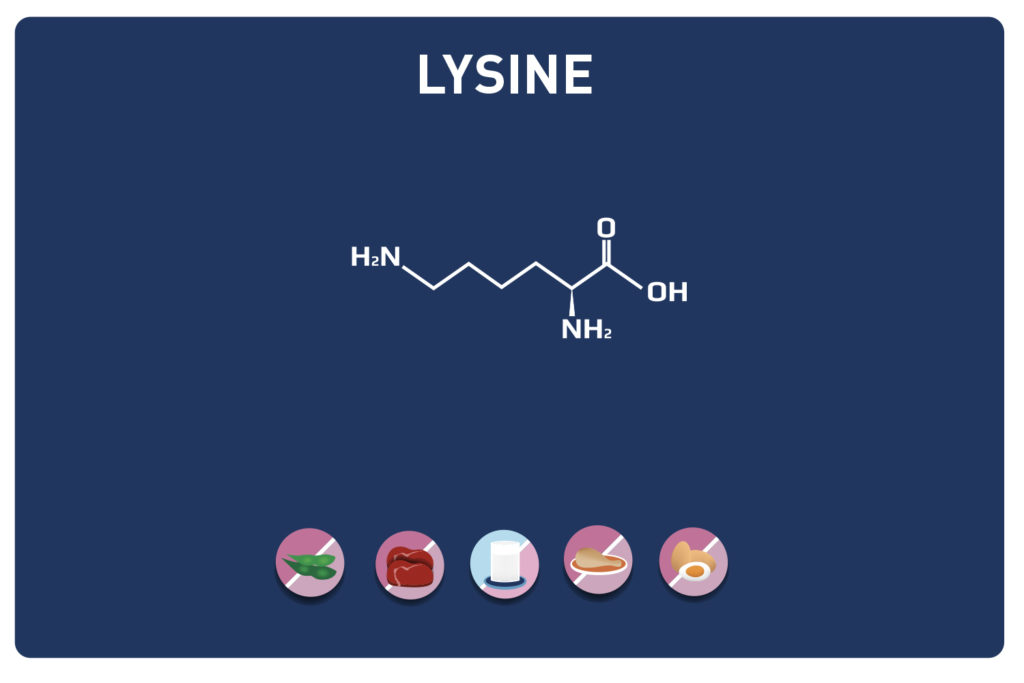
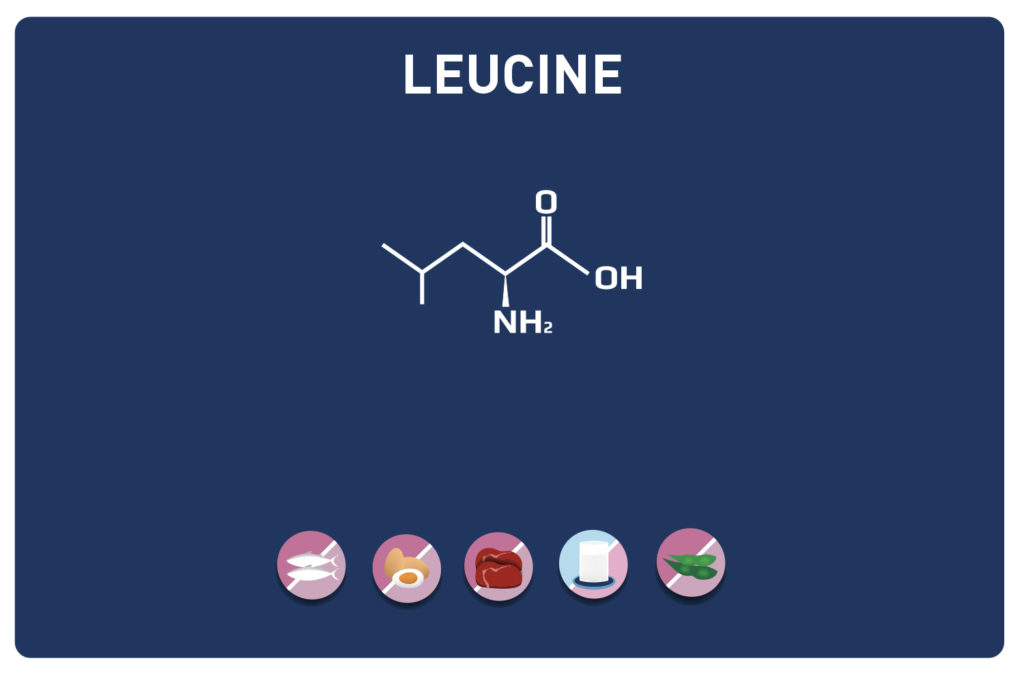
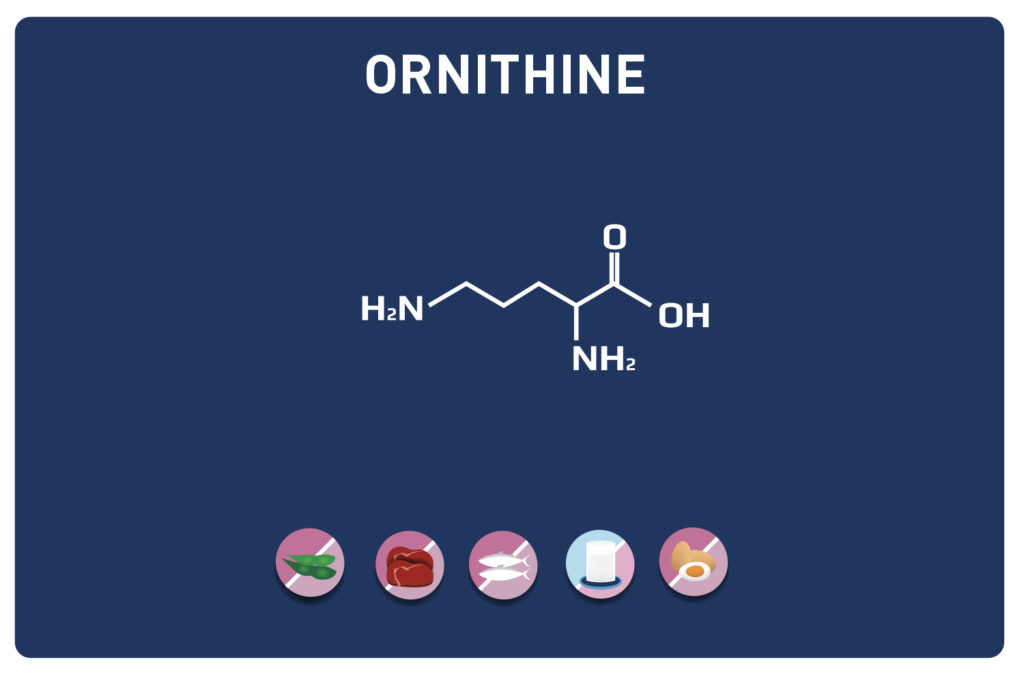
