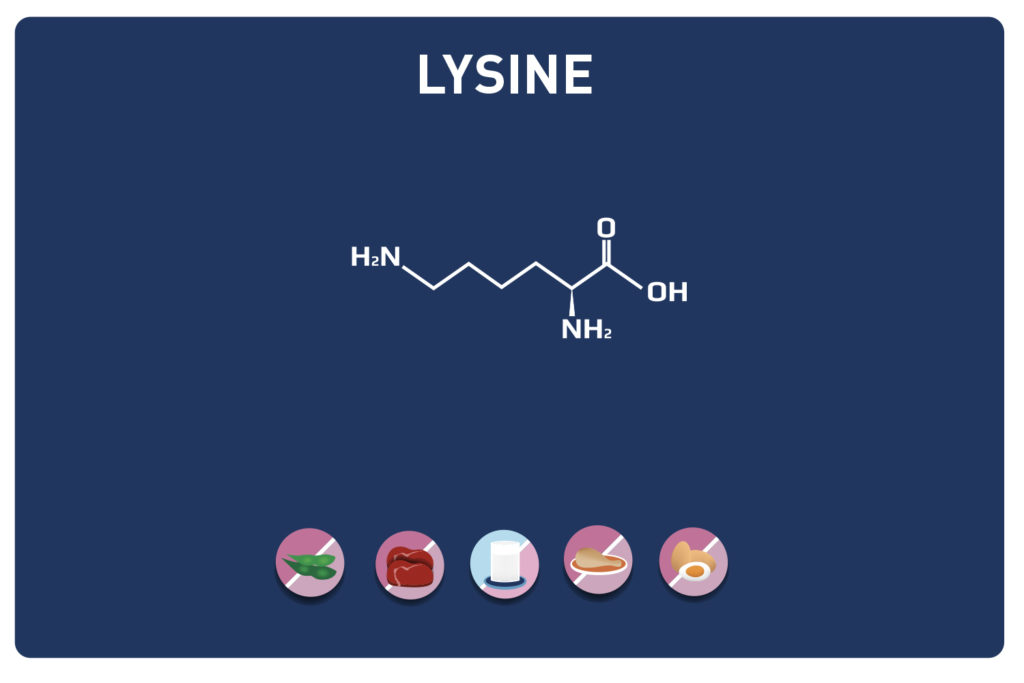
VALINE is a branched chain amino acid (with LEUCINE AND ISOLEUCINE it is part of the BCAA). It is an essential amino acid, so it cannot be synthesised by the body and must therefore be provided by our diet. It represents about 5% of the amino acids of the proteins in our body.
ITS ROLE
- Like the other BCAAs, Valine is actively taken up by muscle tissue to which it provides energy.
- It stimulates muscle growth (anabolism).
- Regulates the immune system.
- Stimulates the nervous system. A deficiency can affect the myelin that covers the nerves.
- Improves tissue recovery and repair.
- Promotes mental alertness and muscle coordination
- Promotes sleep
- Stimulates the production of growth hormone
Valine requirements
Valine requirements are between 1 and 20g per day, beyond which Valine becomes toxic and can cause hallucinations or tingling in the skin.
COACTIVE ELEMENTS
- Minerals:Copper and magnesium
- Vitamins:B1, B2 and B6
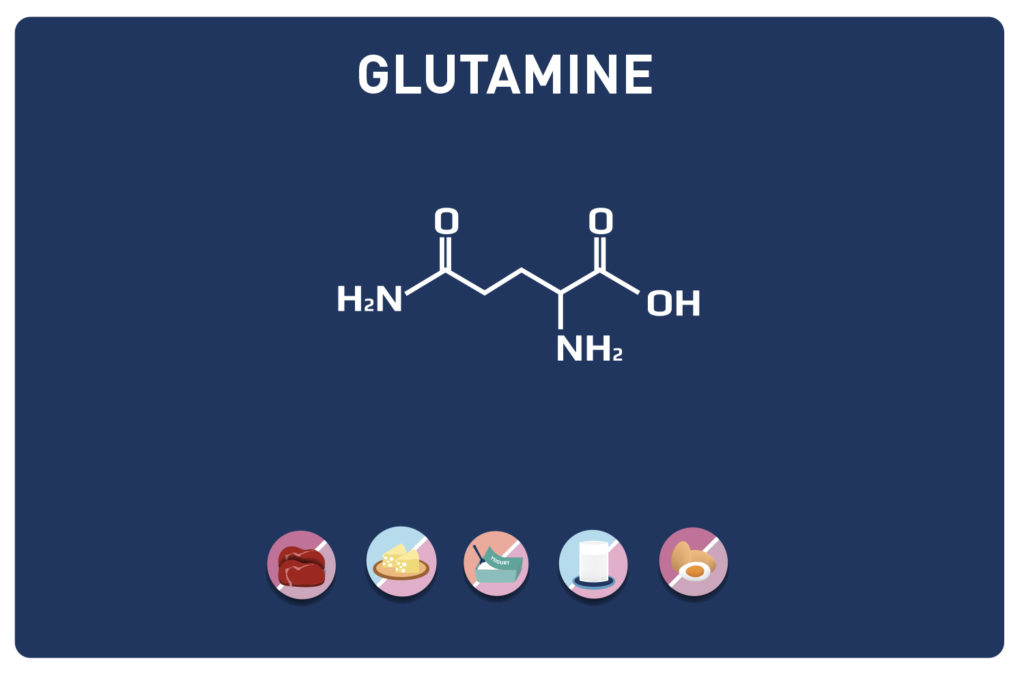
- Amino acids:Leucine, Isoleucine and Glutamine
THERAPEUTIC USES
- Anti-stress
- Helps in the treatment of liver and gall bladder disease. Stimulates regeneration of liver tissue
FOOD SOURCES
- Cottage cheese & dairy products
- Mushrooms
- Meat, fish & poultry
- Eggs
- Soya beans & peanuts
- Rice