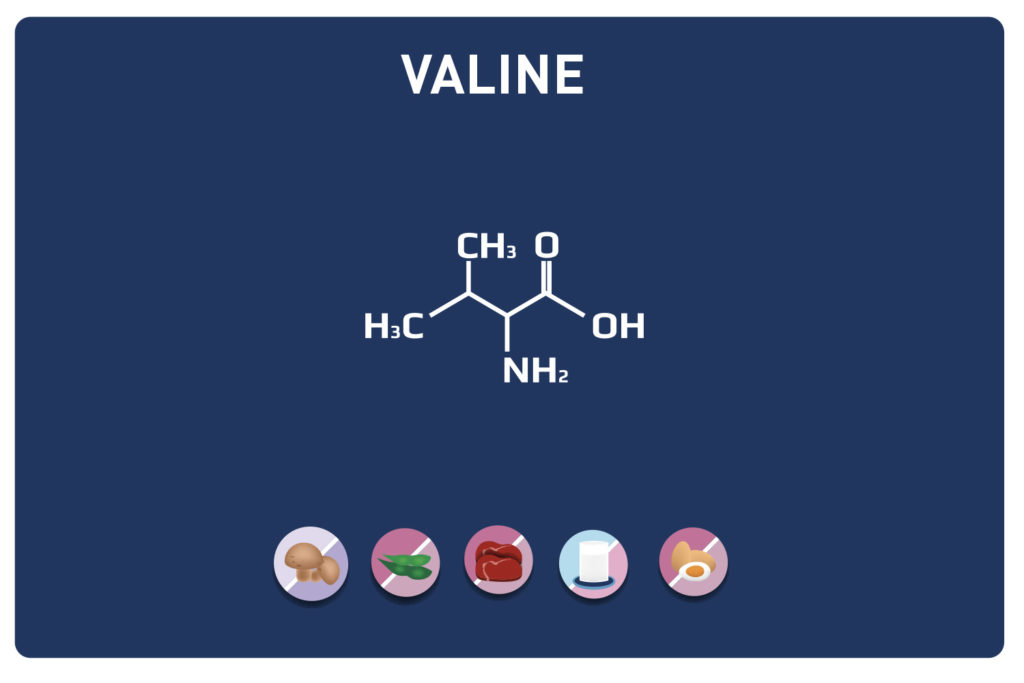
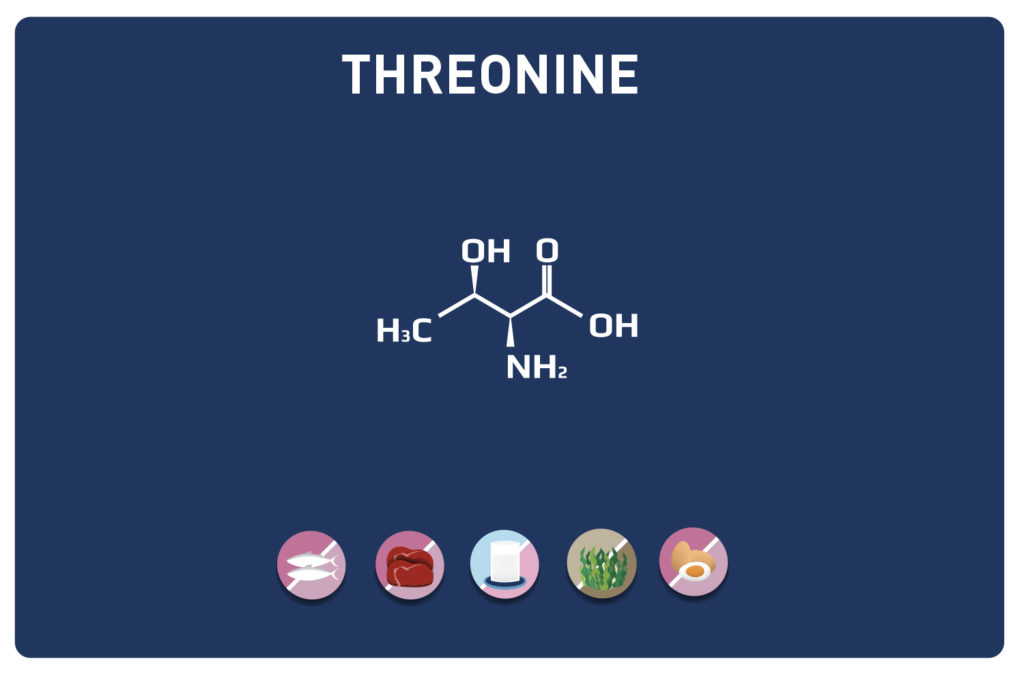
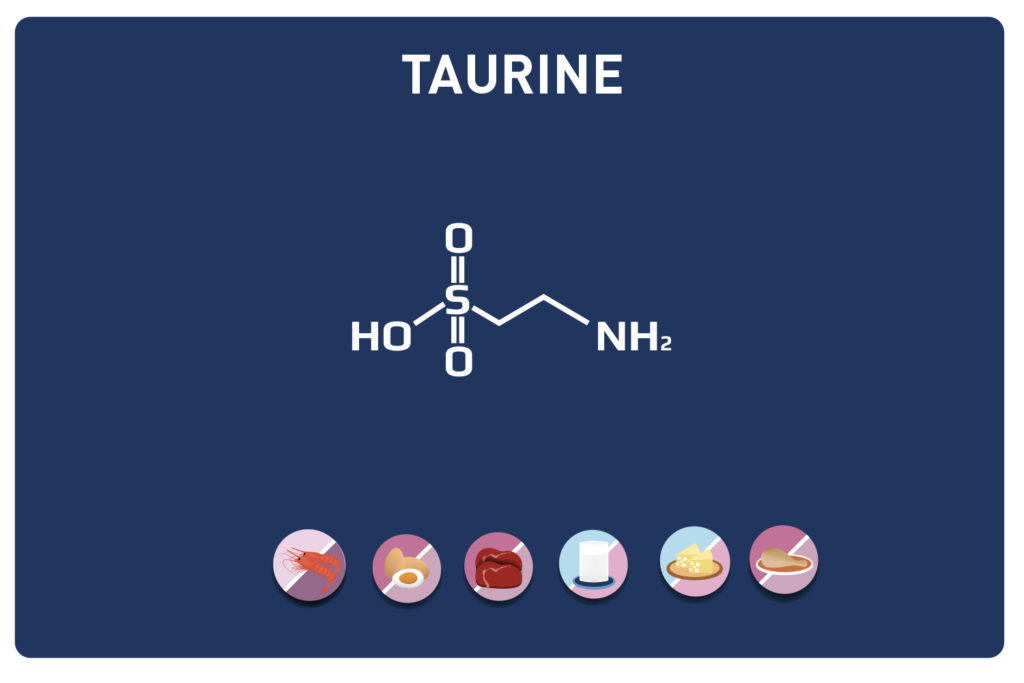
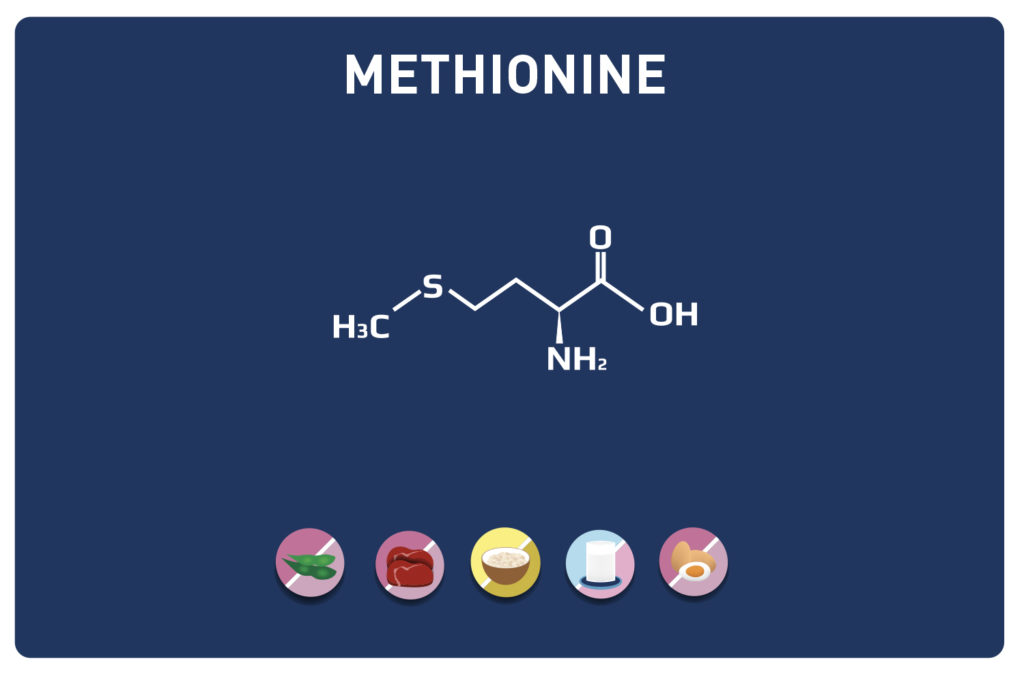
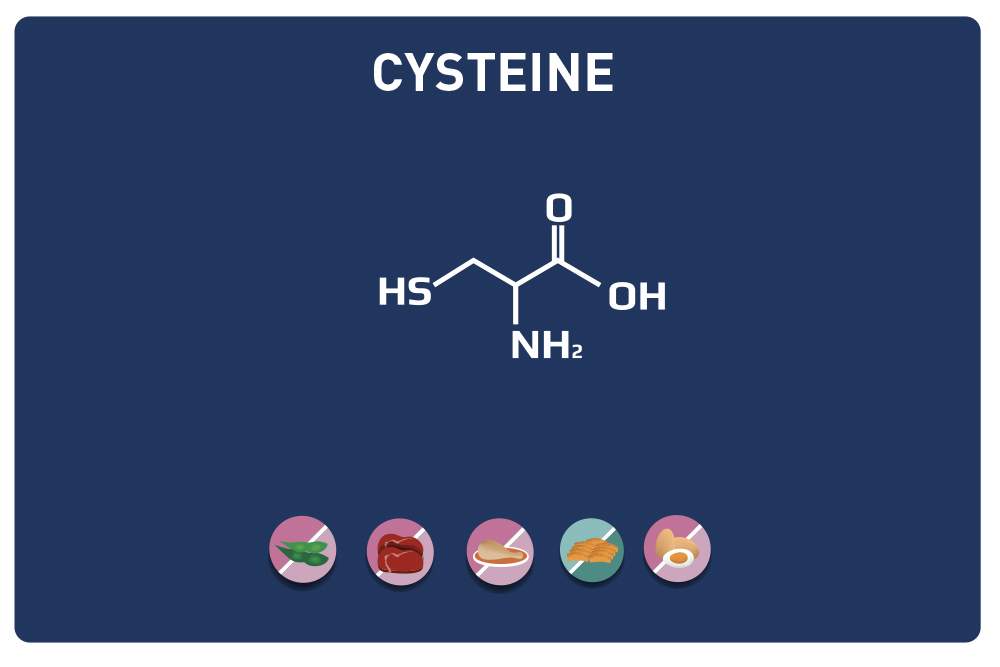
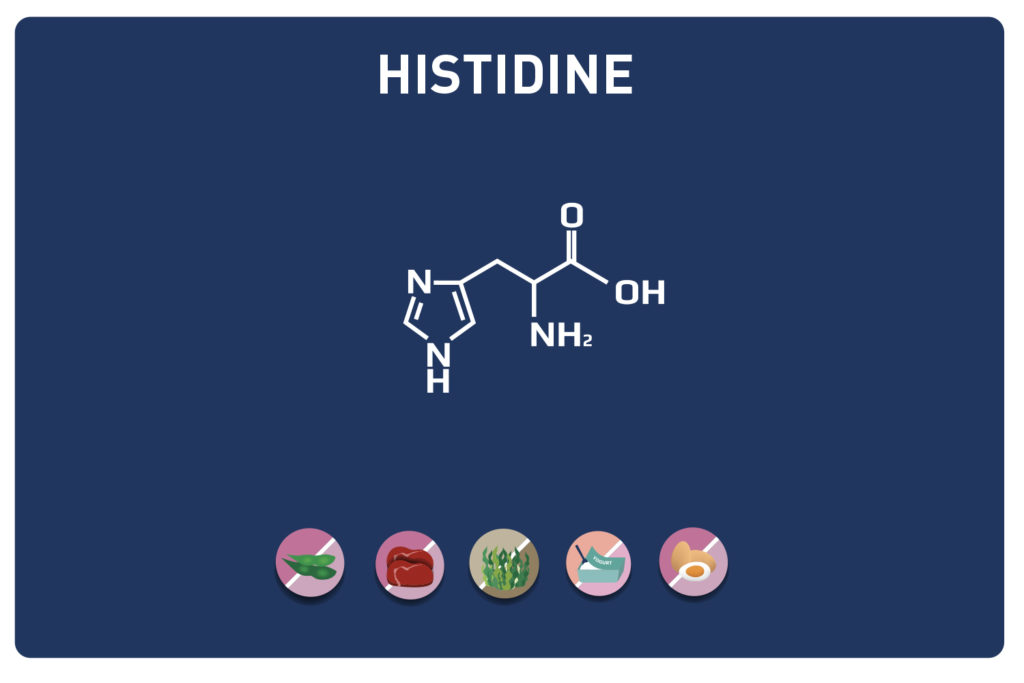
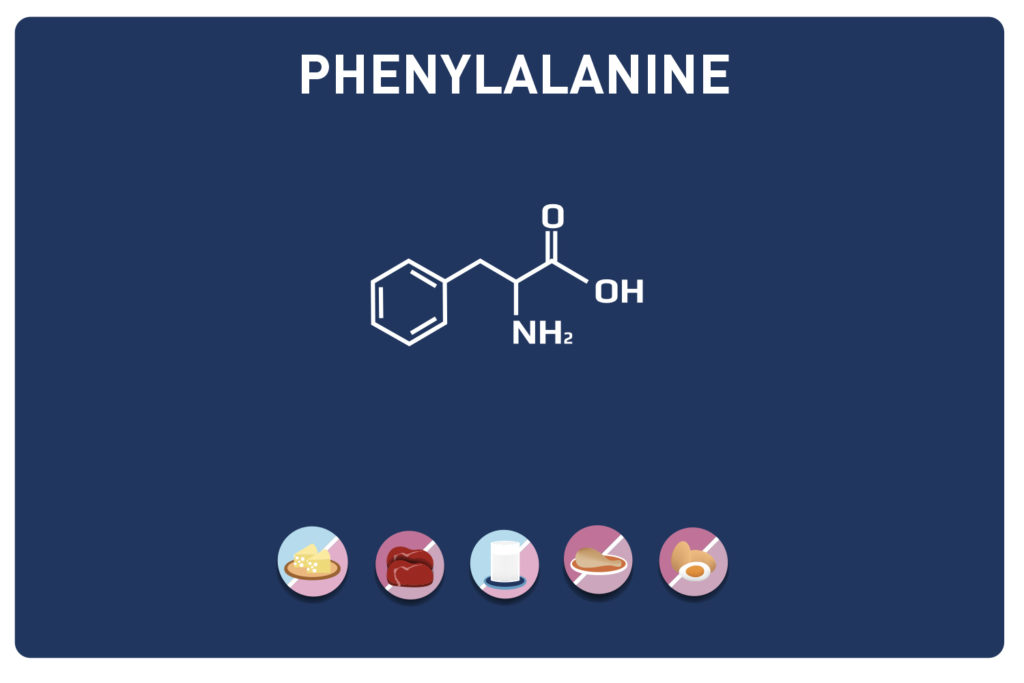
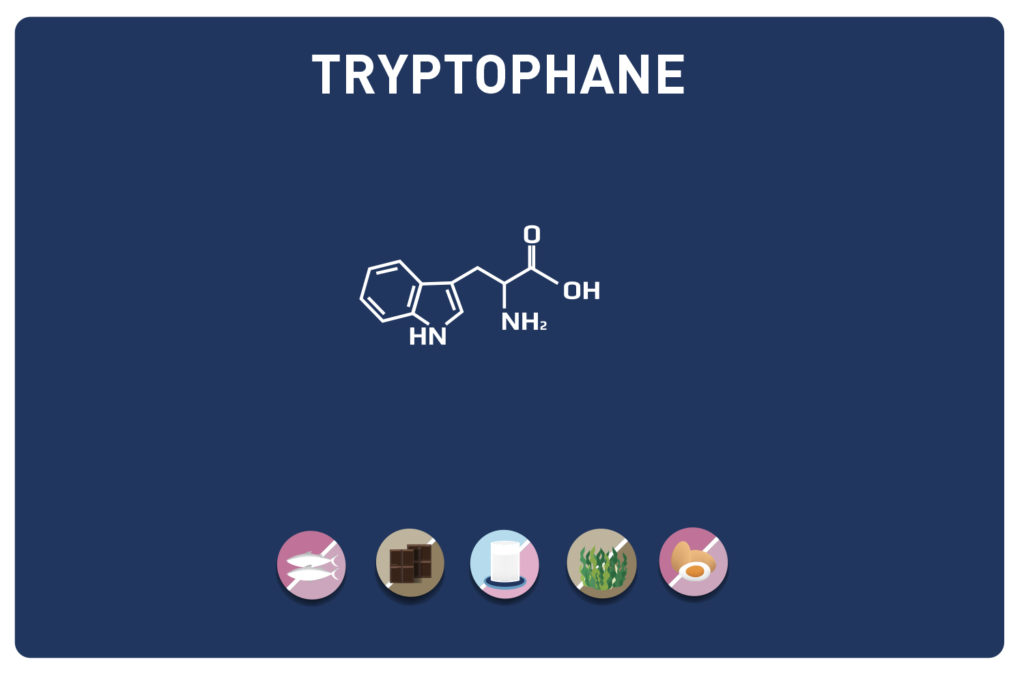
LYSINE is a basic amino acid which was first isolated in 1889 from casein. It is one of the 9 essential amino acids, i. e. our body cannot synthesise it, so it must be provided by the diet. It is contained in large quantities in the muscles and represents approximately 8% of the amino acids of the proteins in our body.
BIOLOGICAL ATTRIBUTES
- Contributes to bone growth and fights osteoporosis
- Contributes to the formation of collagen with the help of vitamin C
- Involves in the metabolism of carbohydrates
- Favours the absorption of fats(precursor of carnitine)
- Detoxicant (lead and heavy metals in the elderly)
- Increases immune defences
- Used to treat herpes labialis
- Precursor of citrulline
ADVISED INTAKE
Between 500mg to 3gr/day. (More generally 1gr/d) In case of stress or intensive training* the dosage can be increased without exceeding 10gr/d otherwise side effects such as nausea, colic, or diarrhea may occur. *(Doses of 3gr/d may be advised for athletes in intensive training phase)
NOTES
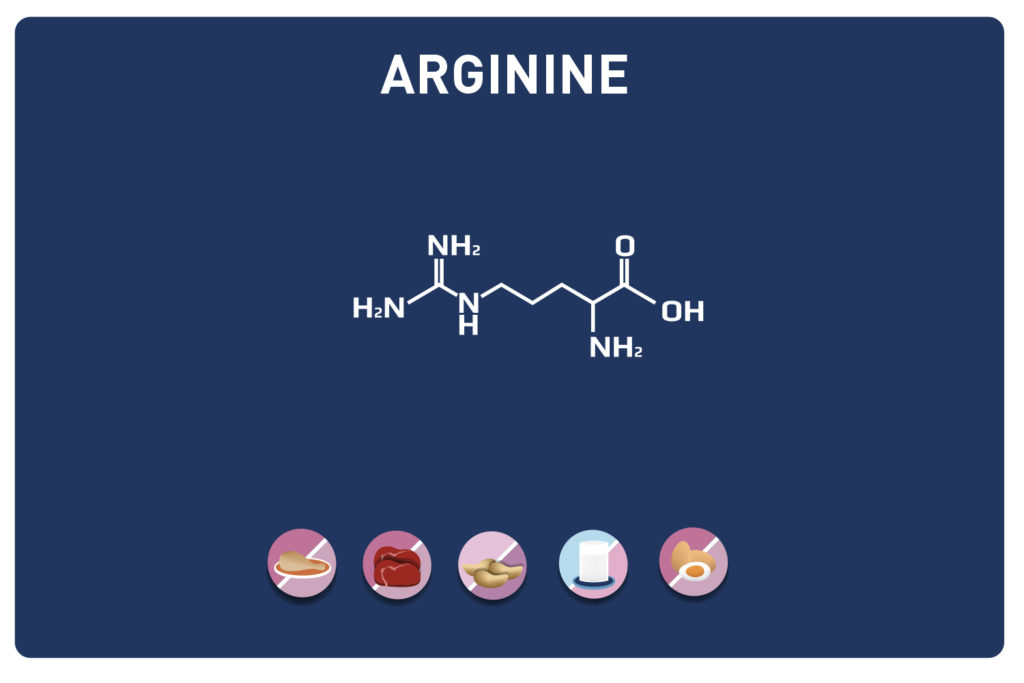
Related to arginine which uses the same metabolic pathways of assimilation, these two amino acids compete with each other. (Ornithine, but especially arginine displace lysine in the brain). Competition also with copper which degrades lysine.
CO-ACTIVE AND METABOLICALLY USEFUL ELEMENTS
- Vitamins: B2 - B3 - B6 - B9 - C -A - E
- Minerals:Selenium - Iron - Zinc - Manganese
- Glutamic acid
- Hyperlysinemia(very rare genetic disease)
- Risk of nephro-toxicity with certain antibiotics
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hyperlysinemia (very rare genetic disease)
Risk of nephro-toxicity with certain antibiotics